Square Pyramids!
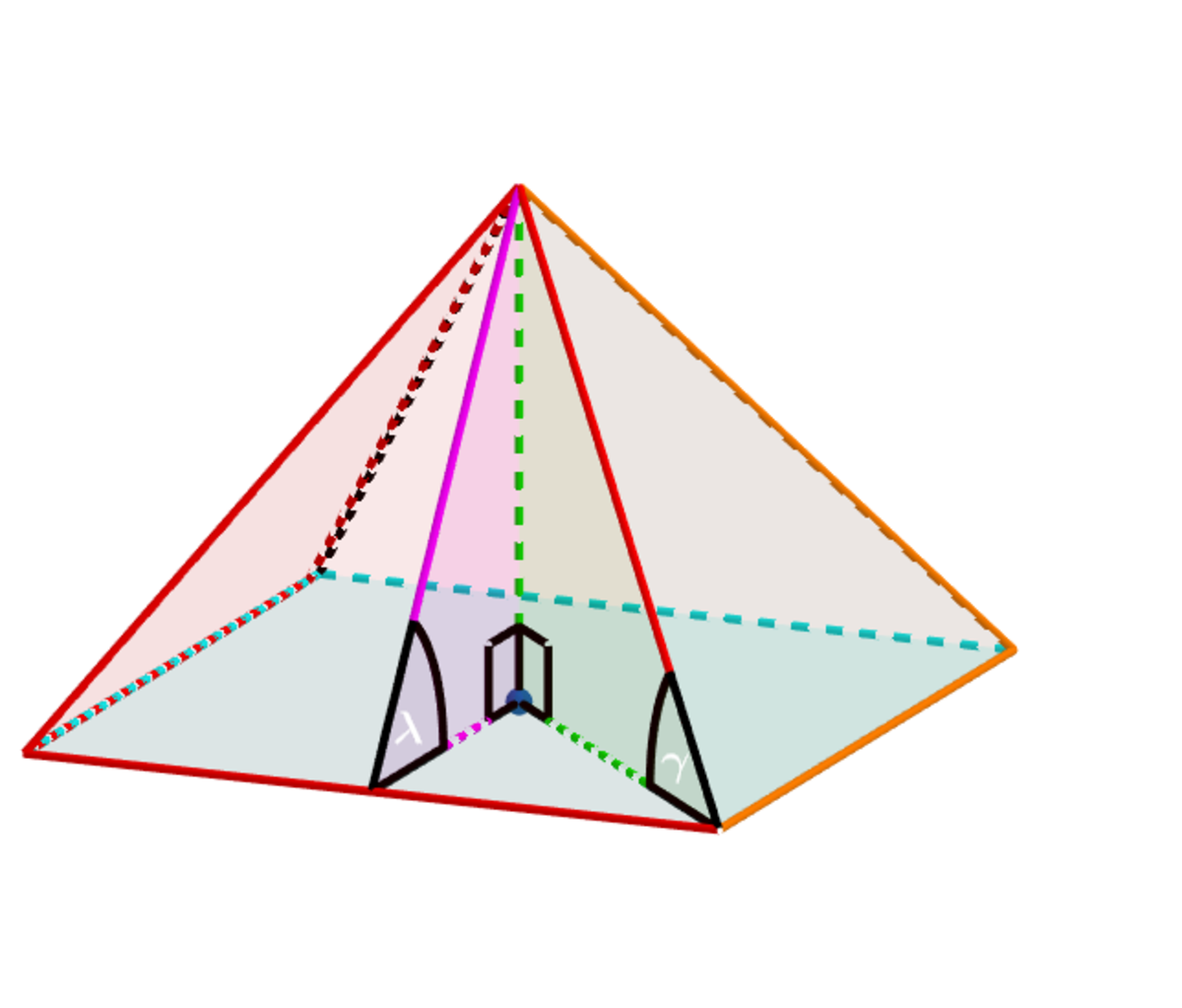
The angles (the slant height angle), (the base edge angle) and (the angle made between two adjacent faces) minimize the lateral surface area of the above square pyramid when the volume is held constant.
Find .
The answer is -6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
s = 2 4 H 2 + x 2 ⟹ the surface area A = 2 x s = x 4 H 2 + x 2
The volume V = 3 1 x 2 H = K ⟹ H = x 2 3 K ⟹ A = x 3 6 K 2 + x 6 ⟹
d x d A = x 2 3 6 k 2 + x 6 2 x 6 − 3 6 k 2 = 0 x = 0 ⟹ x 6 − 1 8 k 2 = 0 ⟹
x = ( 1 8 K 2 ) 6 1 = 3 3 1 2 6 1 k 3 1 ⟹ H = ( 2 3 ) 3 1 K 3 1
⟹ tan ( λ ) = x 2 H = 2 and tan ( γ ) = 1 .
O P = x i + 0 j + 0 k
O R = 0 i − x j + 0 k
O S = 2 x i − 2 x j + H k
U = O P X O S = 0 i − x H j − 2 x 2 k
and
V = O R X O S = − x H i + 0 j + 2 x 2 k
U ∘ V = − 4 x 4
∣ U ∣ = 2 x 4 H 2 + x 2 = ∣ V ∣
⟹ cos ( θ ) = ∣ U ∣ ∣ V ∣ U ∘ V = − 4 H 2 + x 2 x 2 = − 3 1
⟹ cos ( θ ) tan 2 ( λ ) tan ( γ ) = − 6 .
Note: d x 2 d 2 A ∣ x = ( 1 8 k 2 ) 6 1 = 4 3 > 0 ⟹ min occurs at x = ( 1 8 k 2 ) 6 1