Trapezoid and Parallelogram
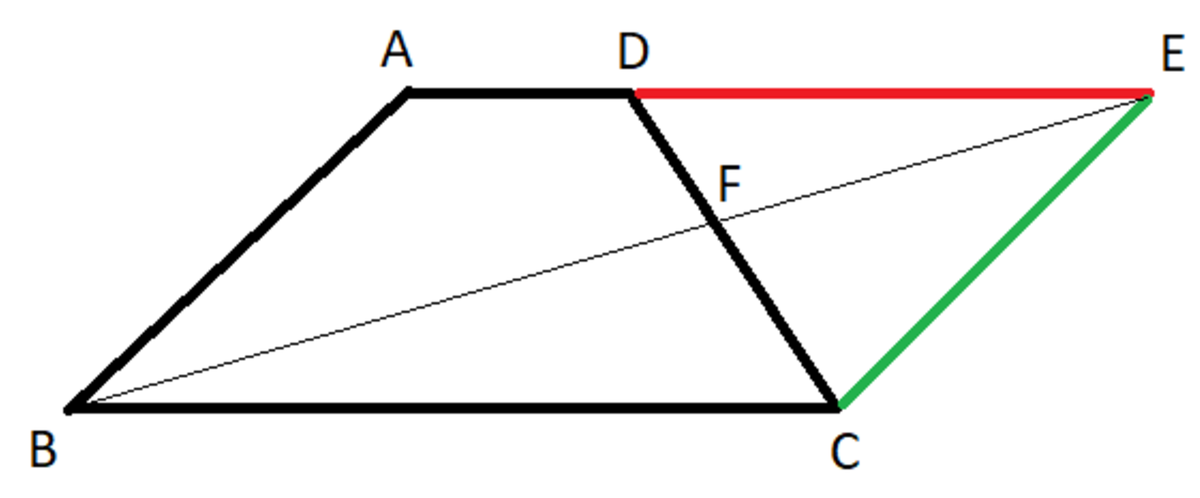
A B C D is a trapezoid with A D ∣ ∣ B C . A D is extended to the right, and a parallel to B A is drawn from point C . The two meet at point E . Now, we draw the segment B E . Find the ratio of A D to B C if the following conditions hold:
- B C = 2 B A
- ∠ B = 6 0 ∘
- B E is perpendicular to C D
Figure not drawn to scale.
The answer is 0.6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Without loss of generality, let A B = E C = 1 , which would make B C = A E = 2 . Place the diagram on a coordinate grid such that B is at B ( 0 , 0 ) and C is at C ( 2 , 0 ) .
Since ∠ B = 6 0 ° and A B = 1 , A is at A ( 2 1 , 2 3 ) and since A D ∣ ∣ B C , A D has an equation of y = 2 3 . Also, since E C ∣ ∣ A B , E is at E ( 2 5 , 2 3 ) .
That means B E has a slope of 5 3 , and since C D is perpendicular to B E and goes through C ( 2 , 0 ) , C D has an equation of y = − 3 5 ( x − 2 ) .
C D and A D intersect at the solution of y = − 3 5 ( x − 2 ) and y = 2 3 , which is D ( 1 0 1 7 , 2 3 ) . A D then has a distance of 1 0 1 7 − 2 1 = 5 6 .
The ratio of A D to B C is then 2 5 6 = 5 3 = 0 . 6
We note that A B C E is a parallelogram and △ D E F and △ B C F are similar. Therefore, B C D E = B C A E − A D = 1 − B C A D = B F E F ⟹ B C A D = 1 − B F E F . We need to find B E and E F to solve the problem.
Since B C = 2 A B , let A B = C E = 1 and B C = E A = 2 . Let ∠ E B C = θ . Then
tan θ ⟹ cos θ ⟹ B F = B G E G = B C + C G E G = B C + C E cos 6 0 ∘ C E sin 6 0 ∘ = 2 + 2 1 2 3 = 5 3 = 2 7 5 = B C cos θ = 2 × 2 7 5 = 7 5
We note that B E = cos θ B G = 2 7 5 2 5 = 7 .
Therefore, B C A D = 1 − B F E F = 1 − B F B E − B F = 2 − B F B E = 2 − 7 5 7 = 5 3 = 0 . 6