Triangle Craze
The problem below is a brilliant problem of the week that I altered.
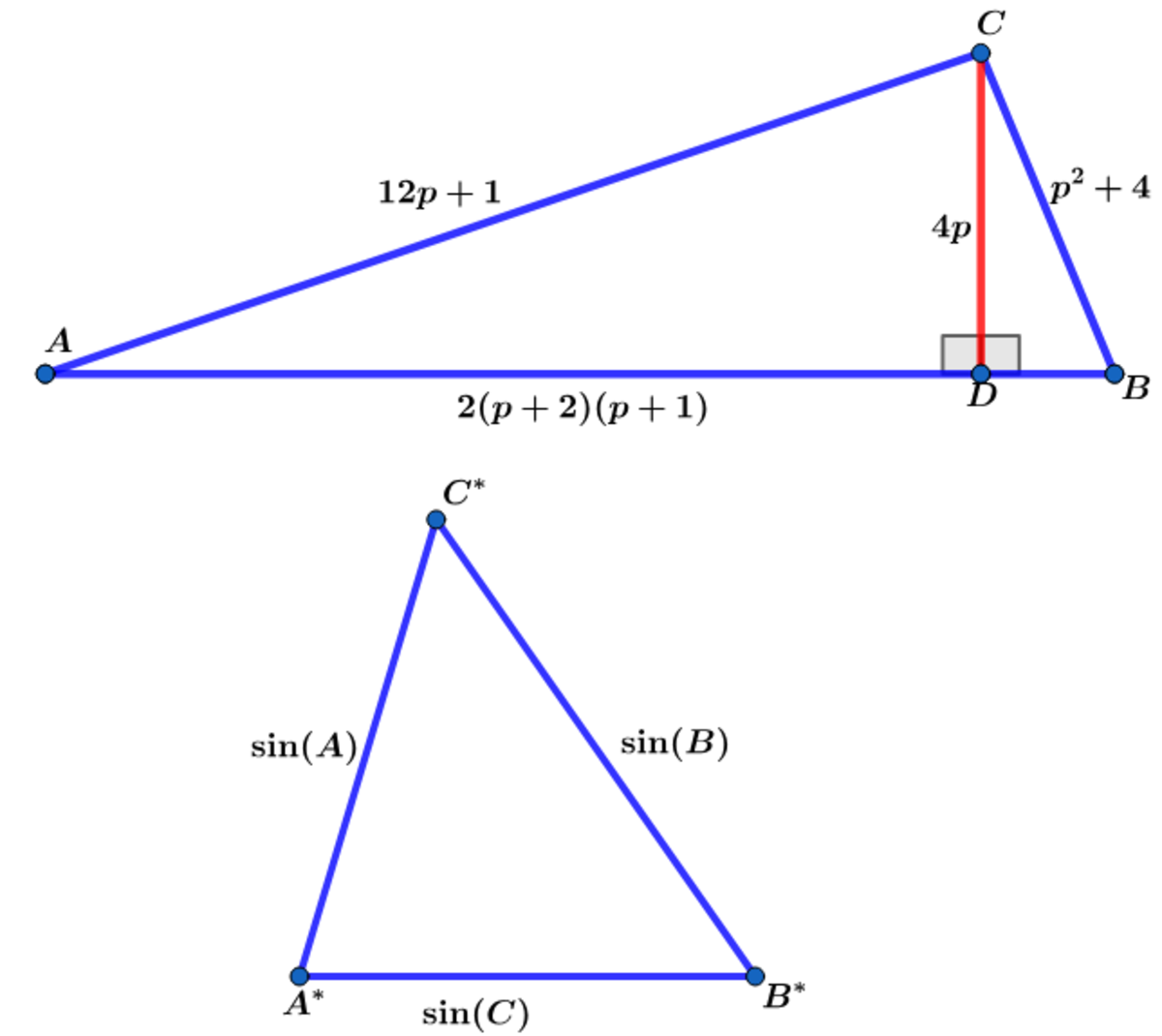
Let be a prime number and .
has side lengths and height as shown above and has side lengths and
If the area , where and are coprime positive integers, find .
The answer is 265921.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Finding the general area for this particular problem simplifies the work.
Using the law of sines on △ A B C we obtain:
sin ( A ) = b a sin ( B )
sin ( C ) = b c sin ( B )
Using the law of cosines on △ A ∗ B ∗ C ∗ we obtain:
sin 2 ( B ) = b 2 a 2 sin 2 ( B ) + b 2 c 2 sin 2 ( B ) − b 2 2 a c sin 2 ( B ) cos ( A ∗ )
⟹ cos ( A ∗ ) = 2 a c a 2 + c 2 − b 2 = cos ( B ) ⟹ sin ( A ∗ ) = 1 − cos 2 ( B ) ) = sin ( B ) ⟹ h ∗ = sin ( A ) sin ( B ) ⟹
A △ A ∗ B ∗ C ∗ = 2 1 sin ( A ) sin ( B ) sin ( C ) = 2 1 ( b 2 a c ) sin 3 ( B ) .
Let prime p > 2 .
( p 2 − 4 , 4 p , p 2 + 4 ) is a primitive pythagorean triple with D B = p 2 − 4 ⟹ A D = p 2 + 6 p + 8 .
For right △ A C D : ( A C ) 2 = ( 1 2 p + 1 ) 2 = ( p 2 + 6 p + 8 ) 2 + ( 4 p ) 2 ⟹ p 4 + 1 2 p 3 − 7 6 p 2 + 7 2 p + 6 3 = 0 .
By inspection p = 3 is a root of p 4 + 1 2 p 3 − 7 6 p 2 + 7 2 p + 6 3 = 0 .
Performing long division we obtain: ( p − 3 ) ∗ ( p 3 + 1 5 p 2 − 3 1 p − 2 1 ) = 0 ⟹ p = 3 and prime p ≥ 3 ⟹ f ( p ) = p 3 + 1 5 p 2 − 3 1 p − 2 1 is monotonic increasing ⟹ f ( p ) ≥ f ( 3 ) = 4 8 ⟹ p = 3 is the only prime root satisfying p 4 + 1 2 p 3 − 7 6 p 2 + 7 2 p + 6 3 = 0 .
Using the general area derived above we obtain:
sin ( B ) = 1 3 1 2 ⟹ A △ A ∗ B ∗ C ∗ = 2 1 3 7 2 ( 1 3 ) ( 4 0 ) ( 1 3 1 2 ) 3 = 4 8 1 2 ( 2 0 ) ( 1 2 3 ) = 2 3 1 3 6 1 3 4 5 6 0 = n m ⟹ m + n = 2 6 5 9 2 1 .
Note: ( p 2 − 4 , 4 p , p 2 + 4 ) is a primitive pythagorean triple for any prime p > 2 and ( 1 2 , 3 5 , 3 7 ) is also a primitive pythagorean triple.