This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
5 solutions
Same as Brian Charlesworth and Edwin Gray.
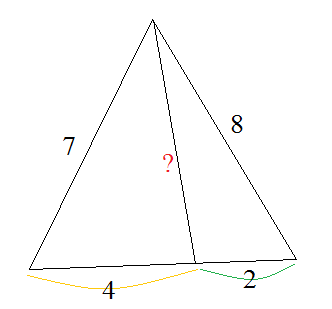
Equating Cos of bottom left angle due to triangles 7-4-? and 7-6-8,
2
∗
7
∗
4
4
9
+
1
6
−
?
2
=
2
∗
7
∗
6
4
9
+
3
6
−
6
4
⟹
2
6
5
−
?
2
=
3
2
1
∴
?
=
5
1
=
7
.
1
4
1
4
2
8
.
L
a
T
e
X
Calculate cos(A), (<A opposite side = 8) by law of cosines. 64 = 36 + 49 - 2 7 6 cos(A) gives cos(A) = 1/4. Now repeat with the desired length being calculated: y^2 = 49 + 16 - 2 7 4 .25 = 51, so y = sqrt(51) = 7.141. Ed Gray
Let the lower left angle of the given triangle be θ . Then by the cosine rule used on the full triangle we find that
8 2 = 6 2 + 7 2 − 2 × 6 × 7 × cos ( θ ) ⟹ 8 4 cos ( θ ) = 3 6 + 4 9 − 6 4 = 2 1 ⟹ cos ( θ ) = 4 1 .
Next, letting the sought after side length be x and using the cosine rule on the triangle with side lengths 4 , 7 , x we find that
x 2 = 4 2 + 7 2 − 2 × 4 × 7 × cos ( θ ) ⟹ x 2 = 6 5 − 5 6 × 4 1 = 6 5 − 1 4 = 5 1 ⟹ x = 5 1 .
A simple application of Stewart's theorem........
Relevant wiki: Pythagorean Theorem
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ h 2 + a 2 = 8 2 h 2 + ( 6 − a ) 2 = 7 2 h 2 + ( a − 2 ) 2 = x 2 . . . ( 1 ) . . . ( 2 ) . . . ( 3 )
From ( 2 ) :
h 2 + a 2 − 1 2 a + 3 6 6 4 − 1 2 a + 3 6 ⟹ a = 7 2 = 4 9 = 4 1 7 Note ( 1 ) : h 2 + a 2 = 8 2
From ( 5 ) :
x 2 = h 2 + a 2 − 4 a + 4 = 6 4 − 4 × 4 1 7 + 4 = 5 1 ⟹ x Note ( 2 ) : a = 4 1 7 = 5 1 ≈ 7 . 1 4 1