Revenge of the deceiving Sangaku
The diagram shows a blue scalene triangle. We extend each segment and draw three circles. Each circle is tangent to one of the triangle's sides and tangent to the extensions of the other two sides. At last, we join each center to form a bigger triangle in which the blue triangle is inscribed. The shortest distances between the sides of the blue triangle and its circumcenter are given : 8 1 7 , 8 8 7 , 8 1 0 5
- The Question : We denote the purple area as α and the blue area as β
- Find β α
- The answer can be expressed as b a where a and b are coprime positive integers
-
Evaluate
4
a
−
b
The answer is 3.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
- We can label the sides as a , b , c and the circumradius as R
- From the law of cosines, we can write this first equality : c ² = a ² + b ² − 2 a b × c o s ( C ^ )
- Now we need to express a , b , c and c o s ( C ^ ) in terms of R
- By the Intersecting chords theorem in the blue triangle's circumcircle we can express a , b , c in terms of R
- c ² = 4 R ² − 1 6 2 8 9
- b ² = 4 R ² − 1 6 7 5 6 9
- a ² = 4 R ² − 1 6 1 1 0 2 5
- From the extended law of sine, we know that : R = 2 s i n ( C ^ ) c < = > c o s ² ( C ^ ) = 1 − 4 R ² 4 R ² − 1 6 2 8 9
- We can now substitute a ² , b ² , c ² in terms of R in the first equality given by the law of cosines :
- 4 R ² − 1 6 2 8 9 = 4 R ² − 1 6 7 5 6 9 + 4 R ² − 1 6 1 1 0 2 5 − 2 a b × c o s ( C ^ )
- < = > 4 R ² − 1 6 1 8 3 0 5 = 2 a b × c o s ( C ^ )
- < = > ( 4 R ² − 1 6 1 8 3 0 5 ) ² = 4 a ² b ² × c o s ² ( C ^ )
- After squaring both side we can now substitute again a ² , b ² and c o s ² ( C ^ ) in terms of R
- ( 4 R ² − 1 6 1 8 3 0 5 ) ² = 4 ( 4 R ² − 1 6 1 1 0 2 5 ) ( 4 R ² − 1 6 7 5 6 9 ) ( 1 − 4 R ² 4 R ² − 1 6 2 8 9 )
- We solve the equation and find several values for R , the only acceptable value is R = 8 1 4 5
- We can now calculate a , b and c :
- a = 2 5
- b = 2 9
- c = 3 6
- Finally we calculate the blue area : β = 4 R a b c = 4 × 8 1 4 5 2 5 × 2 9 × 3 6 = 3 6 0
- Now we need to calculate the area of the bigger triangle, the three circles are actually the excircles of the blue triangle. One way to solve for the triangle's area is to use coordinate geometry.
- We draw a coordinate system with the origin being point A of the blue triangle ABC with A B = c = 3 6 , A C = b = 2 9 , B C = a = 2 5
- Then we place A(0;0) B(36;0) and C(21;20)
- We can label D the center of the excircle tangent to side [AB]
- We can label E the center of the excircle tangent to side [BC]
- We can label F the center of the excircle tangent to side [AC]
- Let's calculate the coordinates of D , E , F , using this general formula is the quickest way:
- x D = − c + b + a − c ⋅ x C + b ⋅ x B + a ⋅ x A = − 3 6 + 2 9 + 2 5 − 3 6 ⋅ 2 1 + 2 9 ⋅ 3 6 + 2 5 ⋅ 0 = 1 6
- y D = − c + b + a − c ⋅ y C + b ⋅ y B + a ⋅ y A = − 3 6 + 2 9 + 2 5 − 3 6 ⋅ 2 0 + 2 9 ⋅ 0 + 2 5 ⋅ 0 = − 4 0
- x E = − a + b + c − a ⋅ x A + b ⋅ x B + c ⋅ x C = − 2 5 + 2 9 + 3 6 − 2 5 ⋅ 0 + 2 9 ⋅ 3 6 + 3 6 ⋅ 2 1 = 4 5
- y E = − a + b + c − a ⋅ y A + b ⋅ y B + c ⋅ y C = − 2 5 + 2 9 + 3 6 − 2 5 ⋅ 0 + 2 9 ⋅ 0 + 3 6 ⋅ 2 0 = 1 8
- x F = − b + a + c − b ⋅ x B + a ⋅ x A + c ⋅ x C = − 2 9 + 2 5 + 3 6 − 2 9 ⋅ 3 6 + 2 5 ⋅ 0 + 3 6 ⋅ 2 1 = − 9
- y F = − b + a + c − b ⋅ y B + a ⋅ y A + c ⋅ y C = − 2 9 + 2 5 + 3 6 − 2 9 ⋅ 0 + 2 5 ⋅ 0 + 3 6 ⋅ 2 0 = 2 4 5
- We can now calculate the sides of the triangle DEF :
- D E = ( x E − x D ) ² + ( y E − y D ) ² = 2 9 5
- F E = ( x E − x F ) ² + ( y E − y F ) ² = 2 9 1 4 5
- D F = ( x F − x D ) ² + ( y F − y D ) ² = 2 2 5 2 9
- By Heron's formula we get the area of the triangle EDF which is 4 6 5 2 5
- We then get the purple area by substraction α = 4 6 5 2 5 − β = 4 5 0 8 5
- β α = 3 2 1 1 3
- 4 1 1 3 − 3 2 = 4 8 1 = 3
Let the blue triangle have sides a , b , and c and a circumradius of R , and label it as follows:
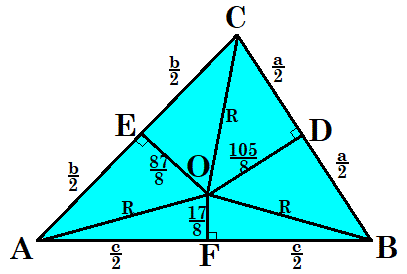
As given, let O D = 8 1 0 5 , O E = 8 8 7 , and O F = 8 1 7 . By the properties of a circumcircle , O D is the perpendicular bisector of B C , O E is the perpendicular bisector of A C , and O F is the perpendicular bisector of A B . By the Pythagorean Theorem on △ O D C , △ O E A , and △ O F B :
( 2 a ) 2 + ( 8 1 0 5 ) 2 = R 2
( 2 b ) 2 + ( 8 8 7 ) 2 = R 2
( 2 c ) 2 + ( 8 1 7 ) 2 = R 2
The area of △ A B C is β = A △ A B C = A △ O B C + A △ O A C + A △ O A B = 2 1 ⋅ 8 1 0 5 ⋅ a + 2 1 ⋅ 8 8 7 ⋅ b + 2 1 ⋅ 8 1 7 ⋅ c , or:
1 6 β = 1 0 5 a + 8 7 b + 1 7 c
and by the properties of a circumcircle:
4 β R = a b c
These five equations solve to a = 2 5 , b = 2 9 , c = 3 6 , R = 8 1 4 5 , and β = 3 6 0 .
The green circles are excircles and the purple and blue triangle is an excentral triangle with an area of α + β = 2 r 2 s a b c β . Substituting β = r s and s = 2 1 ( a + b + c ) and rearranging gives:
α = 4 β ( a + b + c ) a b c − β = 4 5 0 8 5
Therefore, β α = 3 2 1 1 3 , so a = 1 1 3 , b = 3 2 , and 4 a − b = 3 .
Much better than my solution !! Thank you !