Rhombus Riddle

As shown above, A B C D is a rhombus, whose major diagonal is twice the length of its minor one, and the blue B E D F is a rectangle with an area of 24.
What is the area of the yellow region?
Note : Figure not drawn to scale.
The answer is 36.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Suppose the length B D = x . Since A C = 2 × B D , its area equals 2 1 ( 2 x ) ( x ) = x 2 . Then we can draw a square, depicted as red, of side length x , which will have the same area as the rhombus, as shown below:
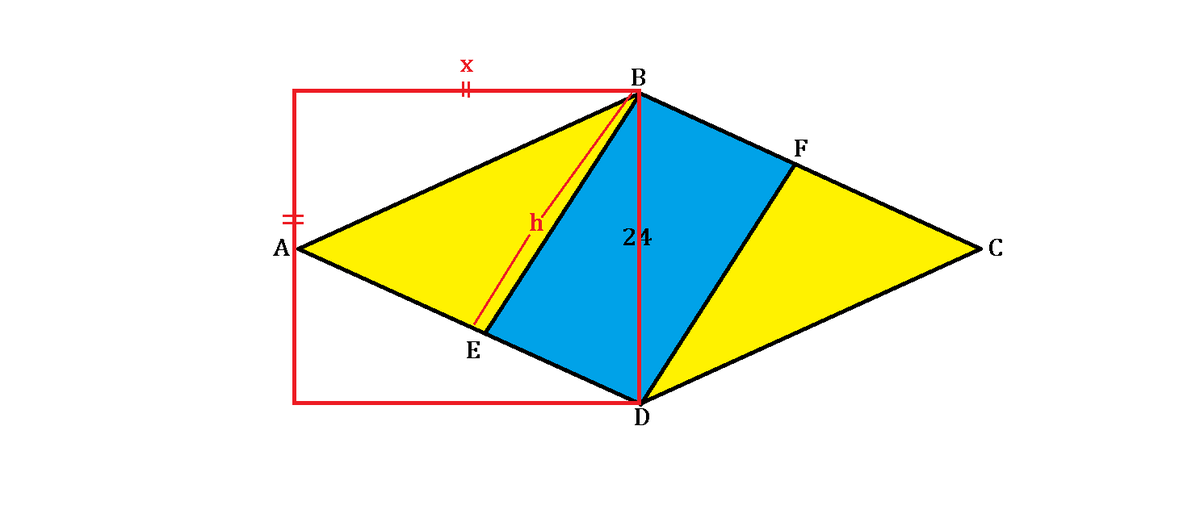
Now let B E = h . Since B E D F is a rectangle, we can conclude that 2 4 = h × E D . Thus, E D = h 2 4 .
Also, by Pythagorean theorem, regarding the quarter congruent triangle of the rhombus, the squared side length of the rhombus equals x 2 + ( 2 x ) 2 = 4 5 ( x 2 ) . The rhombus side length is x 4 5 .
Then considering the △ A B D , there are two ways to calculate its area, depending on the either base A D or B D used. We can set equation of such area:
2 1 ( h ) ( A D ) = 2 1 ( 2 A C ) ( B D ) = 2 1 ( x 2 )
Substituting A D = x 4 5 obtained earlier, we will get:
h x 4 5 = x 2
h = x 5 4
Furthermore, using Pythagorean theorem again, we can set up the equation regarding the side lengths, regarding △ B E D :
h 2 + ( h 2 4 ) 2 = x 2
Substituting h = x 5 4 obtained before, we will get:
5 4 x 2 + 5 4 x 2 2 4 2 = x 2
4 x 2 5 × 2 4 2 = 5 x 2
2 4 2 = ( 5 2 x 2 ) 2
2 4 = 5 2 x 2
x 2 = 6 0
Therefore, the rhombus has an area of 6 0 . Thus, the yellow region has an area of 6 0 − 2 4 = 3 6 .
Alternatively, the rectangle has an area of 5 2 of the rhombus, thus leaving the rest of the yellow region for 5 3 . That is the area ratio between the blue to the yellow is 2 : 3 .
Finally, the yellow region has an area of 2 3 × 2 4 = 3 6 .
Nice solution! My approach was similar but a bit lengthier
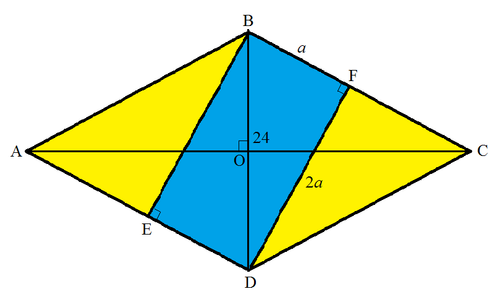
Let the center of the rhombus be O . Then we note that △ B D F and △ B O C are similar. Given that the major diagonal is twice the length of the minor diagonal, ⟹ C O B O = D F B F = 2 1 . Let B F = a . Then D F = 2 a . Since the area of the blue rectangle B E D F is B F × D F = 2 a 2 = 2 4 ⟹ a = 2 3 . By Pythagorean theorem we have B D 2 = B F 2 + D F 2 = 5 a 2 ⟹ B D = 2 1 5 , B O = 2 B D = 1 5 , A C = 4 1 5 , the area of the rhombus 2 × 2 1 × B O × A C = 6 0 , and the area of the yellow region 6 0 − 2 4 = 3 6 .

Let the minor diagonal be (2 m) then the major diagonal is (4 m). It follows that tan ∠ D B F = 2 and therefore, tan ∠ B D F = 2 1 . From this, we deduce that cos 2 ∠ B D F = 5 4 and that sin 2 ∠ B D F = 5 1 . As mentioned above the minor diagonal B D = 2 m . Therefore, B F = 5 2 m , and D F = 5 4 m . Thus, 2 4 = 5 8 m 2 , from which, we have m 2 = 1 5 . Finally the area of the rhombus is 2 1 ( 2 m ) ( 4 m ) = 4 m 2 = 6 0 . Thus the yellow area is 6 0 − 2 4 = 3 6 .