Stringent Numbers 1
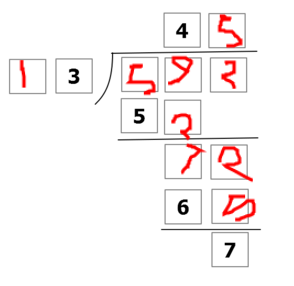
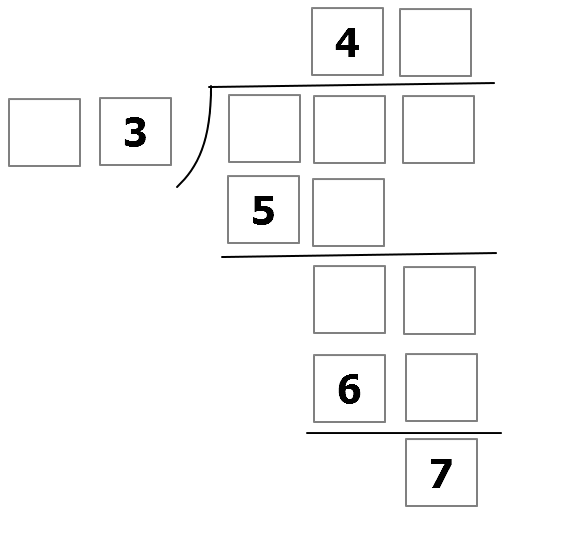 The above shows a long division between 2 integers, with the last box at the bottom representing the remainder of the quotient. Each box represents a single digit non-negative integer.
The above shows a long division between 2 integers, with the last box at the bottom representing the remainder of the quotient. Each box represents a single digit non-negative integer.
What is the sum of all the missing numbers?
The answer is 38.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
in the dividend, if the digit is 0,then multiplying with 4 wont give 5 as left digit, and if the digit is >1, multiplying by four gives us a bigger number. we conclude by ranging that the digit is 1. also 1 3 × 4 = 5 2 , by that we find another digit.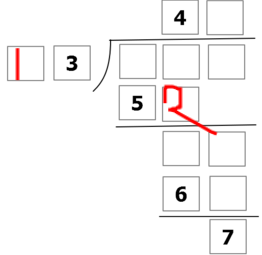 now, by divisibility check, the number above the remainder is
6
5
, as it is the only 2 digit number divisible by 13 stating with 6. also we add 5 in the quotient, we find the number above 65:
x
−
6
5
=
7
⟹
x
=
7
2
. so the digit of the dividend also becomes 2. and
x
−
5
2
=
7
⟹
x
=
5
9
. we are done.
now, by divisibility check, the number above the remainder is
6
5
, as it is the only 2 digit number divisible by 13 stating with 6. also we add 5 in the quotient, we find the number above 65:
x
−
6
5
=
7
⟹
x
=
7
2
. so the digit of the dividend also becomes 2. and
x
−
5
2
=
7
⟹
x
=
5
9
. we are done.