Triangular Paper Folding
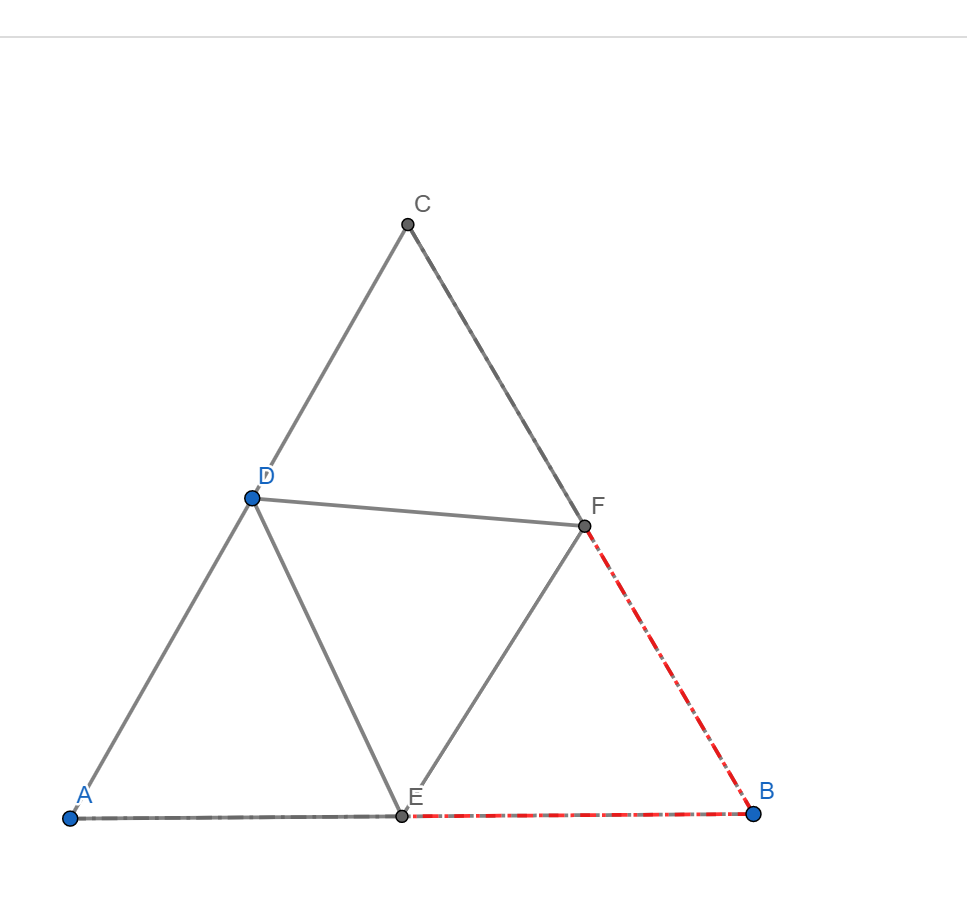
The figure shown above is a piece paper in the shape of an equilateral triangle A B C . Now the paper is folded along the crease E F with the vertex B meeting the edge A C at point D such that A D : D C = 3 : 2 . Find B E : B F .
The answer can be expressed in the form of b a , where a and b are positive coprime integers. Compute a + b .
This is part of the set Fun With Problem-Solving .
The answer is 15.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Well done. Did not thought that cosine rule can be applied here too.
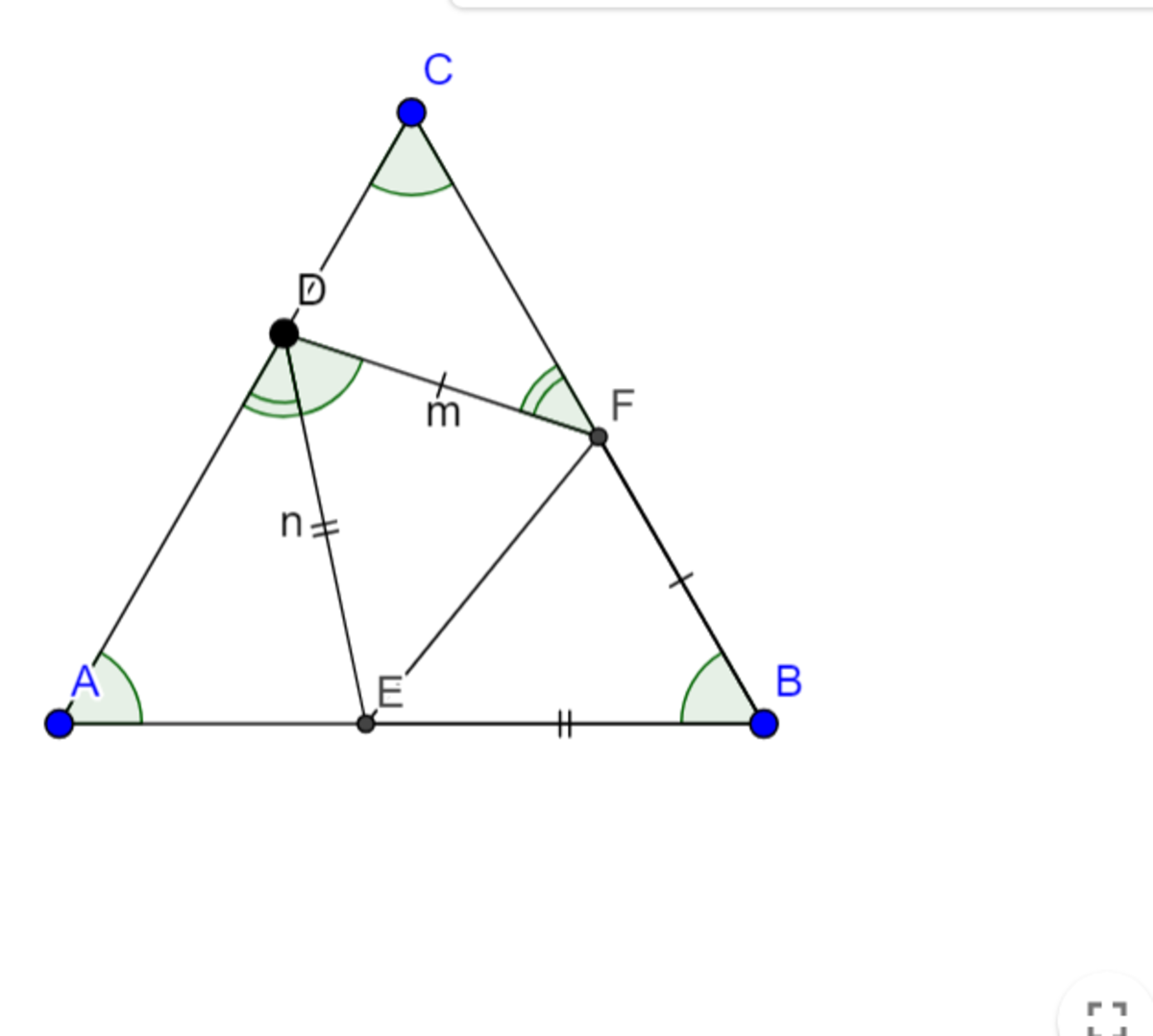
To make things easier, we could let the side length of Δ A B C be 5 .(The final answer demands ratio and the ratio will always be a constant value regardless of side length of triangles.). Then, we have A D = 3 , D C = 2 .
As shown above, Δ C F D ∼ Δ A D E
∴ C F A D = C D A E = D F D E
5 − m 3 = 2 5 − n = m n
2 5 − n = m n
⇒ m = 5 − n 2 n
5 − m 3 = 2 5 − n
5 − 5 − n 2 n 3 = 2 5 − n
⇒ 5 ( 5 − n ) − 2 n = 6
2 5 − 7 n = 6
n = 7 1 9
∴ m = 5 − 7 1 9 2 ⋅ 7 1 9 = 3 5 − 1 9 2 ⋅ 1 9 = 8 1 9
Hence, B F B E = D F D E = 8 1 9 7 1 9 = 7 8
a + b = 8 + 7 = 1 5
Since A D : D C = 3 : 2 , let A D = 3 k and D C = 2 k , and each side of the equilateral triangle 5 k . Also, let B E = x and B F = y . Then E D = x and F D = y , and since each side of the equilateral triangle is 5 k , A E = 5 k − x and C F = 5 k − y . Also, since △ A B C is an equilateral triangle, ∠ D C F = 6 0 ° and ∠ D A E = 6 0 ° .
By law of cosines on △ A D E , D E 2 = A D 2 + A E 2 − 2 ⋅ A D ⋅ A E ⋅ cos ∠ E A D , or x 2 = ( 3 k ) 2 + ( 5 k − x ) 2 − 2 ⋅ 3 k ⋅ ( 5 k − x ) ⋅ cos 6 0 ° , which solves to x = 7 1 9 k .
By law of cosines on △ C D F , D F 2 = C D 2 + C F 2 − 2 ⋅ C D ⋅ C F ⋅ cos ∠ D C F , or y 2 = ( 2 k ) 2 + ( 5 k − y ) 2 − 2 ⋅ 2 k ⋅ ( 5 k − x ) ⋅ cos 6 0 ° , which solves to x = 8 1 9 k .
Therefore, B E : B F = y x = 7 1 9 k 8 1 9 k = 7 8 , which means a = 8 and b = 7 , and a + b = 8 + 7 = 1 5 .