Those two semicircles
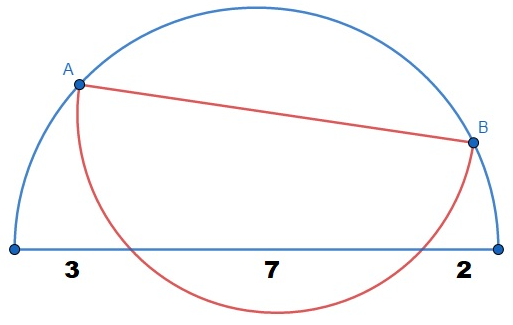
In the figure there are two semicircles. What is the length of A B , the diameter of the red semicircle, to four decimal places?
The answer is 9.7979.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
How did you get the value of OG as 0.5 Please do explain clearly as I am not able to understand.....
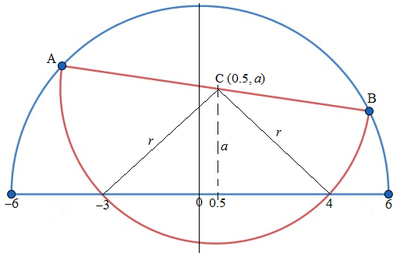 Let the center of the blue semicircle be the origin
O
(
0
,
0
)
, the center of the red semicircle be
C
and its radius be
r
.
Let the center of the blue semicircle be the origin
O
(
0
,
0
)
, the center of the red semicircle be
C
and its radius be
r
.
Since the triangle with vertices at C , ( − 3 , 0 ) and ( 4 , 0 ) is an isosceles triangle. The x coordinate of C is 0.5. Let the y coordinate of C be a .
Then the equation of the blue semicircle is x 2 + y 2 = 3 6 . . . ( 1 ) and that of the red semicircle:
( x − 0 . 5 ) 2 + ( y − a ) 2 x 2 − x + 0 . 2 5 + y 2 − 2 a y + a 2 x 2 − x + y 2 − 2 a y = r 2 = a 2 + 1 2 . 2 5 = 1 2 Note that r 2 = a 2 + 3 . 5 2 . . . ( 2 )
The two points of intersection A and B satisfy ( 1 ) − ( 2 ) : x + 2 a y = 2 4 , which is a straight line joining A and B . For line A B to be the diameter of the red semicircle, it must pass through C ( 0 . 5 , a ) . Therefore,
0 . 5 + 2 a 2 ⟹ a ⟹ r 2 = 2 4 = 2 2 4 − 0 . 5 = 2 4 7 = 4 4 7 + ( 2 7 ) 2 = 2 4
Therefore, the length of A B , the diameter of the red semicircle is 2 r = 2 2 4 ≈ 9 . 7 9 8 0 .
Let O be the center of the red circle, P be the center of the blue circle, D G be the given diameter of the blue circle, and E and F be the intersection points of the two semicircles, as shown below. Extend A B and D G so that they intersect at C , and draw P B and O E .
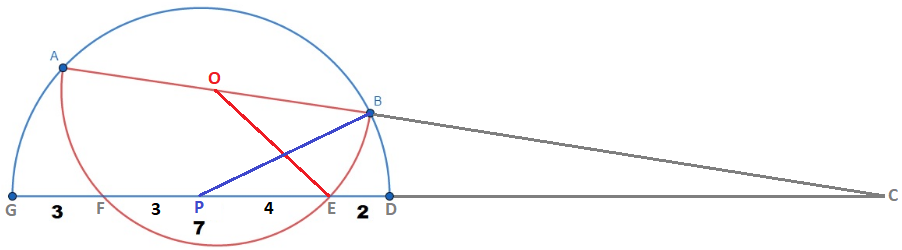
The diameter of the blue circle D G = 3 + 7 + 2 = 1 2 , so the radius is P D = P B = 6 .
By the intersecting secant theorem on the blue circle, A B ⋅ A C = C D ⋅ C G or A B ( A B + B C ) = C D ( C D + 1 2 ) . By the intersecting secant theorem on the red circle, A B ⋅ A C = C E ⋅ C F or A B ( A B + B C ) = ( C D + 2 ) ( C D + 9 ) . Then A B ( A B + B C ) = C D ( C D + 1 2 ) = ( C D + 2 ) ( C D + 9 ) , which means C D = 1 8 , and A B ( A B + B C ) = 5 4 0 .
Using the law of cosines on △ B C P , cos C = 2 ⋅ C P ⋅ B C C P 2 + B C 2 − B P 2 , or cos C = 2 ⋅ 2 4 ⋅ B C 2 4 2 + B C 2 − 6 2 , or cos C = 4 8 ⋅ B C B C 2 + 5 4 0 . Using the law of cosines on △ C E O , cos C = 2 ⋅ C E ⋅ C O C E 2 + C O 2 − E O 2 , or cos C = 2 ⋅ 2 0 ⋅ 2 1 A B 2 0 2 + ( 2 1 A B ) 2 − ( 2 1 A B + B C ) 2 , or since A B ( A B + B C ) = 5 4 0 , cos C = B C 2 + 5 4 0 4 7 ⋅ B C . Then cos C = 4 8 ⋅ B C B C 2 + 5 4 0 = B C 2 + 5 4 0 4 7 ⋅ B C , which means B C = 2 1 4 1 − 2 6 , and since A B ( A B + B C ) = 5 4 0 , A B = 4 6 ≈ 9 . 7 9 7 9 .
G E 2 + h 2 = r 2
O O 2 2 + A O 2 2 = A O 2 ⇒ h 2 + O G 2 + r 2 = A O 2
3 . 5 2 + h 2 = r 2
h 2 + r 2 + 0 . 5 2 = 6 2
Solving these two equations we get value of r = 2 6 ⇒ A B = 4 6 ≈ 9 . 7 9 7 9