This is great
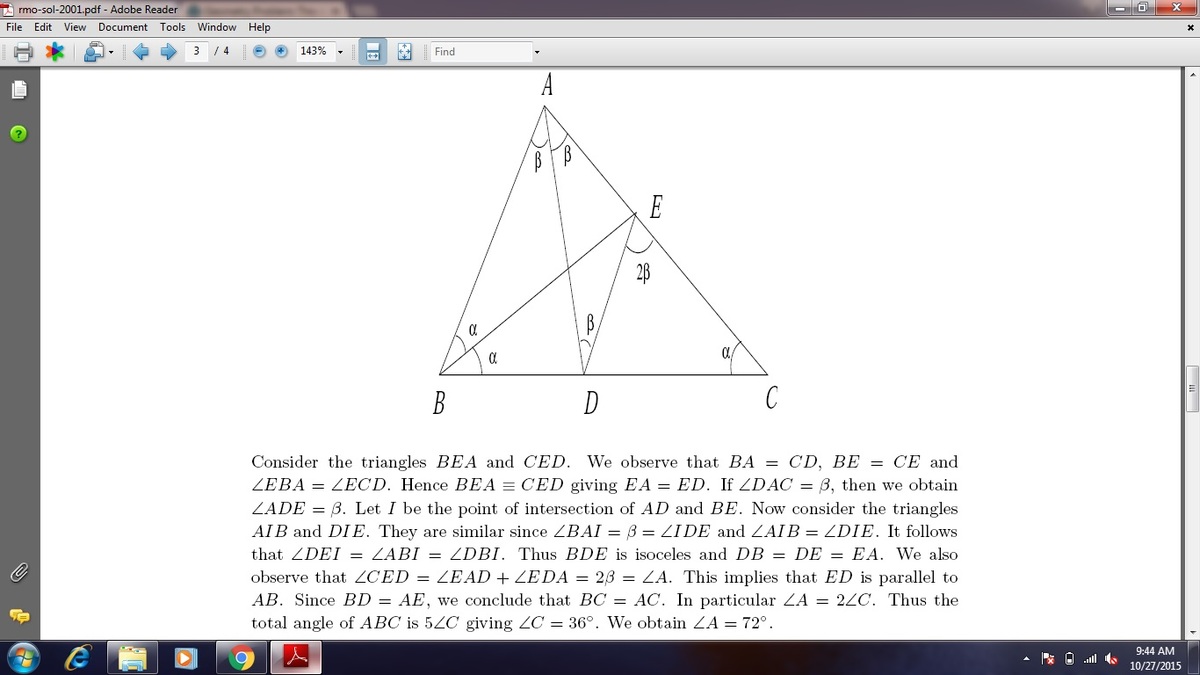
In △ A B C , D is a point on B C such that A D is the internal angle bisector of ∠ A . Suppose ∠ B = 2 ∠ C and C D = A B .
Find ∠ A in degrees.
Source: CRMO 2001
The answer is 72.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
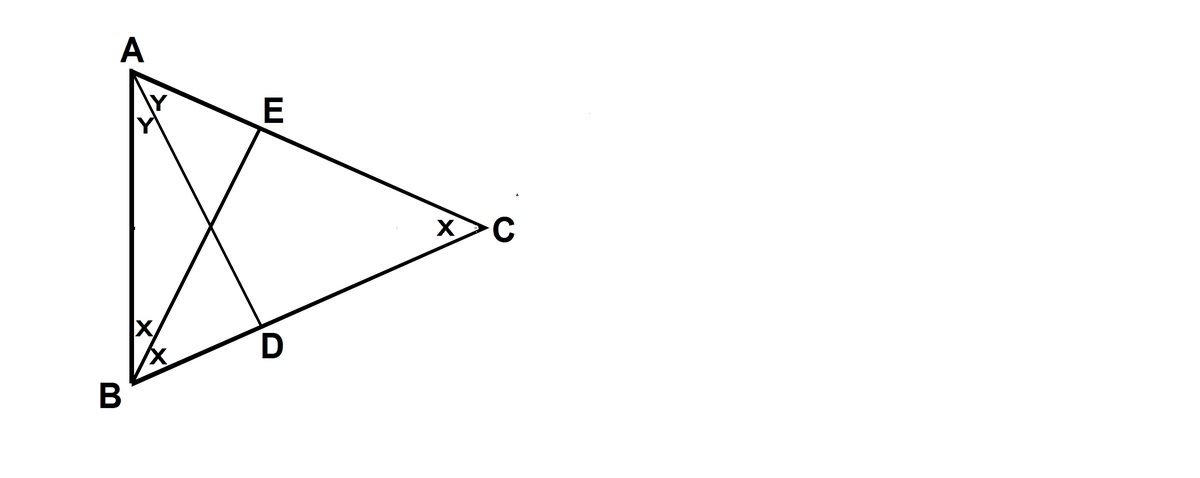 Let BE be the angle bisector of angle B. Angles are shown in the sketch.
A
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
S
i
n
L
a
w
,
b
a
=
S
i
n
B
S
i
n
A
,
w
e
g
e
t
:
−
I
n
Δ
A
B
D
∠
A
D
B
=
X
+
Y
,
i
n
t
e
r
n
a
l
a
n
g
l
e
s
o
f
Δ
A
D
C
.
A
D
A
B
=
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
.
I
n
Δ
A
D
B
S
i
n
(
A
D
)
D
C
=
A
B
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
Y
)
.
∴
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
Y
)
⟹
S
i
n
(
Y
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
∴
S
i
n
(
X
)
C
o
t
(
Y
)
+
C
o
s
(
X
)
=
2
C
o
s
(
X
)
,
expanding Sin of sum.
∴
C
o
t
(
Y
)
=
C
o
t
(
X
)
,
⟹
Y
=
X
.
B
u
t
1
8
0
=
2
Y
+
3
X
=
5
Y
,
⟹
2
Y
=
7
2
o
Let BE be the angle bisector of angle B. Angles are shown in the sketch.
A
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
S
i
n
L
a
w
,
b
a
=
S
i
n
B
S
i
n
A
,
w
e
g
e
t
:
−
I
n
Δ
A
B
D
∠
A
D
B
=
X
+
Y
,
i
n
t
e
r
n
a
l
a
n
g
l
e
s
o
f
Δ
A
D
C
.
A
D
A
B
=
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
.
I
n
Δ
A
D
B
S
i
n
(
A
D
)
D
C
=
A
B
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
Y
)
.
∴
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
Y
)
⟹
S
i
n
(
Y
)
S
i
n
(
X
+
Y
)
=
S
i
n
(
X
)
S
i
n
(
2
X
)
∴
S
i
n
(
X
)
C
o
t
(
Y
)
+
C
o
s
(
X
)
=
2
C
o
s
(
X
)
,
expanding Sin of sum.
∴
C
o
t
(
Y
)
=
C
o
t
(
X
)
,
⟹
Y
=
X
.
B
u
t
1
8
0
=
2
Y
+
3
X
=
5
Y
,
⟹
2
Y
=
7
2
o
Exact Same thing!!
Exactly Same Way.
Let ∠ A B C = 2 α and ∠ B A D = β . If we draw a line segment D F such that ∠ C D F = α we have that triangles A B D and A D F are congruent, so A B = A F and B D = D F . Also we have that triangle C D F is isosceles, so D F = C F . As C D = A F and B D = C F , triangle A B C is isosceles, so β = α = 3 6 o → ∠ A = 7 2 o