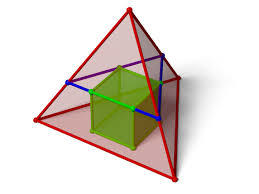
Tetracube
The side length of the largest cube that can fit inside a regular tetrahedron whose edges have an unit length of one, can be represented by the formula
A + A B + B B A B ,
where A and B are coprime positive integers. Find A + B .
The answer is 5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
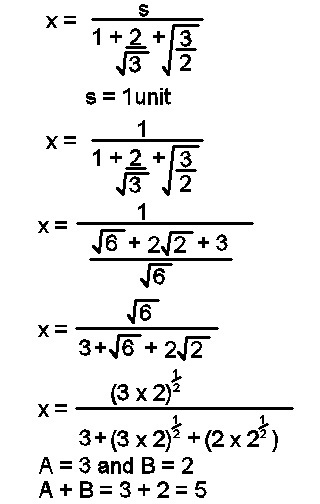
How did you know that x = 1 + 3 2 + 2 3 s ?
The the problem is by replacing 3 by A and 2 by B from the link below. The solution too by Brilliant Member is from the link below.
link text
[[link text]
If the cube has side x, then the blue triangle has side
x
+
3
2
∗
x
,
and so does the small tetrahedron that it cuts off. Since the difference in heights of the small and large tetrahedra is x, their difference in side lengths is
2
3
∗
x
.
S
o
s
=
x
+
3
2
∗
x
+
2
3
∗
x
.
S
i
n
c
e
s
=
1
,
⟹
x
=
3
+
2
∗
3
+
2
2
2
∗
3
A
=
3
,
B
=
2
,
A
+
B
=
5