Three-Phase vs. Single-Phase
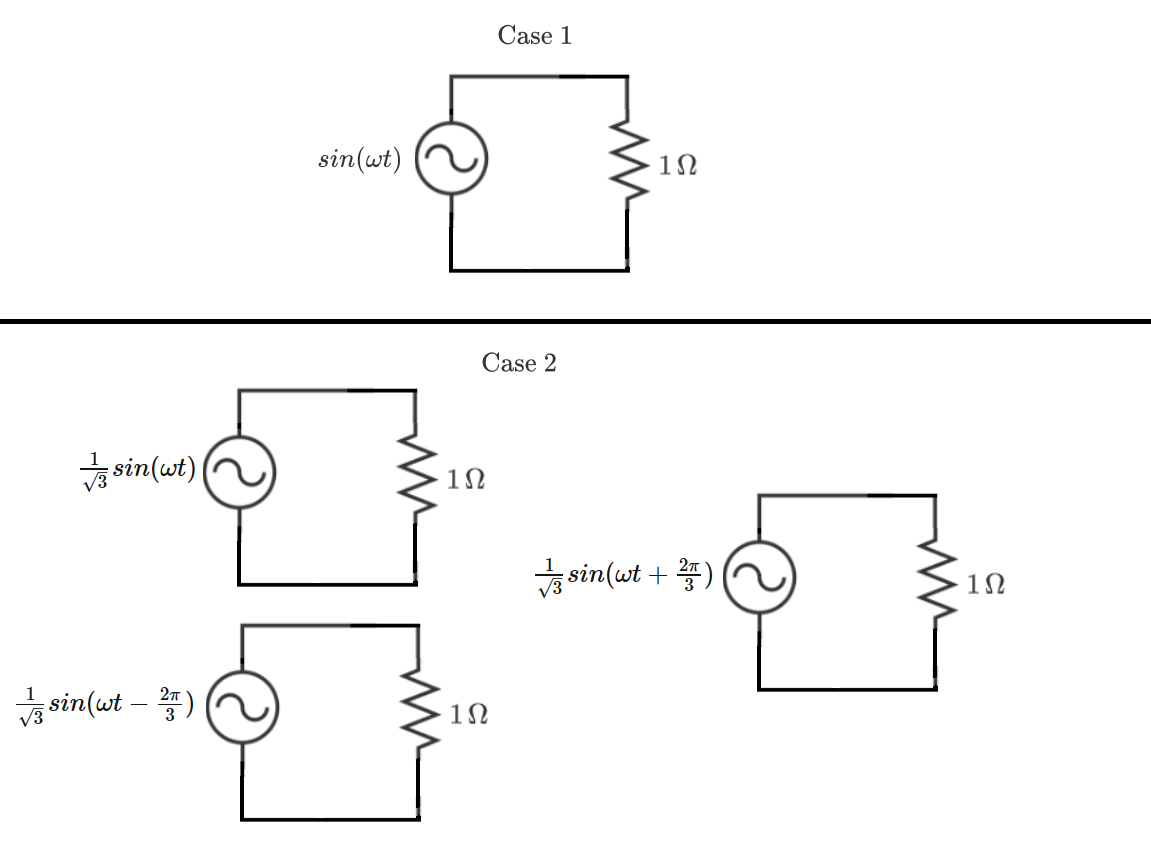
Define as the instantaneous power dissipated in Case 1, and as the total instantaneous power dissipated in Case 2 (in all three circuits combined).
is the average value of , and is the average value of (averaged over an integer number of cycles).
is the maximum instantaneous value of , and is the maximum instantaneous value of .
What is ?
Bonus: What are the implications for building large generators which source huge amounts of power?
The answer is 2.5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
0 solutions
No explanations have been posted yet. Check back later!