The Deathly Hallows
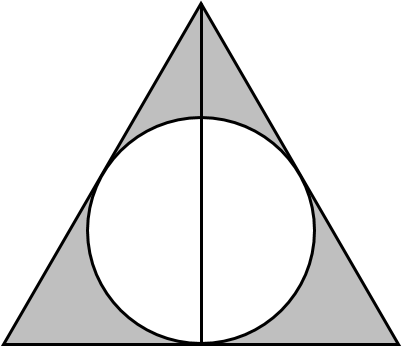 Given that
Given that
- the Invisibility Cloak (the large triangle) is equilateral,
- each side of the triangle is tangent to the Resurrection Stone (the circle in the middle), and
- the Elder Wand (the vertical line down the center) has a length of L ,
what is the area of the shaded region, in terms of L ?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
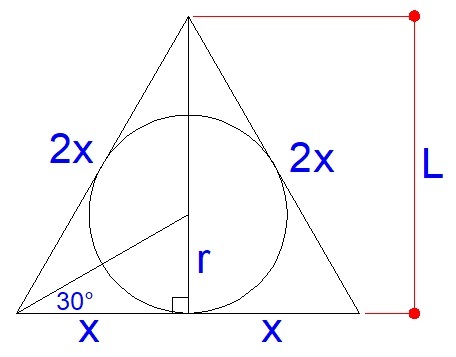 By pythagorean theorem, we have
By pythagorean theorem, we have
( 2 x ) 2 = x 2 + L 2 ⟹ 4 x 2 = x 2 + L 2 ⟹ x 2 = 3 L 2 ⟹ x = 3 L or 2 x = 3 2 L
tan 3 0 = x r ⟹ r = x tan 3 0 = x ( 3 3 ) = 3 3 x = 3 L
The area of the shaded region is equal to the area of the triangle minus the area of the circle. We have
A [ t r i a n g l e ] = 2 1 ( 2 x ) ( L ) = 2 1 ( 3 2 L ) ( L ) = 3 L 2
A [ c i r c l e ] = π r 2 = π ( 3 L ) 2 = 9 π L 2
A [ s h a d e d ] = 3 L 2 − 9 π L 2 = 9 3 9 L 2 − π L 2 3
Multiplying the fraction by 3 3 , we get
A [ s h a d e d ] = 2 7 9 3 L 2 − π L 2 ( 3 )
Simplifying further, we have
A [ s h a d e d ] = 2 7 9 3 L 2 − 3 π L 2 = 9 3 3 L 2 − π L 2 = 9 2 7 L 2 − π L 2 = 9 L 2 ( 2 7 − π )
Tell me where I made a mistake,
we know that de area of the triangle is A 1 = 4 3 L 2 , we know that de radius of the circle is r = 6 3 L
So the area of the circle is A 2 = 1 2 π L 2
Hence the shaded region must be A 1 − A 2 = 1 2 ( 2 7 − π ) L 2
The length from the centre of the circle O to one of the vertices is 3 2 L . Connect O to all three vertices we have 3 equal triangles, and each of them has the area of 2 1 ( 3 2 L ) ( 3 2 L ) sin 6 0 ∘ = 9 3 L 2 , so the area of the triangle is 9 3 3 L 2 = 9 2 7 L 2 .
From here you can already found the answer, but for the sake of a complete solution, I'll do the calculation for the circle as well.
The radius of the circle is then 3 1 L , so the area is π 9 1 L 2 . Hence the area of the shaded region is 9 2 7 − π L 2