Triangle, Hard from every angle!!
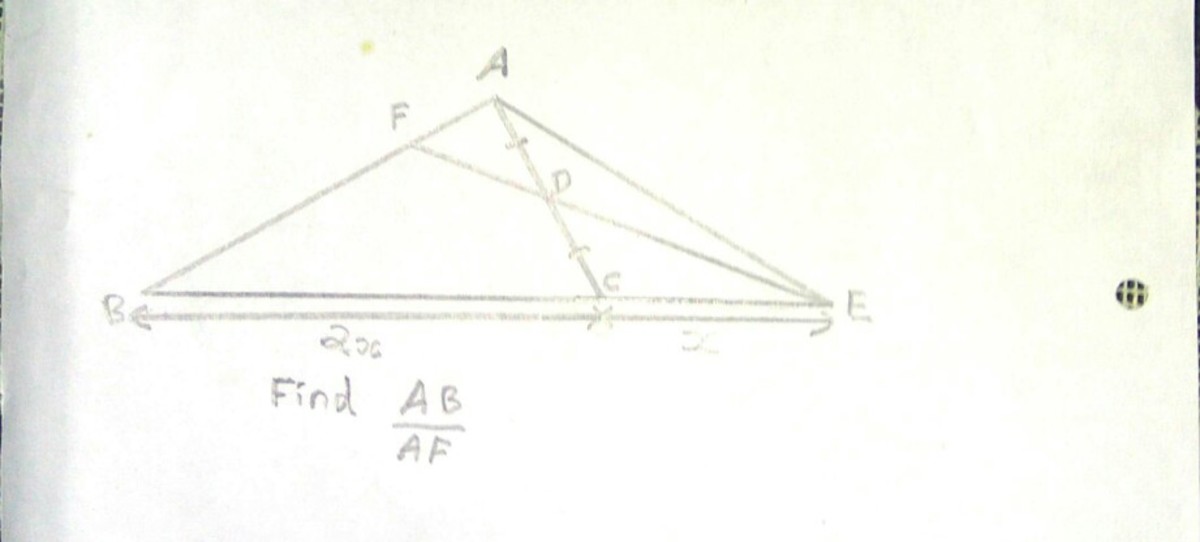
In the above figure, in ∆ABC, BC is extended to E such that CE= BC. IF D is the mid point of AC and ED cuts AB at F, Find the value of
The answer is 4.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Construction: Through D, draw a line parallel to AB cutting AE at G and BE at H. Now, through C, draw a line parallel to BA cutting AE at I and ED at J.
Solution:
In ∆EFB
FD= 2 1 ED. (Basic Proportionality Theorem)
In ∆CAB
CH=BH= 2 1 BC (Mid-Point Theorem)
=> HC=EC
In ∆EDH
EJ=DJ= 2 1 ED. (Mid-Point Theorem)
=> DJ=DF
=> ∆AFD is congruent to ∆CJD
=> AF=JC=a
In ∆AEF
IJ= 3 1 AF. (Basic Proportionality Theorem)
c= 3 1 a
In ∆AEB
CI= 3 1 BA= 3 b . (Basic Proportionality Theorem)
3 b =c+a (CI=a+c)
3 b = 3 a +a
a= 4 b
a b =4