This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
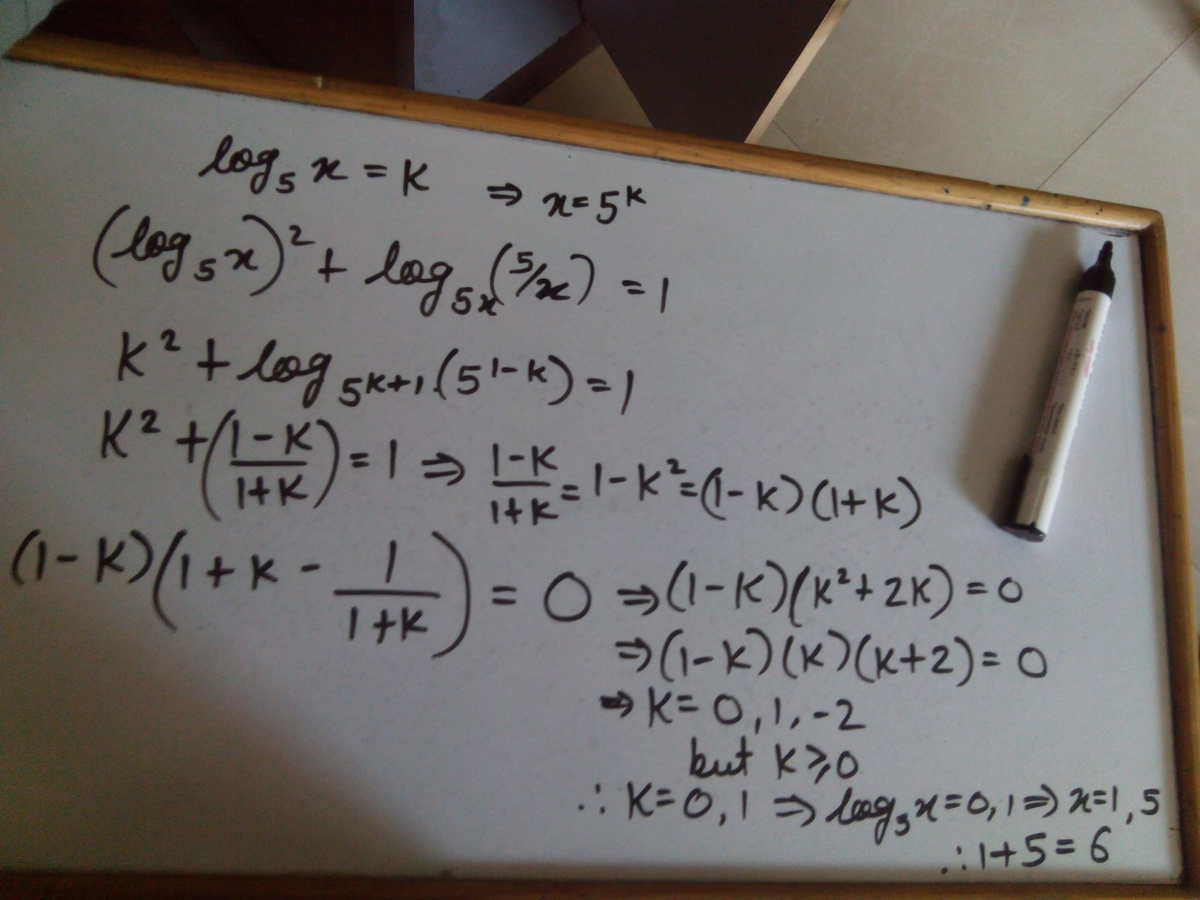
First look at y = lo g 5 x x 5 ⟹ ( 5 x ) y = x 5
⟹ x y + 1 = 5 1 − y
⟹ ( y + 1 ) lo g 5 ( x ) = 1 − y
⟹ y ( 1 + lo g 5 ( x ) ) = 1 − lo g 5 ( x )
⟹ y = 1 + lo g 5 ( x ) 1 − lo g 5 ( x ) .
Now let a = lo g 5 ( x ) . Then the given equation becomes
a 2 + 1 + a 1 − a = 1 ⟹ a 3 + a 2 − a + 1 = 1 + a
⟹ a ( a 2 + a − 2 ) = 0 ⟹ a ( a + 2 ) ( a − 1 ) = 0 .
So we have solutions a = lo g 5 ( x ) = 0 , 1 , − 2 ⟹ x = 1 , 5 , 2 5 1 .
The only integral values are 1 and 5 , the sum of which is 6 .