The Art of Zig-zag Geometry
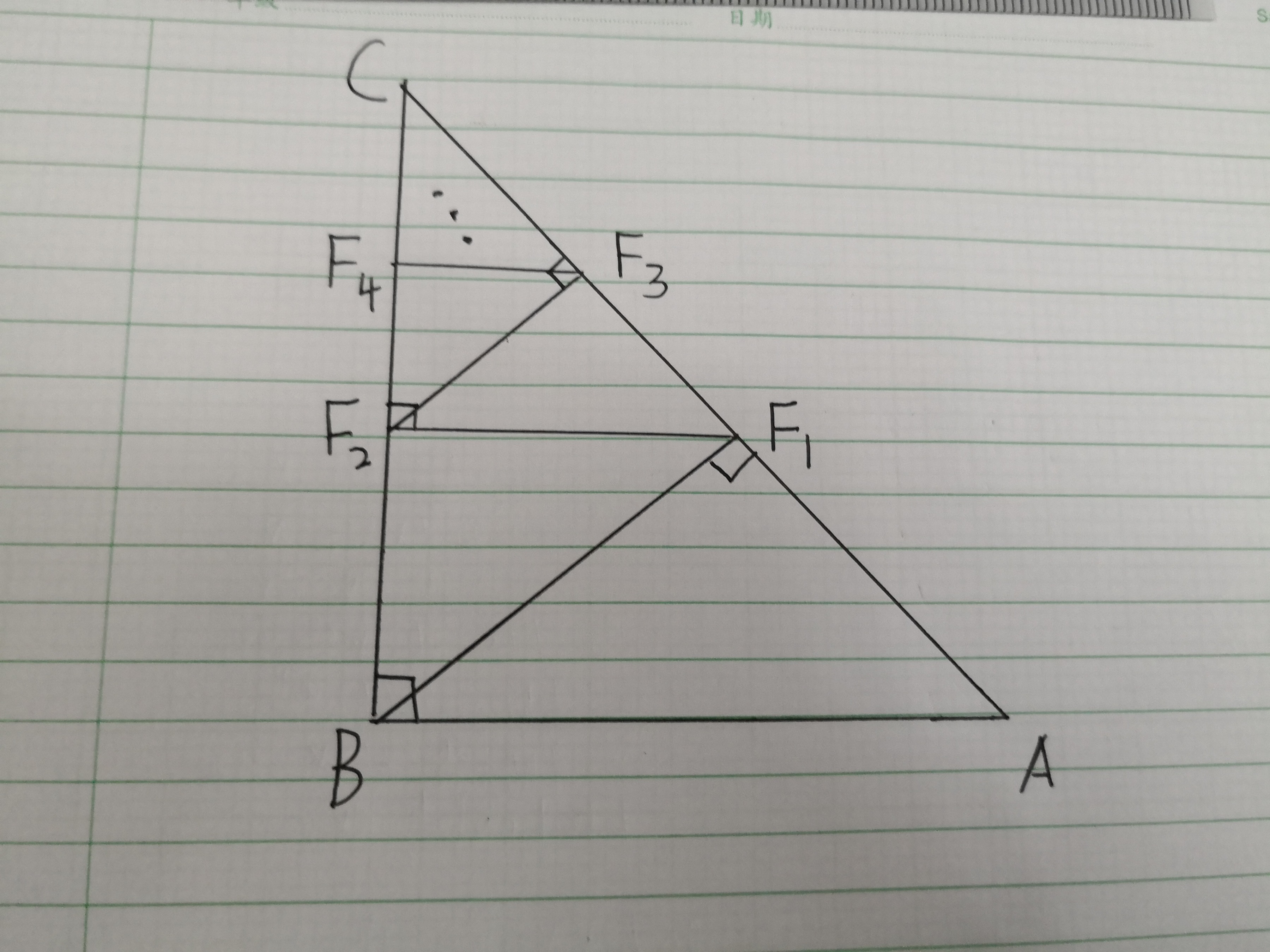
Given a triangle Δ A B C with ∠ A B C = 9 0 ∘ and ∣ A B ∣ = 1 5 , ∣ B C ∣ = 2 0 , ∣ A C ∣ = 2 5 , From B, a perpendicular line is drawn to A C such that the perpendicular foot on AC is at F 1 . From F 1 , a perpendicular line is drawn from F 1 to B C such that the perpendicular foot on BC is at F 2 . The similiar process continues up to n times such that n → ∞ . Let the sum of areas of Δ B F 1 F 2 , Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 , Δ F 4 F 5 F 6 , ..., and Δ F 2 n − 2 F 2 n − 1 F 2 n be S x and the area of Δ A B C be S t . If S t S x = b a such that a and b are co-prime positive integers, then find a + b .
This is part of the set Fun With Problem-Solving .
The answer is 57.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Lol I entered the other surface and thought:whaaaaat? So I checked the answer and it turned out I did everything right.... I didn't use the cosine at start. The equivalence of the triangles followed quickly to me by the fact 2 of 3 angles are always the sane here(for instance by using Z-angle)
What do u mean by other surface?
Triangles ΔABC, ΔBF1F2, ΔF1F2F3, are similar.By similarity : AC/BC = AB/BF1, So we can find BF1=12. By the same way, we can find F1F2=9.6, BF2=7.2,and F2F3=7.68. ΔBF1F2, ΔF1F2F3,...form geometric progression with tha ratio r = (7.68/12)^2 = (16/25)^2. We can find Sx = (9.6)(3.6)/[1 – (16/25)^2] = (3.84)(625)/41 The area of ΔABC, St = 150. So Sx/St = 16/41., and a+b=57
@rab gani
You can use LaTeX to beautify your answer or question. Use "\" with "(" to start and use "\" with ")" to end it. We apply on variables (such as ), number (), point (point , line ). This is the basic use of :
https://brilliant.org/profile/chan-n20gy9/sets/latex/485571/beginner-latex-guide/
For instance, the solution you proposed, when written in LaTeX becomes:
Triangles Δ A B C , Δ B F 1 F 2 , Δ F 1 F 2 F 3 , are similar.
By similarity : B C A C = B F 1 A B ,
So we can find B F 1 = 1 2 .
By the same way, we can find F 1 F 2 = 9 . 6
B F 2 = 7 . 2 and F 2 F 3 = 7 . 6 8 .
Δ B F 1 F 2 , Δ F 1 F 2 F 3 ,...form geometric progression with the ratio r = ( 7 . 6 8 / 1 2 ) 2 = ( 1 6 / 2 5 ) 2 .
We can find S x = ( 9 . 6 ) ( 3 . 6 ) / [ 1 − ( 1 6 / 2 5 ) 2 ] = ( 3 . 8 4 ) ( 6 2 5 ) / 4 1
The area of Δ A B C , S t = 1 5 0 .
So S t S x = 4 1 1 6 ., and a + b = 5 7
Let A F 1 = h and ∠ B A C = θ
cos θ = 2 5 1 5 = 5 3
cos θ = 1 5 h
1 5 h = 5 3
h = 9
So, A F 1 = 9 , C F 1 = 1 6
A r e a o f Δ C B F 1 A r e a o f Δ A B F 1 = C F 1 A F 1 = 1 6 9
A r e a o f Δ A B C A r e a o f Δ C B F 1 = 2 5 1 6
S i n c e F 1 F 2 ⊥ B C ,
F 1 F 2 ∥ B A
Δ F 1 F 2 C ∼ Δ A B C
C B C F 2 = C A C F 1 = 2 5 1 6
A r e a o f Δ C F 1 B A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 = C B F 2 B = C A F 1 A = 2 5 9
A r e a o f Δ A B C A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 = A r e a o f Δ C F 1 B A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ A B C A r e a o f Δ C F 1 B = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6
S i n c e Δ F 1 F 2 C ∼ Δ A B C ,
A r e a o f Δ A B C A r e a o f Δ F 1 F 2 C = ( A C F 1 C ) 2 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2
It follows that Δ B F 1 F 2 ∼ Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 , Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 ∼ Δ F 4 F 5 F 6 , . . . , Δ F 2 n − 4 F 2 n − 3 F 2 n − 2 ∼ Δ F 2 n − 2 F 2 n − 1 F 2 n
From above, A r e a o f Δ A B C A r e a o f Δ B 1 F 2 = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6
⇒ A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ A B C
A r e a o f Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ⋅ 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ A B C
A r e a o f Δ F 4 F 5 F 6 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 4 ⋅ 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ A B C
..............................................................
A r e a o f Δ F 2 n − 2 F 2 n − 1 F 2 n = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ F 2 n − 3 F 2 n − 2 F 2 n − 1 = ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 n − 2 ⋅ 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ A r e a o f Δ A B C
A r e a o f Δ B F 1 F 2 + A r e a o f Δ F 2 F 3 F 4 + A r e a o f Δ F 4 F 5 F 6 + . . . A r e a o f Δ F 2 n − 2 F 2 n − 1 F 2 n = A r e a o f Δ A B C ⋅ 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ ( n t e r m s ( 2 5 1 6 ) 0 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 4 + . . . + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 n − 2 )
S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ ( n t e r m s ( 2 5 1 6 ) 0 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 4 + . . . + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 n − 2 ) ⋅ S t
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ ( n t e r m s ( 2 5 1 6 ) 0 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 4 + . . . + ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 n − 2 )
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ 1 − ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ( 2 5 1 6 ) 0 × ( 1 − ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 n )
As n → ∞
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ 1 − ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 ( 2 5 1 6 ) 0 × ( 1 − 0 )
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ 1 − ( 2 5 1 6 ) 2 1
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ ( 1 − 2 5 1 6 ) ( 1 + 2 5 1 6 ) 1
S t S x = 2 5 9 ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ ( 2 5 9 ) ( 2 5 4 1 ) 1
S t S x = ⋅ 2 5 1 6 ⋅ 2 5 4 1 1
S t S x = 4 1 1 6