Symmetrical Sliding
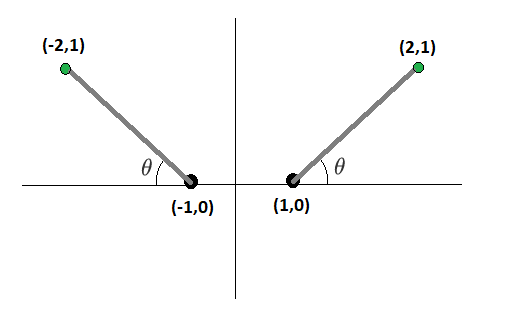
Two beads of mass are positioned so that they slide down two smooth, symmetrically positioned rods. The start and end points of the rods are shown in the diagram, and the beads are shown in green at their initial locations, where they begin at rest.
There is no ambient gravity field in this problem. The only gravity is the mutually attractive force between the beads.
How long does it take each bead to get to the other end of its respective rod?
Details and Assumptions:
- All distances in meters
- Gravitational constant
-
=
-
- The rods do not move
The answer is 8.903.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!