Radical Integral Of Radicals
∫ 3 6 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) d x
If the definite integral above can be expressed as a b where a , b are positive integers with b square free, then what is the value of a b ?
The answer is 18.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
7 solutions
wow, nice solution :o :o :o
I wanna ask why it's root 3- root t
Not root t -root 3
I tried both and the result in each one is differernt
Log in to reply
I have tried to evaluate the integral using this way also, and I got ab=12 in the end.
Hi! I know it's been a long time but I believe the reason why it should be sqrt(3)-sqrt(t) is that for the range of values we are working with ( x = 3 to x = 6) gives a negative value for sqrt(t)-sqrt(3), which is just invalid because we want the principal root of the expression t+3-2sqrt(t). Thus, we had to flip them over.
Log in to reply
Yep, that’s exactly right. By definition the principle square root function outputs a positive value, so for example the sqrt((-5)^2) would be 5, not -5.
Can someone tell me how i d9d it wong, i got 4root 3=12 but i used u=sqrt(12x-36)
Log in to reply
Actually, you made the same mistake I made. We should take the mode of the term after the square and square root is cancelled, as the above solution has discussed.
Wait, you can also get 4sqrt3 if you write ( sqrt3 -sqrtx) as (sqrtx-sqrt3), try it out
So 4sqrt3 for asqrtb is also another possible answer, so 12 is also right
Log in to reply
It’s not, because the principle square root function is always positive by definition therefore if root x - root 3 is negative (in this case, it is), the principle square root of its square would return the positive counterpart which is root 3 - root x, leading to the correct answer. for example the sqrt((-5)^2) would be 5, not -5.
let f ( x ) = x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ,
we have
f ( x ) 2 = x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + 2 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 ) ( x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 = 2 x + 2 x 2 − ( 1 2 x − 3 6 ) = 2 x + 2 ( x − 6 ) 2 = 2 x + 2 ( 6 − x ) ( a 2 = a ∀ a ≥ 0 ) = 1 2
thus
∫ 3 6 f ( x ) d x = ( 6 − 3 ) 1 2 = 6 3
at starting i made mistake in opening the square root with positive sign but later i realised that intergration in from 3 to 6 so the square root should be opened with negative sign. Nice one.
We can also use u 2 = x − 3 , then:
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ x = 6 x = 3 x = u 2 + 3 ⇒ u = 3 ⇒ u = 0 ⇒ d x = 2 u d u
Let the integral be I , then:
I = ∫ 3 6 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) d x = ∫ 0 3 ( u 2 + 3 + 1 2 u + u 2 + 3 − 1 2 u ) 2 u d u = ∫ 0 3 ( u 2 + 2 3 u + 3 + u 2 − 2 3 u + 3 ) 2 u d u = ∫ 0 3 ( ( 3 + u ) 2 + ( 3 − u ) 2 ) 2 u d u = ∫ 0 3 ( 3 + u + 3 − u ) 2 u d u = ∫ 0 3 4 3 u d u = 2 3 [ u 2 ] 3 0 = 6 3
⇒ a b = 6 × 3 = 1 8 .
We can substitute x = 3 sec^2 z to finish the job mentally...
We have I = ∫ 3 6 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) d x Puting 1 2 x − 3 6 = u 2 ⇒ x = 1 2 u 2 + 3 6 and differentiating we get d x = 1 2 1 u d u Rewriting the expressions I = ∫ 3 6 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) d x I = ∫ 3 6 ( 1 2 u 2 + 3 6 + u + 1 2 u 2 + 3 6 − u ) 1 2 1 u d u I = 1 2 1 ∫ 3 6 ( 1 2 ( u + 6 ) 2 + 1 2 ( u − 6 ) 2 ) u d u
I = 1 2 1 ∫ 3 6 ( 1 2 ( u + 6 ) 2 + 1 2 ( u − 6 ) 2 ) u d u I = 1 2 1 2 1 ∫ 3 6 2 u 2 d u I = 3 × 1 2 1 2 2 [ u 3 ] 3 6
I = 3 × 1 2 1 2 2 [ 1 2 x − 3 1 2 x − 3 ] 3 6 I = 6 1 2 3 6 × 6 ⇒ 6 3 = a b
Therefore, a b = 6 × 3 ⟹ 1 8
Let the function we are integrating be K. Then, K^2 = 2x + 2(x^2-12x+36)^0.5. Since our values of x range from 3 to 6, we want the negative square root, so K^2 = 2x - 2(x-6) = 12. So K = 2 (3^.5). So our antiderivative is 2 (3^.5)x, giving us an answer of 2 (3^.5)(6-3) = 6 (3^.5). Therefore, 6*3 = 18.
The title of the problem made it very easy maybe it should be changed.
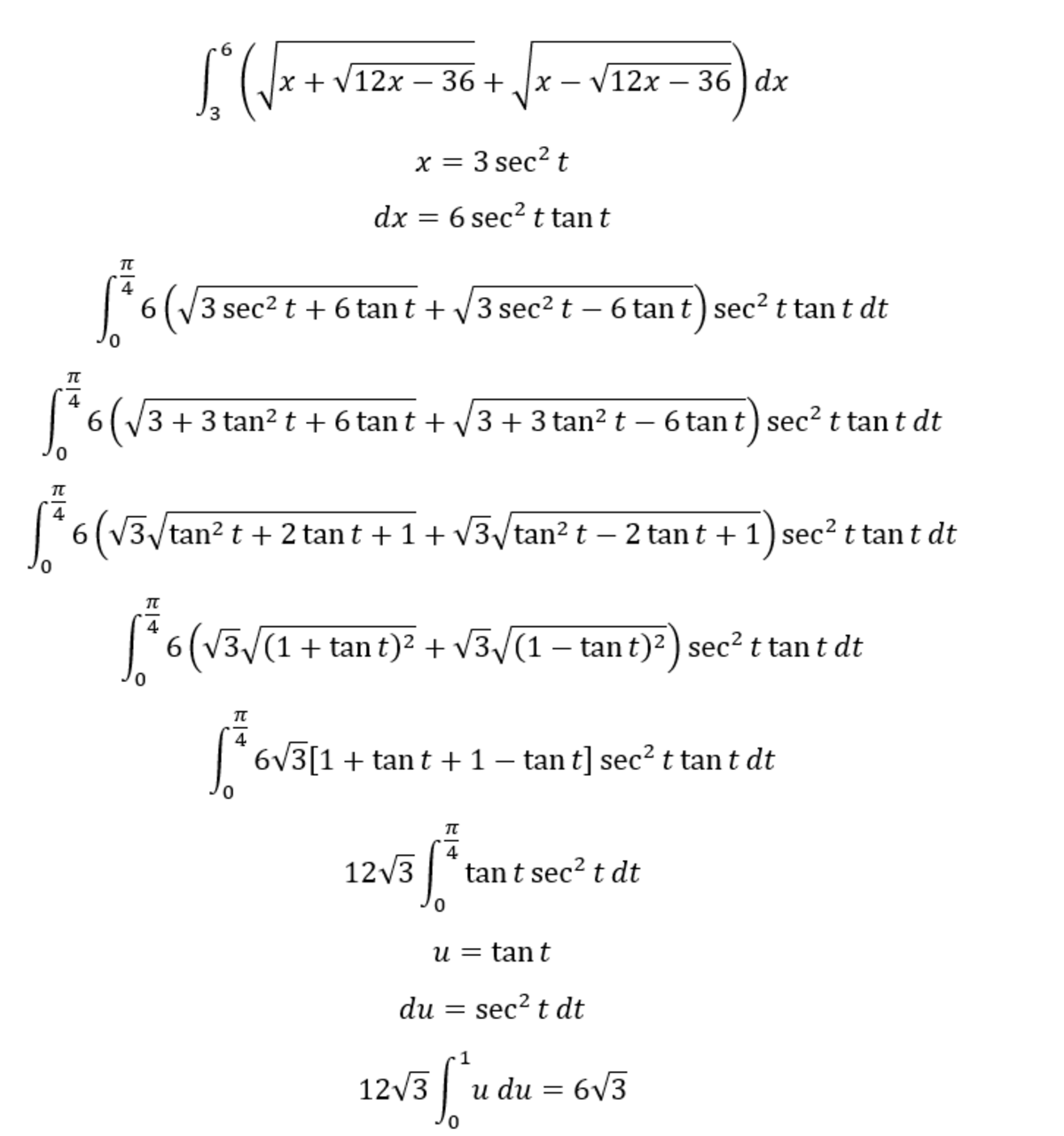
∫ 3 6 ( x + 1 2 x − 3 6 + x − 1 2 x − 3 6 ) d x
put t = x − 3 . Rewrite given integral in terms of t .
⇒ ∫ 0 3 ( t + 3 + 2 3 t + t + 3 − 2 3 t ) d t
= ∫ 0 3 ( ( t + 3 ) 2 + ( 3 − t ) 2 ) d t = ∫ 0 3 ( t + 3 + 3 − t ) d t ( ∵ ( 3 − t ) 2 = 3 − t ∀ t ∈ ( 0 , 3 ) ) = ∫ 0 3 2 3 d t = 6 3 ⇒ a × b = 1 8