Shadow of a disc inside a cube
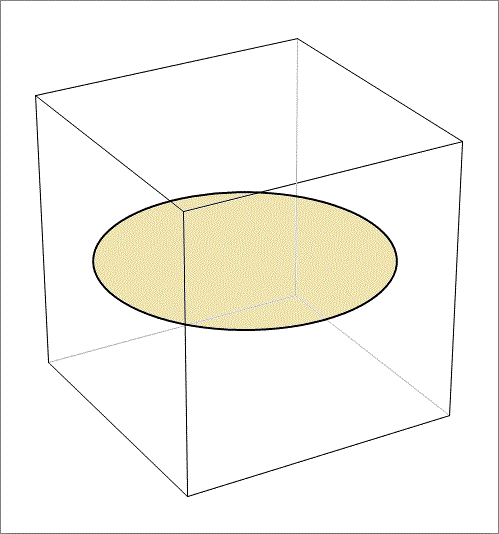
An opaque hollow cube of side length 6 has a horizontal opaque disc inside it of radius 3 touching its vertical faces at their centers, as shown in the figure above. If we place a point light source at one of the top corners of the cube, what will be the area of the disc shadow on the faces of the cube.
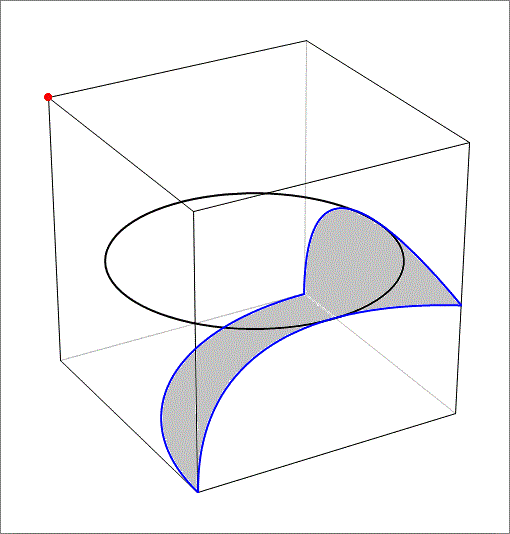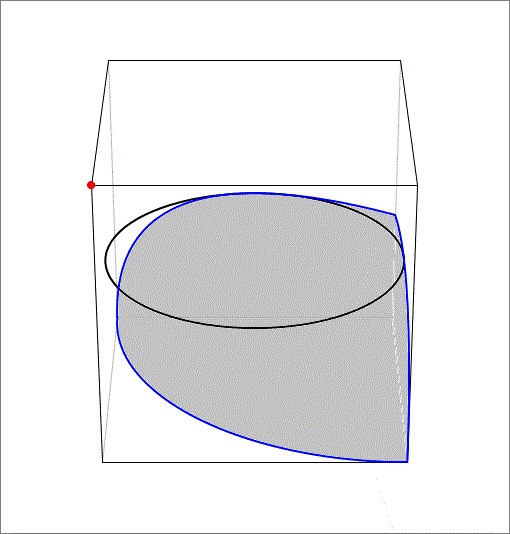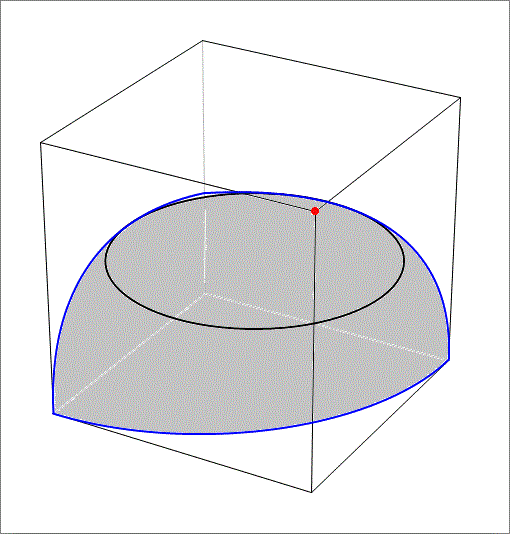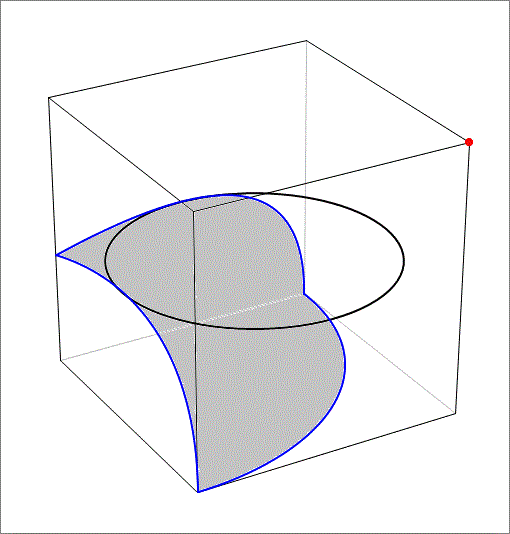
The answer is 60.156.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Let the cube lie in the first octant with one corner at the origin, and the opposite corner at ( 6 , 6 , 6 ) , and let the light source be at A = ( 0 , 0 , 6 ) . The disc is centered at H = ( 3 , 3 , 3 ) , and its circular edge has the parametric equation q ( t ) = H + cos t v 1 + sin t v 2 , where v 1 = ( 3 , 0 , 0 ) and v 2 = ( 0 , 3 , 0 ) . The rays from the source to the edge of the disc are given by
r = A + s M v
where s ≥ 0 is a scalar, and v = [ cos t , sin t , 1 ] T and
M = [ v 1 , v 2 , H − A ] = ⎣ ⎡ 3 0 0 0 3 0 3 3 − 3 ⎦ ⎤
Noting that v T Q 0 v = 0 , where Q 0 = ⎣ ⎡ 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 − 1 ⎦ ⎤
It follows that, the rays lie on a cone whose equation is
( r − A ) T M − T Q 0 M − 1 ( r − A ) = 0
The inverse of matrix M is easily computable to be,
M − 1 = 3 1 ⎣ ⎡ 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 − 1 ⎦ ⎤
Hence,
Q c = M − T Q 0 M − 1 = 9 1 ⎣ ⎡ 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 ⎦ ⎤
so that the equation of the cone is
( r − A ) T Q c ( r − A ) = 0
intersecting this cone with the plane z = 0 , gives
r − A = ⎣ ⎡ x y − 6 ⎦ ⎤
so that the equation of the intersection is,
x 2 + y 2 + 3 6 − 1 2 x − 1 2 y = 0
by completing the squares for x and y , this becomes,
( x − 6 ) 2 + ( y − 6 ) 2 = 3 6
which is the equation of a circle centerd at ( 6 , 6 , 0 ) with a radius 6 , hence the area bounded by this circle and the edges of the cube is A 1 = 4 1 π ( 3 6 ) = 9 π
Next, intersecting the cone with the plane y = 6
r − A = ⎣ ⎡ x 6 z − 6 ⎦ ⎤
so that the equation of the intersection is,
x 2 + 3 6 + ( z − 6 ) 2 + 2 x ( z − 6 ) + 1 2 ( z − 6 ) = 0
which is a quadratic in ( z − 6 ) , its solution (using the quadratic formula) is
( z − 6 ) = 2 1 [ − ( 2 x + 1 2 ) ± ( 2 x + 1 2 ) 2 − 4 ( x 2 + 3 6 ) ]
= 2 1 [ − ( 2 x + 1 2 ) ± 4 8 x ]
= − ( x + 6 ) ± 2 3 x
so that
z = − x ± 2 3 x
since we want z ≥ 0 , then z = − x + 2 3 x
now the area is A 2 = ∫ x = 0 x = 6 ( − x + 2 3 x ) d x = − 1 8 + 2 4 2
Since this is the same area of the shadow on the plane x = 6 , then the total shadow area is A Shadow = A 1 + 2 A 2 = 9 π − 3 6 + 4 8 2 ≈ 6 0 . 1 5 6
Let the center of the cube be ( 0 , 0 , 0 ) and the light source be A ( 3 , 3 , 3 ) . Let B ( p , q , 0 ) be a point on the edge of the disc that is projected to C ( − 3 , y , z ) on the far wall of the cube.
Since B ( p , q , 0 ) is on the disc with a radius of 3 , p 2 + q 2 = 9 , or q = 9 − p 2 .
The vector A B has an equation of ( x , y , z ) = ( p − 3 , q − 3 , 0 − 3 ) t + ( 3 , 3 , 3 ) . C ( − 3 , y , z ) is also on that vector, so from the x -coordinate we have − 3 = ( p − 3 ) t + 3 , which solves to t = − p − 3 − 6 . Therefore, y = ( q − 3 ) t + 3 = p − 3 − 6 ( q − 3 ) + 3 and z = ( 0 − 3 ) t + 3 = p − 3 1 8 + 3 .
Substituting q = 9 − p 2 into y = p − 3 − 6 ( q − 3 ) + 3 gives y = p − 3 − 6 ( 9 − p 2 − 3 ) + 3 , and this with z = p − 3 1 8 + 3 after eliminating p and simplifying gives z = y − 2 3 3 − y − 6 .
The area of the shadow on one of the far walls is then A wall = ∫ − 3 3 ( y − 2 3 3 − y − 6 + 3 ) d y = 2 4 2 − 1 8 .
The area of the shadow on the floor is one fourth of a circle with a radius of 6 , or A floor = 4 1 π 6 2 = 9 π .
The total area is therefore A total = A floor + 2 A wall = 9 π + 2 ( 2 4 2 − 1 8 ) = 9 π + 4 8 2 − 3 6 ≈ 6 0 . 1 5 6 .