Reflect point
In the interior of the square A B C D , a point P lies in such a way that ∠ D C P = ∠ C A P = 2 5 ∘ . Find the sum of all possible values of ∠ P B A .
The answer is 40.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Let ∠ P B A = α . We can easily see that ∠ C A P = ∠ C A D − ∠ P A D = 4 5 ° − 2 0 ° = 2 5 °
Similarly, ∠ A C P = 2 0 °
So, ∠ B A P = 4 5 ° + 2 5 ° = 7 0 °
∠ B C P = 4 5 ° + 2 0 ° = 6 5 ° .
Applying sine rule to △ B A P , we can write
∣ B P ∣ ∣ A B ∣ = sin 7 0 ° sin ( 7 0 ° + α )
Applying sine rule to △ B C P ,
∣ B P ∣ ∣ B C ∣ = sin 6 5 ° sin ( 2 5 ° + α )
Since ∣ A B ∣ = ∣ B C , therefore
sin 6 5 ° sin ( 7 0 ° + α ) = sin 7 0 ° sin ( 2 5 ° + α )
⟹ tan α = sin 7 0 ° cos 2 5 ° − sin 6 5 ° cos 7 0 ° sin 7 0 ° ( sin 6 5 ° − sin 2 5 ° )
⟹ α = 4 0 ° .
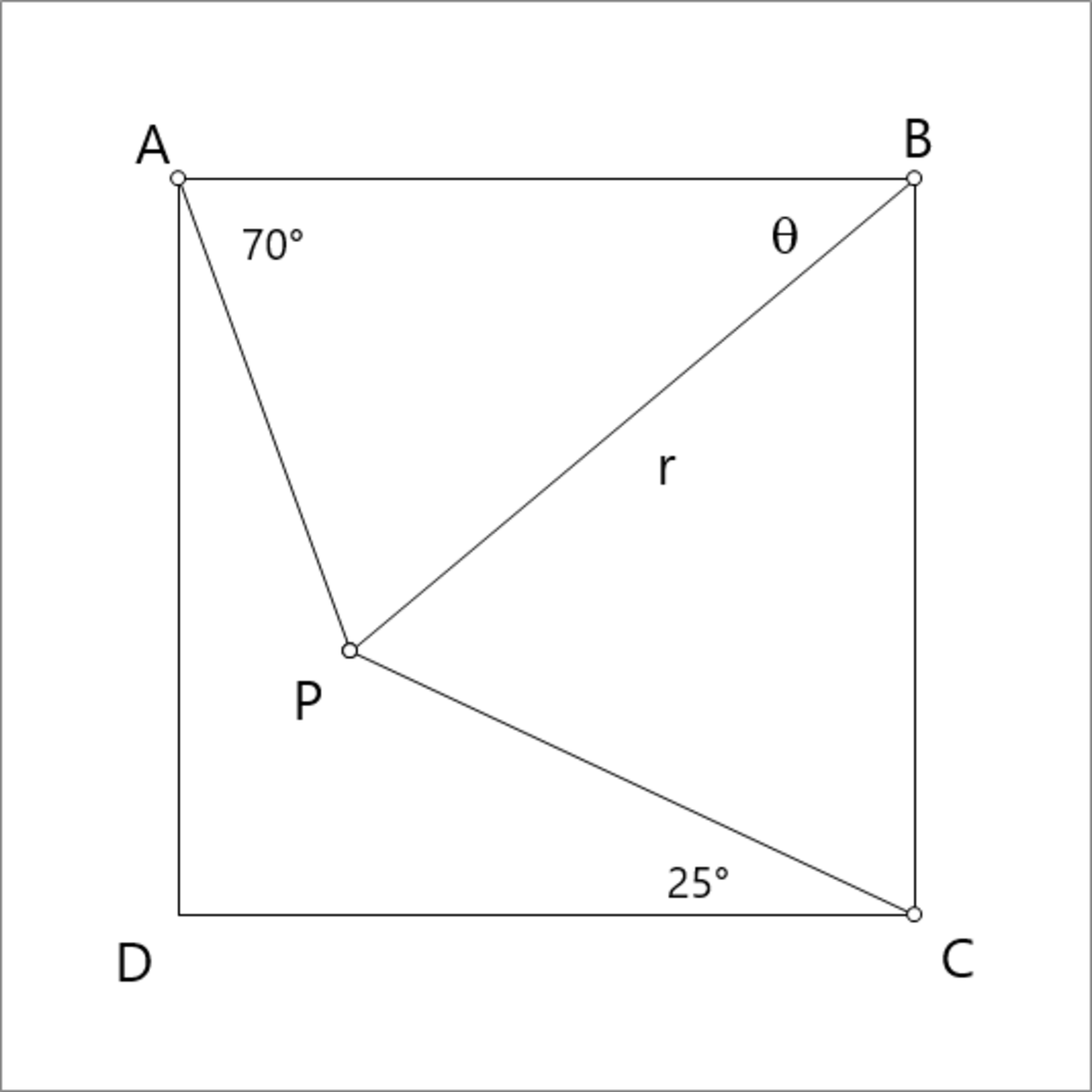
Let the side length of the square be 1 , so that A = ( 0 , 1 ) , B = ( 1 , 1 ) , C = ( 1 , 0 ) , D = ( 0 , 0 ) , and let θ = ∠ P B A , and let r = P B
The coordinates of P are:
P = ( 1 − r cos θ , 1 − r sin θ )
C P makes an angle of 2 5 ∘ with the horizontal, this translates into,
− r cos θ 1 − r sin θ = − tan 2 5 ∘
and
A P makes an angle of 7 0 ∘ with the horizontal, this translates into,
1 − r cos θ − r sin θ = − tan 7 0 ∘
These two equations yield,
r ( sin θ + tan 7 0 ∘ cos θ ) = tan 7 0 ∘
and,
r ( tan 2 5 ∘ cos θ + sin θ ) = 1
dividing r out,
sin θ + tan 7 0 ∘ cos θ = tan 7 0 ∘ ( tan 2 5 ∘ cos θ + sin θ )
dividing by cos θ ,
tan θ = 1 − tan 7 0 ∘ tan 7 0 ∘ ( tan 2 5 ∘ − 1 ) = 0 . 8 3 9 0 9 9 6 3 1 1 7 7 2 8 0 . . .
From which θ = 4 0 ∘
It is easy to compute that ∠ A P C = 1 3 5 ∘ . Since this is half of reflex angle ∠ A B C , which is 2 7 0 ∘ , P lies on the circle centered at B with radius A B . Then ∠ P B A = 2 ∠ P C A = 4 0 ∘ .