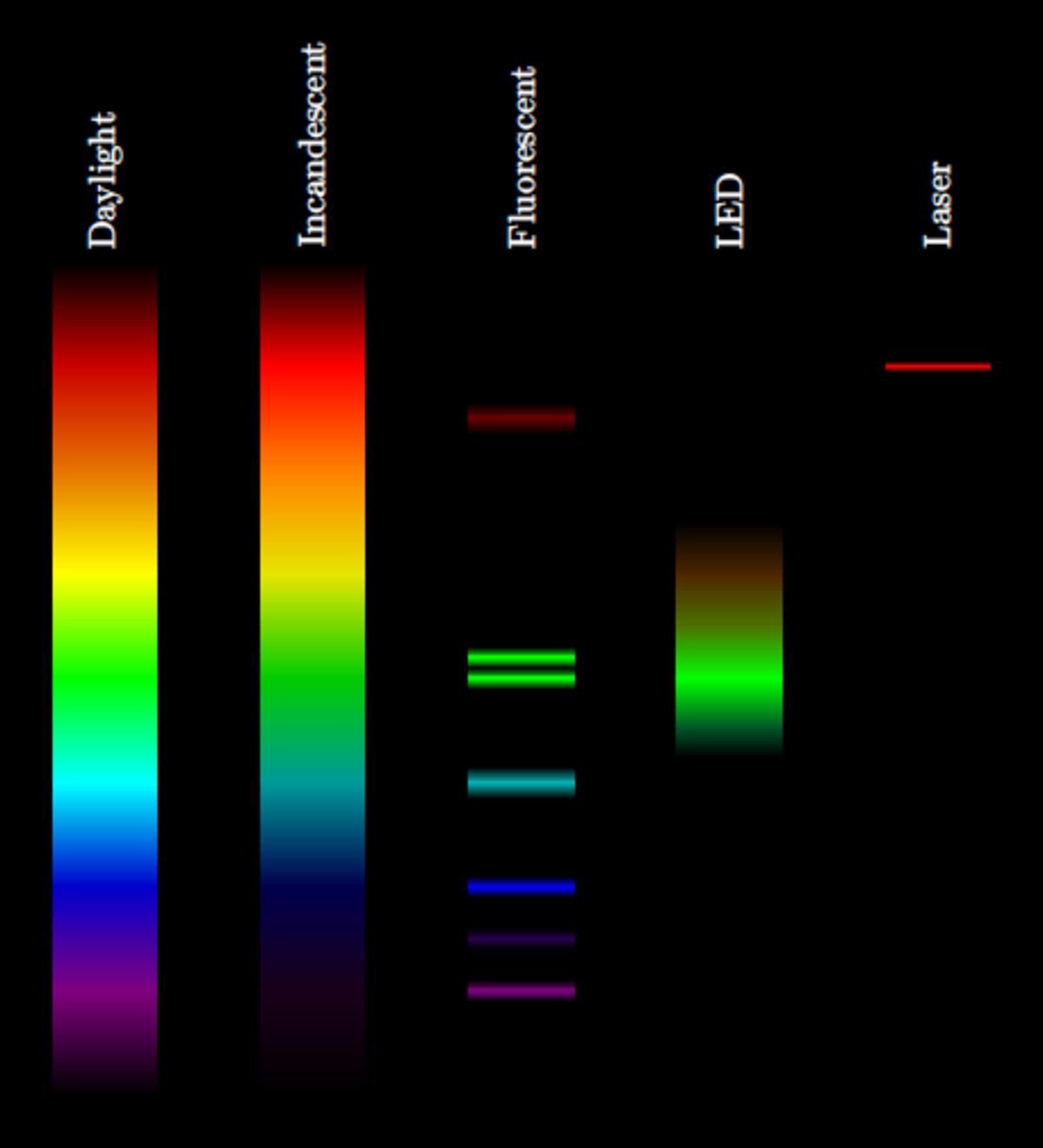
Spectral lines
Electricity and Magnetism
Level
3
A light beam is split by a prism into its spectral colors, so that the spectrum shown below results. What is the light source of this beam?
Fluorescent light bulb
Laser
LED
Daylight
Incandescent light bulb
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.