Similar Curves
 Let two curves
and
be
similar
in the range
if for all
in the range
we have
.
Let two curves
and
be
similar
in the range
if for all
in the range
we have
.
Let be the half-hyperbola and let be a parabola with equation .
If and are similar in the range where , then the largest possible value of can be expressed as for positive integers with square-free. Find .
The answer is 30.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
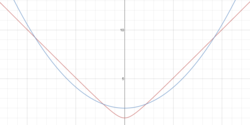
We can draw a rough graph of y = a x 2 + b , y = x 2 + 1 , and their difference, y = a x 2 + b − x 2 + 1 . They are show above, in blue, red, and green respectively.
Obviously to have q − p to be the greatest we must have the green graph take up as much space in the y-range [ − 1 , 1 ] as possible. This means it is tangent to the line y = − 1 and y = 1 . It follows that y = a ( 0 ) 2 + b − 0 2 + 1 = 1 , so b = 2 .
Now we must solve for a by using the information that y = a x 2 + 2 − x 2 + 1 is tangent to y = − 1 .
We plug in y = − 1 and rearrange to get a x 2 + 3 = x 2 + 1 .
Squaring both sides gives a 2 x 4 + 6 a x 2 + 9 = x 2 + 1 .
Rearranging gives a 2 x 4 + ( 6 a − 1 ) x 2 + 8 = 0
We use the quadratic equation with respect to x 2 to obtain x 2 = 2 a 2 1 − 6 a ± 4 a 2 − 1 2 a + 1 .
Remembering that since the green graph is tangent to y = − 1 , we must have that the discriminant of this quadratic is zero. Thus, we have 4 a 2 − 1 2 a + 1 = 0 .
Using the quadratic formula with respect to a , we obtain a = 2 3 ± 2 . However, if a = 2 3 + 2 , then x 2 is negative, thus x is imaginary; bad. Thus, a = 2 3 − 2 .
We have figured out that the blue graph's equation is y = ( 2 3 − 2 ) x 2 + 2 . The green graph's equation is then y = ( 2 3 − 2 ) x 2 + 2 − x 2 + 1 . We now must find the points of intersection of this graph and y = 1 to determine the values of p and q .
Setting y = 1 and simplifying, we get ( 2 3 − 2 ) x 2 + 1 = x 2 + 1 .
Squaring both sides and subtracting 1 , we have ( 2 3 − 2 ) 2 x 4 + ( 3 − 2 2 ) x 2 = x 2 .
Dividing both sides by x 2 (allowed because x = 0 is not the root we want) we get ( 2 3 − 2 ) 2 x 2 + 3 − 2 2 = 1 .
Simplifying: ( 4 1 7 − 3 2 ) x 2 = 2 2 − 2 .
Isolating x 2 we have x 2 = 4 1 7 − 3 2 2 2 − 2
Rationalizing, we get x 2 = 5 6 + 4 0 2
Taking the square root and simplifying, we finally get that q = 2 1 4 + 1 0 2 . Also, p = − 2 1 4 + 1 0 2 .
Thus, we have that q − p = 4 1 4 + 1 0 2 , and so our answer is 4 + 1 4 + 1 0 + 2 = 3 0 . □