Triangle and a semicircle
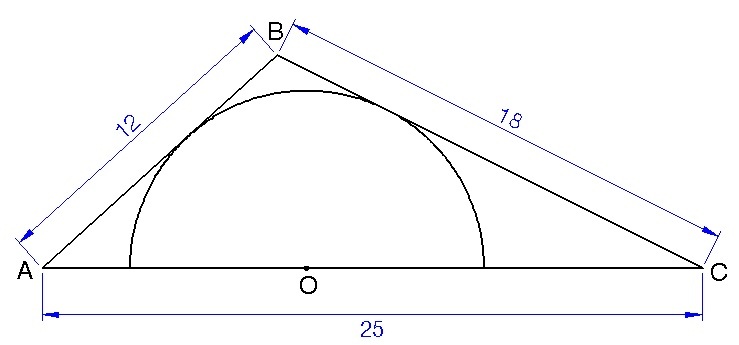 In the triangle shown above,
A
B
=
1
2
,
B
C
=
1
8
and
A
C
=
2
5
. A semicircle is drawn so that its center lies on
A
C
and so that it is tangent to
A
B
and
B
C
. If
O
is the center of the semicircle, find the area of the region inside the triangle but outside the semicircle. If your answer is of the form
b
a
6
4
7
9
−
6
4
7
9
π
, where
a
and
b
are positive integers, give your answer as
a
+
b
.
In the triangle shown above,
A
B
=
1
2
,
B
C
=
1
8
and
A
C
=
2
5
. A semicircle is drawn so that its center lies on
A
C
and so that it is tangent to
A
B
and
B
C
. If
O
is the center of the semicircle, find the area of the region inside the triangle but outside the semicircle. If your answer is of the form
b
a
6
4
7
9
−
6
4
7
9
π
, where
a
and
b
are positive integers, give your answer as
a
+
b
.
The answer is 648.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Best solution by far!
Very simple and elegant solution
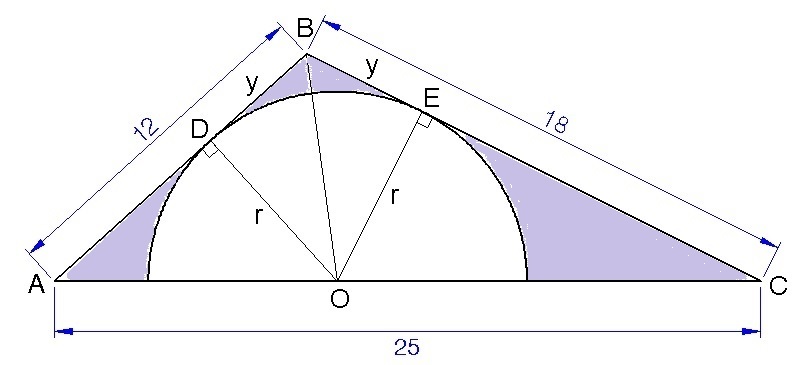
Using @Marvin Kalngan's figure above, where O D and O E are radius r from the centre O to the points of contact of A B and B C respectively. We note that:
⎩ ⎨ ⎧ sin A = A O r sin C = C O r ⟹ A O = sin A r ⟹ C O = sin C r .
From cosine rule , we have:
1 8 2 cos A ⟹ sin A = 1 2 2 + 2 5 2 − 2 ( 1 2 ) ( 2 5 ) cos A = 2 ( 1 2 ) ( 2 5 ) 1 2 2 + 2 5 2 − 1 8 2 = 1 2 0 8 9 = 1 2 0 6 4 7 9
From sine rule , we have:
A B sin C ⟹ sin C = B C sin A = B C A B ⋅ sin A = 1 8 1 2 ⋅ 1 2 0 6 4 7 9 = 1 8 0 6 4 7 9
Now we have:
A O + C O = A C ⟹ sin A r + sin C r r ( 6 4 7 9 1 2 0 + 6 4 7 9 1 8 0 ) ⟹ r = 2 5 = 2 5 = 2 5 = 1 2 6 4 7 9
The area of shaded region is equal to the area of △ A B C less that of the semicircle:
A = 2 1 A B ⋅ A C ⋅ sin A − 2 π r 2 = 2 1 2 ⋅ 2 5 ⋅ 1 2 0 6 4 7 9 − 2 π ⋅ 1 4 4 6 4 7 9 = 2 8 8 3 6 0 6 4 7 9 − 6 4 7 9 π
⟹ a + b = 3 6 0 + 2 8 8 = 6 4 8 .
Can you please tell how you could use Mr. Marvin Kalngan's figure? Often when I wanted I am not able to.
Log in to reply
At the image, just right-click to copy the image and then paste it at Paint. Save it and then use the picture button to paste it at solution box.
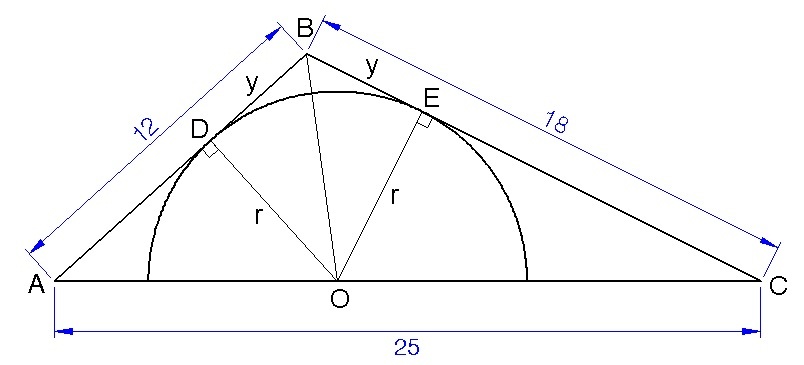 Draw
O
D
and
O
E
to the points of contact of tangents
A
B
and
B
C
, respectively. Let
D
B
=
B
E
=
y
,
r
= radius of the semicircle,
A
= area of the region inside the triangle but outside the semicircle,
A
T
= area of the triangle and
A
C
= area of the semicircle
Draw
O
D
and
O
E
to the points of contact of tangents
A
B
and
B
C
, respectively. Let
D
B
=
B
E
=
y
,
r
= radius of the semicircle,
A
= area of the region inside the triangle but outside the semicircle,
A
T
= area of the triangle and
A
C
= area of the semicircle
In △ A B C , B O bisects ∠ B so that A O A B = C O C B ,
then,
A O 1 2 = 2 5 − A O 1 8
1 2 ( 2 5 − A O ) = 1 8 ( A O )
3 0 0 − 1 2 ( A O ) = 1 8 ( A O )
3 0 0 = 3 0 ( A O )
1 0 = A O
It follows that,
O C = 2 5 − A O = 2 5 − 1 0 = 1 5
consider △ A D O , by Pythagorean Theorem , we have
1 0 2 = r 2 + ( 1 2 − y ) 2
− 4 4 + 2 4 y − y 2 = r 2 ( 1 )
consider △ C E O , by Pythagorean Theorem , we have
1 5 2 = r 2 + ( 1 8 − y ) 2
− 9 9 + 3 6 y − y 2 = r 2 ( 2 )
equate ( 1 ) and ( 2 )
− 4 4 + 2 4 y − y 2 = − 9 9 + 3 6 y − y 2
5 5 = 1 2 y
1 2 5 5 = y
Substitute the above in ( 1 ) or ( 2 )
r 2 − ( 1 2 5 5 ) 2 + 2 4 ( 1 2 5 5 ) − 4 4
r 2 = 1 4 4 6 4 7 9
r = 1 4 4 6 4 7 9
solving for the area of the semicircle
A c = 2 π r 2 = 2 8 8 6 4 7 9 π
solving for the area of the triangle by Heron's Formula
s = 2 1 2 + 1 8 + 2 5 = 2 5 5
s − 1 2 = 2 3 1
s − 1 8 = 2 1 9
s − 2 5 = 2 5
Substituting, we obtain
A T = ( 2 5 5 ) ( 2 3 1 ) ( 2 1 9 ) ( 2 5 ) = 1 6 1 6 1 9 7 5
A T = 4 5 6 4 7 9
Finally,
A = A T − A C = 4 5 6 4 7 9 − 2 8 8 6 4 7 9 π = 2 8 8 3 6 0 6 4 7 9 − 6 4 7 9 π
It follows that,
a = 3 6 0 and b = 2 8 8
so
a + b = 3 6 0 + 2 8 8 = 6 4 8
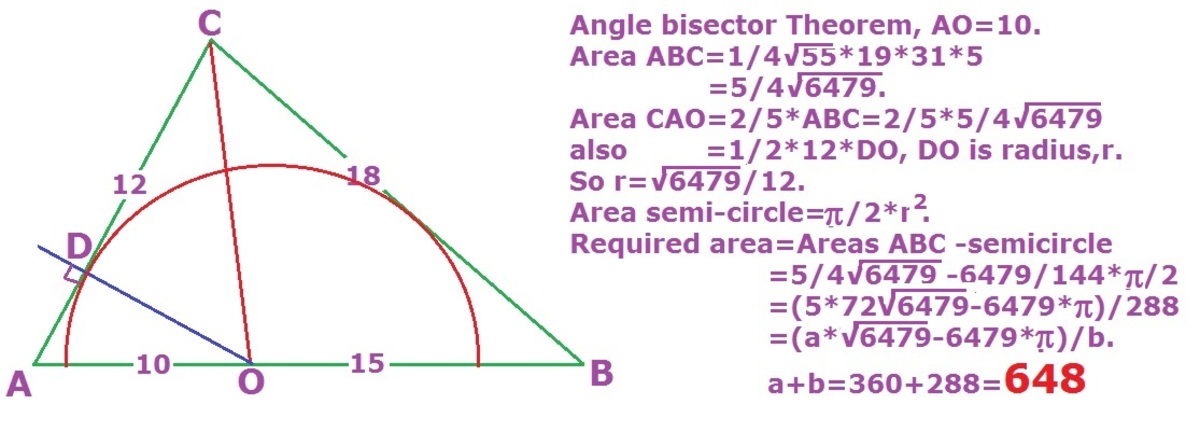
Sorry. I did not see Mr. Marta Reece's solution. I saw it now. It is almost the same.
A = s ( s − 1 2 ) ( s − 1 8 ) ( s − 2 5 ) = 4 5 6 4 7 9
This is equal to the sum of the areas of △ A O B and △ B O C which are:
A A O B = 2 1 2 R = 6 R ... This comes from the base 12 and the height perpendicular to it,which is the radius R of the half circle.
A B O C = 2 1 8 R = 9 R ... Calculated from the base 18 and the height, which is again the radius R .
Equation 6 R + 9 R = 4 5 6 4 7 9 has a solution R = 1 2 6 4 7 9
Area of the half circle is A h c = 2 π × 1 2 2 6 4 7 9
So the area inside the triangle but outside the half circle is A = A A B C − A h c = 4 5 6 4 7 9 − 2 8 8 6 4 7 9 π = 2 8 8 3 6 0 6 4 7 9 − 6 4 7 9 π
a + b = 3 6 0 + 2 8 8 = 6 4 8