There's Circles Everywhere!
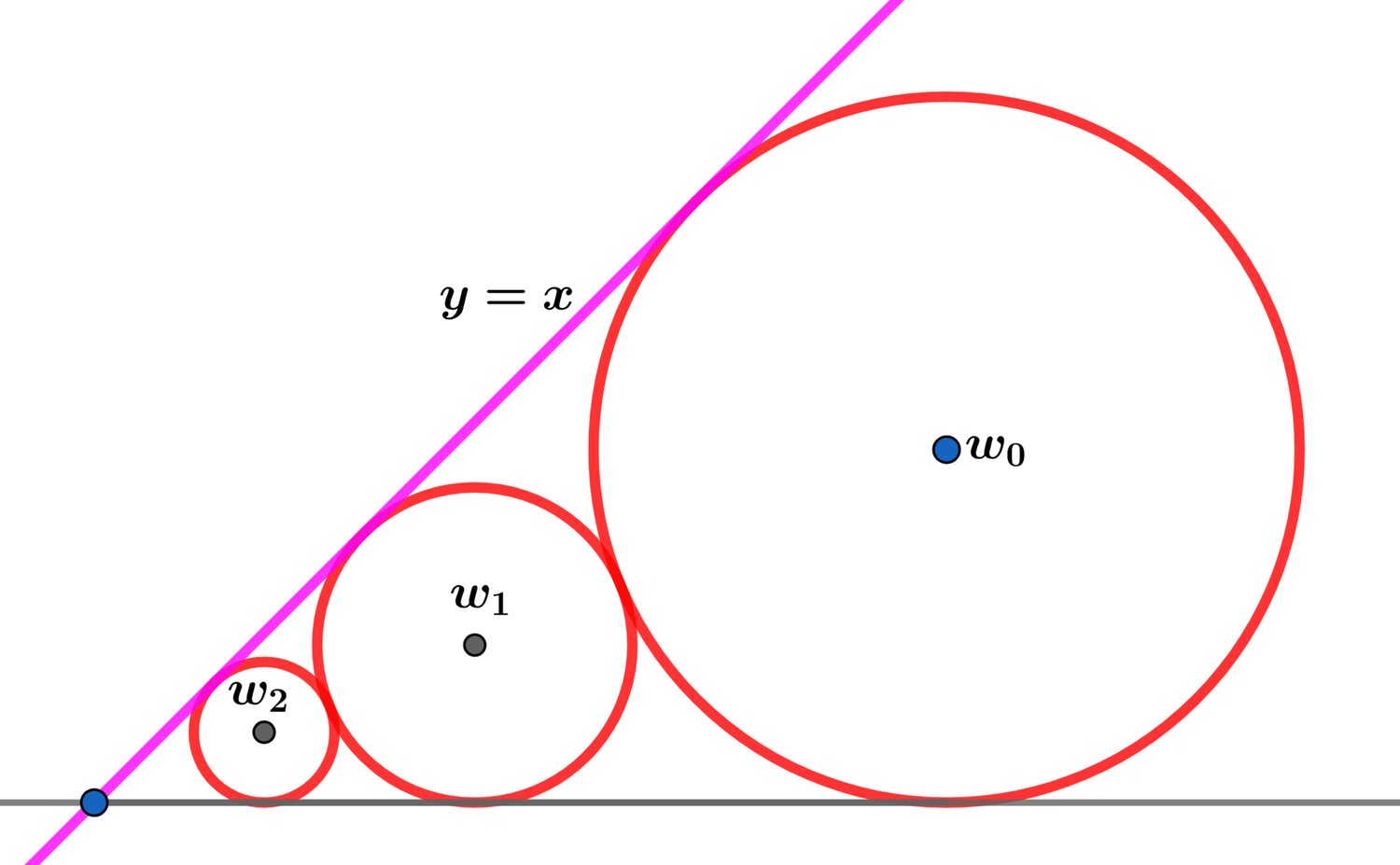
Extend the diagram above to an infinite number of circles. For each integer n ≥ 1 , circle w n is tangent to w n − 1 and tangent to the line y = x and the positive x -axis.
Let C n and A n be the circumference and the area of the n th circle respectively. Find:
∑ n = 1 ∞ A n ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ C n ) 2
The answer is 32.8375088952649884.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
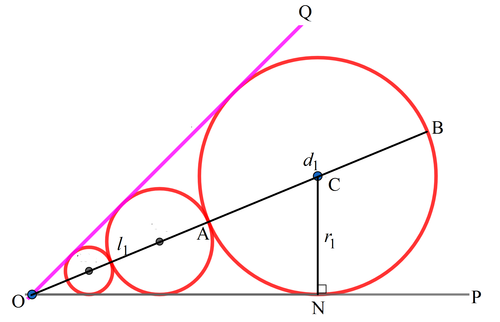
For any measure of ∠ O , as the pattern repeats, the ratio of the shortest distance of any circle (for example: O A = l 1 ) to the apex O and the diameter of the circle ( A B = d 1 ) is a constant. Let the constant be k then:
d 1 l 1 = d 2 l 2 = d 3 l 3 = ⋯ = k
We note that:
l n − 1 k d n − 1 d n ⟹ r n = d n + l n = d n + k d n = 1 + k k d n − 1 = 1 + k k r n − 1 = ( 1 + k k ) n − 1 r 1 where r n = 2 d n , the radius of n th circle.
Then we have:
n = 1 ∑ ∞ C n n = 1 ∑ ∞ A n ⟹ ∑ n = 1 ∞ A n ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ C n ) 2 = n = 1 ∑ ∞ 2 π r n = n = 0 ∑ ∞ 2 π ( 1 + k k ) n r 1 = 1 − 1 + k k 2 π r 1 = 2 π r 1 ( 1 + k ) = n = 1 ∑ ∞ π r n 2 = 1 − ( 1 + k k ) 2 π r 1 2 = 1 + 2 k π r 1 2 ( 1 + k ) 2 = 1 + 2 k π r 1 2 ( 1 + k ) 2 ( 2 π r 1 ( 1 + k ) ) 2 = 4 π ( 1 + 2 k )
Let us find k for ∠ O = 4 π . Then k = d 1 l 1 = 2 r 1 l 1 = 2 r 1 r 1 csc 8 π − r 1 = 2 csc 8 π − 1 = 2 4 + 2 2 − 1 . Then
∑ n = 1 ∞ A n ( ∑ n = 1 ∞ C n ) 2 = 4 π ( 1 + 2 k ) = 2 π 4 + 2 2 ≈ 3 2 . 8
O w 0 = 4 + 2 2 R 1
△ O A 1 w 0 ∼ △ w 1 A 2 w 0 ⟹ R 1 4 + 2 2 R 1 = R 1 − R 2 R 1 + R 2 ⟹
( 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) R 1 = ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 ) R 2 ⟹ R 2 = 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 R 1
R 3 = 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 R 2 = ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) 2 R 1
In General: R n = ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) n − 1 R 1
⟹ A n = π R n 2 = π R 1 2 ( ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) 2 ) n − 1
⟹ A = ∑ n = 1 ∞ A n = π R 1 2 ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) 2 ) n − 1
= 4 4 + 2 2 ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 ) 2 π R 1 2
and
C n = 2 π R n = 2 π R 1 ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) n − 1
⟹ C = ∑ n = 1 ∞ C n = 2 π R 1 ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( 4 + 2 2 + 1 4 + 2 2 − 1 ) n − 1 =
( 4 + 2 2 ) π R 1 ⟹ C 2 = ( 4 + 2 2 ) 2 π 2 R 1 2
⟹ A C 2 = 4 π 4 + 2 2 ≈ 3 2 . 8 3 7 5 0 8 8 9 5 2 6 4 9 8 8 4 .