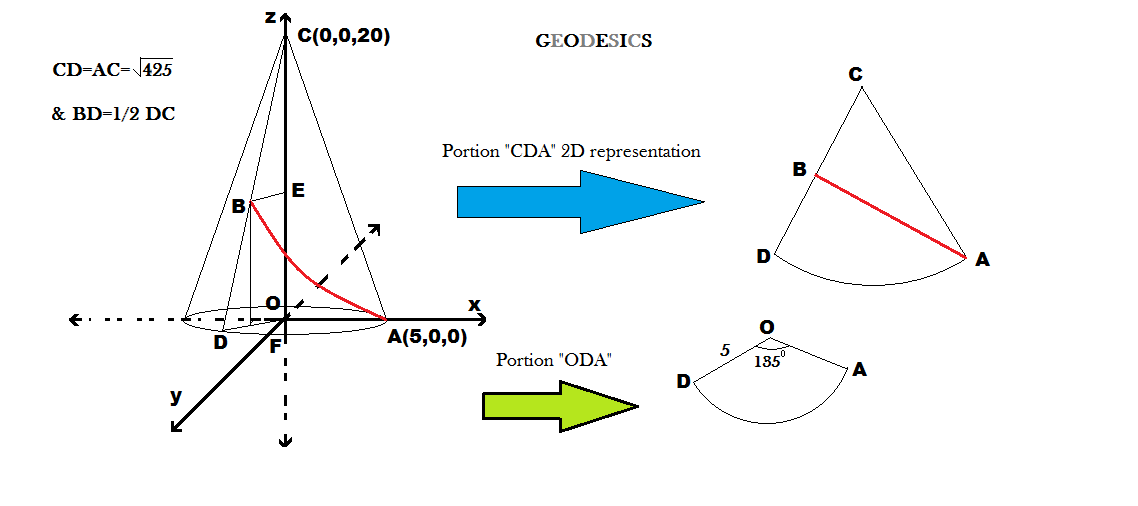
Shortest path on the surface of a cone
A cone has its axis extending along the z axis, with its base of radius 5 centered at the origin. Its height is 2 0 units. Two points are on its surface, A ( 5 , 0 , 0 ) , and B ( 2 2 − 5 , 2 2 5 , 1 0 ) . Find the length of the shortest path between points A and B , such that the path lies entirely on the surface of the cone.
The answer is 13.18.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Points on the cone can written as
p = ( s sin θ c c o s ϕ , s sin θ c s i n ϕ , H − s cos θ c )
where tan θ c = R / H = 5 / 2 0 = 1 / 4 , from which cos θ c = 1 + 1 6 1 1 = 1 7 4
and sin θ c = 1 7 1
Now if we unfold the surface of the cone onto a plane, the surface of the cone
is mapped into a circular sector, which can be described by polar
coordinates ( r , ψ ) , that can obtained by the identities:
r = s
r ψ = s ( sin θ c ) ϕ (equal arc length)
hence, ψ = ( sin θ c ) ϕ
So, let's compute the polar coordinates of the unfolded points A and B,
For point A, we have , s A sin θ c = 5 , from which s A = 5 1 7
and ϕ A = 0 , hence ψ A = 0 .
For point B, a similar computation, reveals that s B = 2 . 5 1 7 , and ϕ B = 4 3 π , hence ψ B = 4 1 7 3 π
Now the shortest path is the straight line segment connecting the unfolded A and B, and its length is given by
the distance fromula
d = ( s A cos ψ A − s B cos ψ B ) 2 + ( s A sin ψ A − s B sin ψ B ) 2 ≈ 1 3 . 1 8