Right within Equilateral
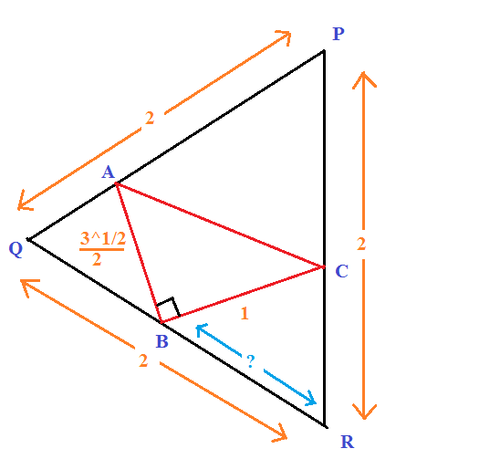 In
,
,
and
.
is an equilateral triangle with sides
,
and
passing through the points
,
an
respectively and each having length
.
In
,
,
and
.
is an equilateral triangle with sides
,
and
passing through the points
,
an
respectively and each having length
.
If the sum of the possible lengths of the segment be expressed as , where , are coprime positive integers, find the value of
The answer is 41.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Since nobody is posting a solution (only 2 solvers till now though) and there are many who could not solve it, i think id better post one. So here it goes. First let ∠ Q B A = x . Then ∠ C B R = 9 0 ∘ − x . Note ∠ Q = ∠ R = ∠ P = 6 0 ∘
Applying Law's of sines in △ Q B A , we have
sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ − x ) Q B = sin 6 0 ∘ A B = s i n 6 0 ∘ 2 3 = 1
⟹ B Q = sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ − x ) . . . . . . ( i )
Again applying Laws of sines in △ R B C we will have after some simplification
B R = 3 2 sin ( 3 0 ∘ + x ) . . . . . ( i i )
Adding ( i ) and ( i i ) we get
B Q + B R = sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ − x ) + 3 2 sin ( 3 0 ∘ + x )
⟹ 2 = sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ − x ) + 3 2 sin ( 3 0 ∘ + x )
⟹ 2 3 = 3 sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ − x ) + 2 sin ( 3 0 ∘ + x )
After breaking up the compound angles by the well known formula and furthur simplifations we have
4 3 = 5 cos x + 3 3 sin x ⟹ 3 ( 4 − 3 sin x ) = 5 cos x
Now squaring both sides and using cos 2 x + s i n 2 x = 1 we have
5 2 sin 2 x − 7 2 sin x + 2 3 = 0 ⟹ ( 2 sin x − 1 ) ( 2 6 sin x − 2 3 ) = 0
Therefore either sin x = 2 1 ⟹ x = 3 0 ∘ or sin x = 2 6 2 3
x = 3 0 ∘ implies △ C R B is equilateral and hence B R = 1 . And if sin x = 2 6 2 3 , cos x = 2 6 7 3 . Therefore we have
B R = 3 2 ( 2 cos x + 2 3 sin x )
= 3 2 ( 2 × 2 6 7 3 + 2 × 2 0 3 × 2 3
= 2 6 7 + 2 6 2 3 = 2 6 3 0 ⟹ B R = 1 3 1 5
Hence the sum of all possible values of B R is 1 + 1 3 1 5 = 1 3 1 3 + 1 5 = 1 3 2 8
Hence a + b = 2 8 + 1 3 = 4 1