Interesting Series
1 + 4 1 ( 2 1 + 3 1 ) + 4 2 1 ( 4 1 + 5 1 ) + 4 3 1 ( 6 1 + 7 1 ) + ⋯
If the value of the series above is equal to ln A , find A .
The answer is 12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
very good...............wosks
Moderator note:
Once you recognize the series, it is often easier to quote the Maclaurin series expansion, instead of trying to derive it all.
Amazing solution
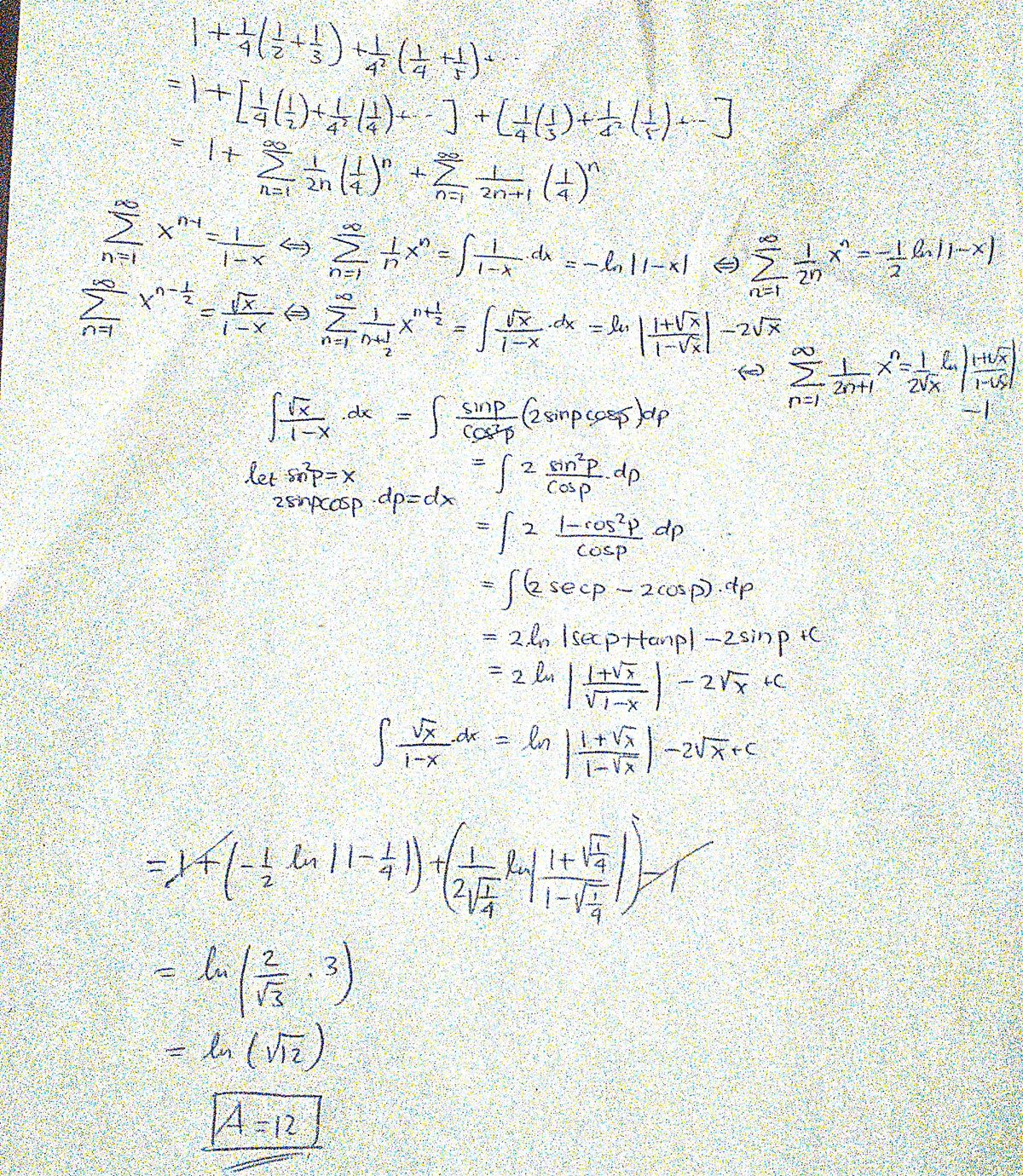
Let the sum be S .
S = 1 + 4 1 ( 2 1 + 3 1 ) + 4 2 1 ( 4 1 + 5 1 ) + 4 3 1 ( 6 1 + 7 1 ) + . . . = 2 ( 2 1 + 3 1 ˙ ( 2 1 ) 3 + 5 1 ˙ ( 2 1 ) 5 + . . . ) + ( 2 1 ˙ ( 2 1 ) 2 + 4 1 ˙ ( 2 1 ) 4 + 6 1 ˙ ( 2 1 ) 6 + . . . ) = ln ( 1 + 2 1 ) − ln ( 1 − 2 1 ) − 2 1 ( ln ( 1 + 2 1 ) + ln ( 1 − 2 1 ) ) See Note. = 2 1 ln ( 2 3 ) − 2 3 ln ( 2 1 ) = ln ( 2 3 × 2 2 ) = ln 1 2
⇒ A = 1 2
Note:
We know that for 0 ≤ x < 1 , { ln ( 1 + x ) = x − 2 1 x 2 + 3 1 x 3 − 4 1 x 4 + . . . ln ( 1 − x ) = − x − 2 1 x 2 − 3 1 x 3 − 4 1 x 4 − . . .
⇒ { ln ( 1 + x ) − ln ( 1 − x ) − ln ( 1 + x ) − ln ( 1 − x ) = 2 ( x + 3 1 x 3 + 5 1 x 3 − 7 1 x 7 + . . . ) = 2 ( 2 1 x 2 + 4 1 x 4 − 6 1 x 6 − 8 1 x 8 − . . . )