Square in Square 2
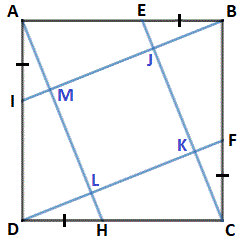
In the diagram, A B C D is a square with an area of 2 5 , J K L M is a square with an area of 1 8 , and A I = B E = C F = D H .
Find B E A E .
(Diagram not drawn to scale.)
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
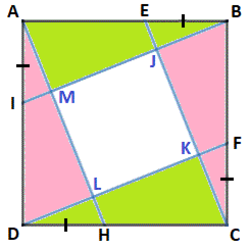
We notice that the green and pink triangles are congruent. Therefore the area of one of these triangles is A △ = 4 [ A B C D ] − [ J K L M ] = 4 2 5 − 1 8 = 4 7 . Let A M = a and B M = b ; then A △ = 2 1 a b = 4 7 ⟹ a b = 2 7 . Since the area of square A B C D is 2 5 , ⟹ A B = 5 . By Pythagorean theorem we have:
a 2 + b 2 a 2 + ( 2 a 7 ) 2 4 a 4 + 4 9 4 a 4 − 1 0 0 a 2 + 4 9 ( 2 a 2 − 1 ) ( 2 a 2 − 4 9 ) = 2 5 = 2 5 = 1 0 0 a 2 = 0 = 0 Since a b = 2 7 Multiply both sides by 4 a 2 Rearrange
Note that both a and b satisfy the equation. ⟹ { a = 2 1 b = 2 7 , since b > a . Now we note that △ A M B and △ E J B are similar. Therefore,
B J B E b − J M B E ⟹ B E = B M A B = b 5 = 2 7 5 ( 2 7 − 3 2 ) = 7 5 Since [ J K L M ] = 1 8 , ⟹ J M = 3 2
Therefore, B E A E = B E A B − B E = 7 5 5 − 1 = 6 .
Nice approach!
ah , df and bi are two letter variable names.
ah = y = 5 − δ 5 x
df = y = 5 δ x
bi = y = ( 5 − δ ) + 5 δ x
m = { x , y } /. Solve [ ah ∧ bi ] [ [ 1 ] ] ⇒ { δ 2 + 2 5 5 δ 2 , δ 2 + 2 5 5 ( δ 2 − 5 δ + 2 5 ) }
l = { x , y } /. Solve [ ah ∧ df ] [ [ 1 ] ] ⇒ { δ 2 + 2 5 2 5 δ , δ 2 + 2 5 5 δ 2 }
δ = ( δ /. Solve [ SquaredEuclideanDistance [ m , l ] = 1 8 ] ) [ [ 1 ] ] ⇒ 7 5
δ 5 − δ ⇒ 6
Of course, the simplier answer is − s 2 − 1 s ( 2 − s 2 + s ) with s being set to 2 5 1 8 giving 6 .
With central square areas of 1, 5, 10 and 18, rational results of 3 1 , 1 , 2 and 6 are availed, respectively.
Since A B C D has an area of 2 5 , A B = 5 , and since J K L M has an area of 1 8 , J M = 3 2 . Let x = B E = A I and y = A M = B J .
Since △ A M B is a right triangle, by Pythagorean's Theorem y 2 + ( 3 2 + y ) 2 = 5 2 which solves to y = 2 2 , and since △ H A B ∼ △ A M B by the AA similarity postulate, 5 x = 3 2 + y y so that with y = 2 2 this solves to x = 7 5 .
Therefore the ratio B E A E = 7 5 5 − 7 5 = 6 .