Tandem Reactions and Super Acids
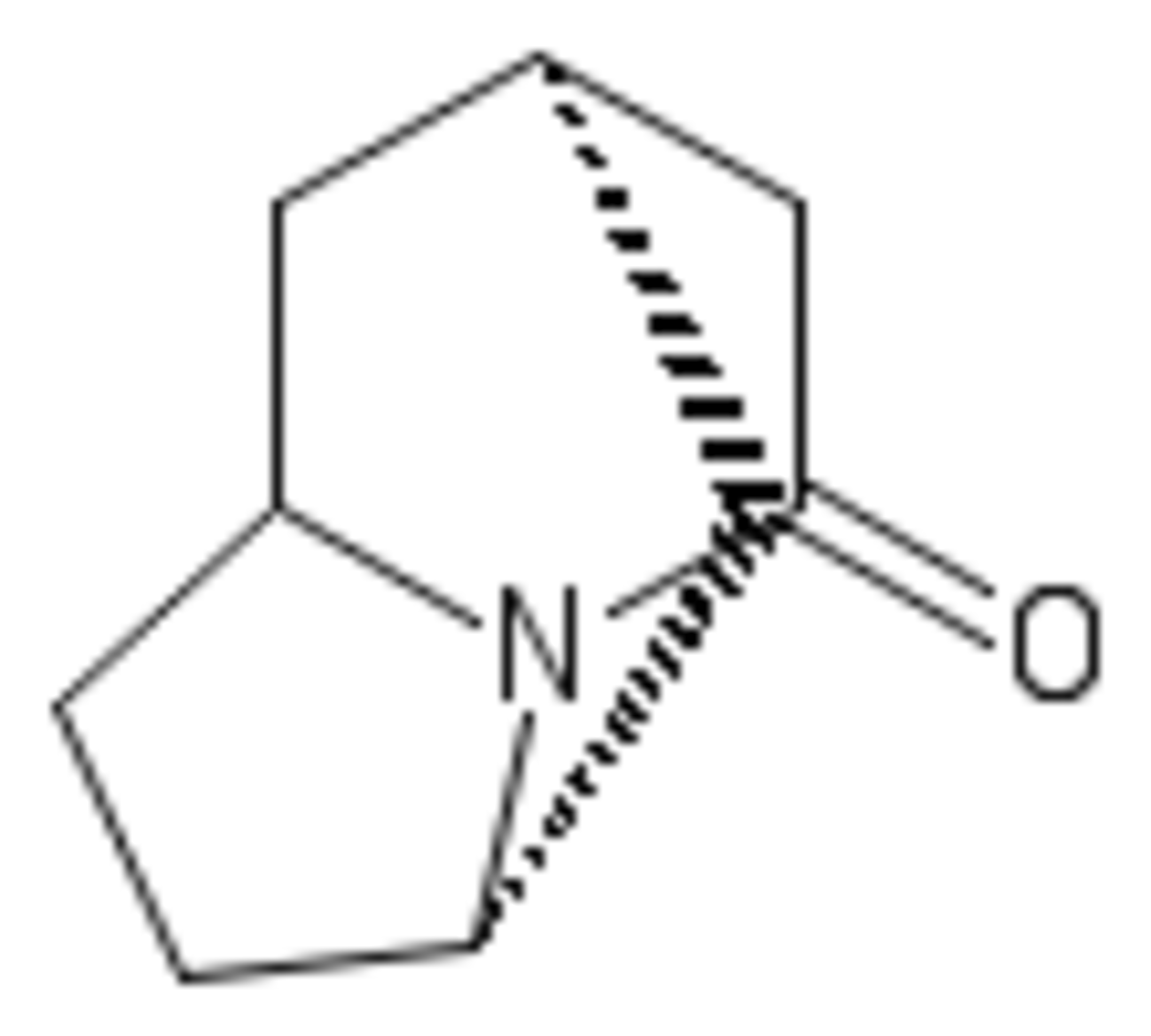
You are tasked to synthesise the above compound's derivative.
You start with Succinaldehyde , Benzylamine and b-ketoglutaric acid whose formulae are , , respectively.
These compounds undergo a tandem reaction to give precursor P . Now,
- P is reduced with and then reacts with in presence of to give A
- A reacts with DIBAL-H to form B after hydrolysis.
- B reacts with 2-chloro ethanol in presence of piperidine and a catalytic amount of to give C after hydrolysis.
- C is now oxidised in acidic to give D
- D is decarboxylated to give precursor E whose formula is
- E undergoes hydrogenation in presence of palladium to give the precursor F
- F forms its silver salt and on reaction with gives G
- G undergoes an intramolecular reaction to form the target molecule.
You call the target molecule X and carry out the next set of reactions on it:
- X on hofmann exhaustive methylation gives an unstable compound Y
- Y immediately rearranges in presence of and heat to give W
- W on mono chlorination followed by reaction with gives a compound T
T reacts with to give a complex of antimony and a very stable cation V .
However V can be thought of as a tropylium cation derivative and it exceeds the tropylium carbocation's mass by b units.
In B let a denote the sum of double bonds between carbons and the number of oxygen atoms.
Calculate the value of b - a - 1
Inspirations:
- Problem 7 in 2016's IChO
- Teleanu Florin's problem
The answer is 9.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The structures of the starting components are:
These components, when combined under go a tandem reaction called Robinson's Troponine synthesis . This reaction was involved in Problem 7 of 2016's IChO . These components form P its structure is shown:
P is first reduced and then substituted to give A .
Since A contain's a cyanide group and DIBAL-H is a mild reducing agent, an aldehyde is formed after hydrolysis of the resultant imine. This is B , it contains 3 double bonds and 1 oxygen. Hence a = 4 
B reacts with the next set of reagents to add a carbon chain at the α position of the aldehyde. Hence C is:
In presence of acidic K M n O 4 , both alcohol and aldehyde are oxidised to carboxylic acids, to give D :
On decarboxylation, one of the carboxy groups is lost resulting in compound E . The fact that only one group is lost can be seen by observing E 's molecular formula.
During hydrogenation the benzyl group bonded to nitrogen is replaced with a hydrogen. This gives us F
The silver salt and addition of bromine are the reagents used in Hunsdiecker Reaction to give us G :
G contains a nucleophillic nitrogen and primary carbon bonded to a bromine. This results in an intramolecular S N 2 reaction, giving us the target molecule X :
On hofmann exhaustive methylation we get compound Y . It is unstable since its double bonds aren't in conjugation and can hence rearrange to ensure conjugation is achieved.
Y now rearranges to form a conjugated system in presence of H + . On heating, this intermediate can undergo a [1 7] electrocyclic shift that results in compound W . Teleanu Florin's problem looks into the interesting chemistry brought about by one such electrocyclic shift.
W 's major mono chlorination product is at its tertiary s p 3 carbon. This reacts with A g F to precipitate A g C l out to give T :
Super acids played a very large role in isolating carbocations . Tl;dr, we get the superacid S b F 6 − and carbocation V :
Tropylium has a mass of 91 units and the species V has a mass of 105 units. It exceeds tropylium's mass by 14 units. Hence b = 1 4 .
Therefore the answer is 14 - 4 - 1 = 9