Three-phase induction motor
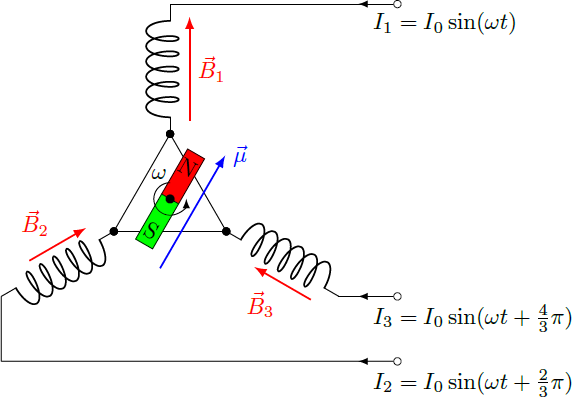
In an induction motor three coils are arranged symmetrically about a permanent magnet, which is rotatably mounted. The coils are operated with a three-phase alternating current, so that the currents have a phase difference of relative to each other. At the location of the permanent magnet, the -th coil generates a magnetic field with an amplitude . The unit vectors are parallel to the corresponding coil axis and have an angle of relative to each other. The permanent magnet with the magnetic moment is set in uniform rotation by the magnetic field.
What is the maximum torque , that the three-phase induction motor can produce?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The unit vectors of the coil directions are e k = ( − sin ( ϕ k ) cos ( ϕ k ) ) = ( − sin ( 3 2 π ( k − 1 ) ) cos ( 3 2 π ( k − 1 ) ) ) , k = 1 , 2 , 3 = ( 0 1 ) , ( − 3 / 2 − 1 / 2 ) , ( 3 / 2 − 1 / 2 ) where the angle ϕ k = 3 2 π ( k − 1 ) corresponds also to the phase angle of the currents I k = I 0 sin ( ω t + ϕ k ) . The total magnetic field is calculated via a vector sum: B ( t ) = k = 1 ∑ 3 B k ( t ) = k = 1 ∑ 3 B 0 sin ( ω t + ϕ k ) e k = k = 1 ∑ 3 B 0 [ sin ( ω t ) cos ( ϕ k ) + cos ( ω t ) sin ( ϕ k ) ] ( − sin ( ϕ k ) cos ( ϕ k ) ) = B 0 sin ( ω t ) ( − ∑ k = 1 3 cos ( ϕ k ) sin ( ϕ k ) ∑ k = 1 3 cos 2 ( ϕ k ) ) + B 0 cos ( ω t ) ( − ∑ k = 1 3 sin 2 ( ϕ k ) ∑ k = 1 3 sin ( ϕ k ) cos ( ϕ k ) ) = B 0 sin ( ω t ) ( 0 2 3 ) + B 0 cos ( ω t ) ( 2 3 0 ) = 2 3 B 0 ( cos ( ω t ) sin ( ω t ) ) In line three, we used the addition theorem of sine. The total magnetic field B has an amplitude of ∣ B ∣ = 2 3 B 0 and makes a circular motion with the frequency ω of the alternating current. At idle, the magnet simply follows the circular motion of the magnetic field, so that μ ∥ B . Under load, both vectors point in different directions with an angle α = ∠ ( B , μ ) between the two. The torque exerted by the engine results T = ∣ μ × B ∣ = 2 3 μ B 0 sin ( α ) A right angle α = 9 0 ∘ results in a maximal torque T max = 2 3 μ B 0 = 2 3 ⋅ 1 0 0 0 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 0 − 2 N m = 3 0 N m