The answer is not 4 !!
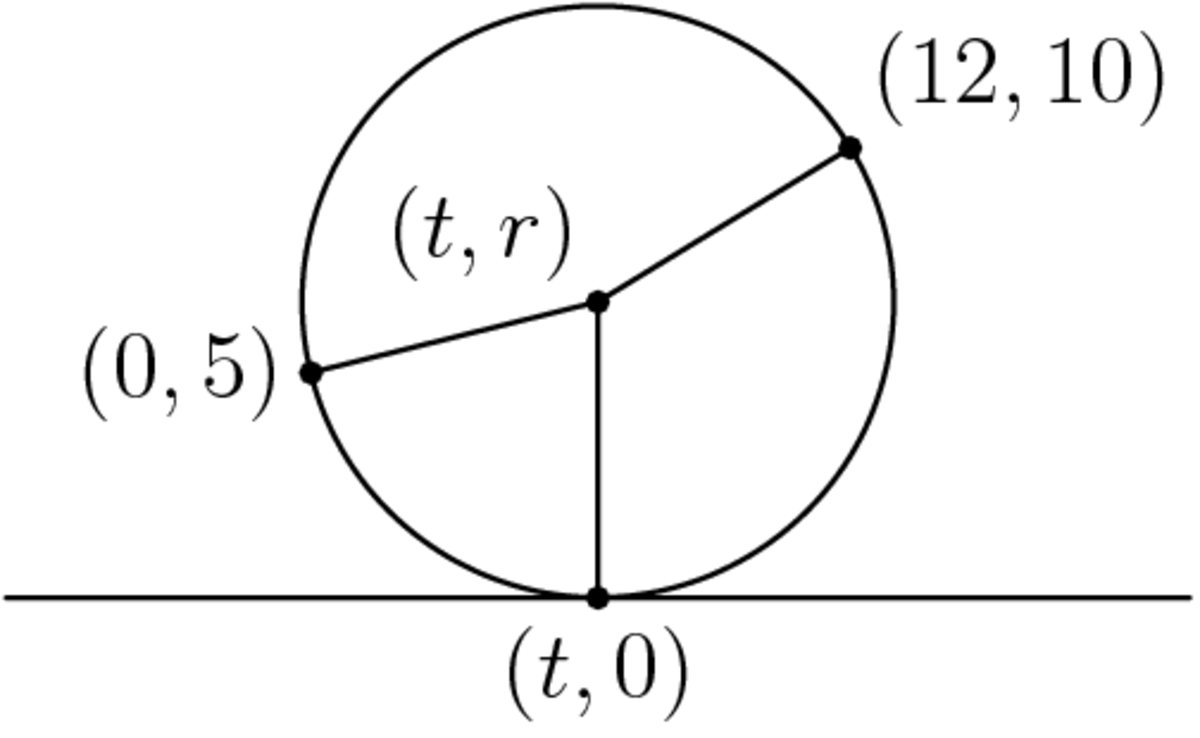
Three points in the x y plane are given as P ( 0 , 5 ) , Q ( 1 2 , 1 0 ) and a third point R ( t , 0 ) , where t ∈ R . Here point R is sliding on the x -axis. Find the value of t that will result in a maximum angle θ = ∠ P R Q .
The answer is 6.385.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
For the point R that maximizes ∠ P R Q , the circumcircle of triangle P Q R is tangent to the x -axis.
Let r be the radius of the circle. Then the center of the circle is ( t , r ) , so t 2 + ( r − 5 ) 2 ( t − 1 2 ) 2 + ( r − 1 0 ) 2 = r 2 , = r 2 .
We can solve for t to get − 1 2 ± 1 3 2 . The root that makes sense is − 1 2 + 1 3 2 .
Slope of P R = m 1 = − t 5 .
That of Q R = m 2 = 1 2 − t 1 0
So tan ∠ P R Q = 1 + m 1 m 2 m 1 − m 2 =
t 2 − 1 2 t + 5 0 5 ( t + 1 2 )
This will be extrimum when it's first differential coefficient with respect to t is zero :
⟹ t 2 + 2 4 t − 1 9 4 = 0 ⟹ t ≈ 6 . 3 8 5 , − 3 0 . 6 8 5
For the angle to be maximum , the second derivative should be negative. This happens for t ≈ 6 . 3 8 5 .
By the distance equation, P Q = ( 0 − 1 2 ) 2 + ( 5 − 1 0 ) 2 = 1 3 , P R = ( 0 − t ) 2 + ( 5 − 0 ) 2 = t 2 + 2 5 , and Q R = ( 1 2 − t ) 2 + ( 1 0 − 0 ) 2 = t 2 − 2 4 t + 2 4 4 .
By the law of cosines, cos ∠ P R Q = 2 ⋅ P R ⋅ Q R P R 2 + Q R 2 − P Q 2 , or cos θ = 2 ⋅ t 2 + 2 5 ⋅ t 2 − 2 4 t + 2 4 4 ( t 2 + 2 5 ) 2 + ( t 2 − 2 4 t + 2 4 4 ) 2 − 1 3 2 , which can be rearranged to cos 2 θ = t 4 − 2 4 t 3 + 2 6 9 t 2 − 6 0 0 t + 6 1 0 0 t 4 − 2 4 t 3 + 2 4 4 t 2 − 1 2 0 0 t + 2 5 0 0 .
By implicit differentiation, 2 cos θ sin θ d t d θ = ( t 4 − 2 4 t 3 + 2 6 9 t 2 − 6 0 0 t + 6 1 0 0 ) 2 ( t 4 − 2 4 t 3 + 2 6 9 t 2 − 6 0 0 t + 6 1 0 0 ) ( 4 t 3 − 7 2 t 2 + 4 8 8 t − 1 2 0 0 ) − ( t 4 − 2 4 t 3 + 2 4 4 t 2 − 1 2 0 0 t + 2 5 0 0 ) ( 4 t 3 − 7 2 t 2 + 5 3 8 t − 6 0 0 ) , and when d t d θ = 0 (for a maximum θ ), this simplifies to ( t + 1 2 ) ( t 2 − 1 2 t + 5 0 ) ( t 2 + 2 4 t − 1 9 4 ) = 0 , which solves to t = 1 3 2 − 1 2 ≈ 6 . 3 8 5 for 0 < t < 1 2 .