Trigonometry for Pros Repost
Evaluete if :
-
is equilateral triangle of side
-
Circle is tangent to at point in the middle of and its radius is
-
Line is tangent to the circle
Good Luck !
The answer is 0.1499738192744.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
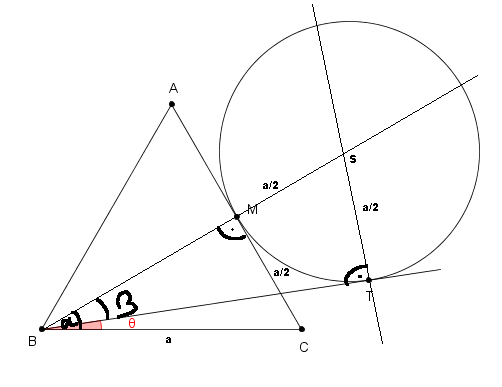
Let's start with drawing a perpendicular lines from the line BT intersecting T and from CM intersecting M. Let's call the intersection of those two lines S, which is also a center of a circle, since we know that the circle is tangent to AC at point M. Then call the CBM angle alpha.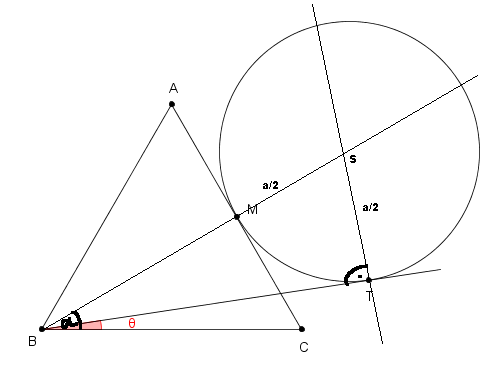 Line BM is also a height of a triangle BCA and since the triangle is equilateral, we can say that alfa = 30 degrees, since it's half of an angle CBA, which is always 60 degrees like all the angles in equilateral triangles. We can now tell, that if we knew the angle TBM, which we can call beta, we could just substract alfa from it and it will give us theta - but for that we need to know lengths of at least two sides of a right triangle BTS. We can compute height BM of a triangle BCA by using pythagorean theorem.
Line BM is also a height of a triangle BCA and since the triangle is equilateral, we can say that alfa = 30 degrees, since it's half of an angle CBA, which is always 60 degrees like all the angles in equilateral triangles. We can now tell, that if we knew the angle TBM, which we can call beta, we could just substract alfa from it and it will give us theta - but for that we need to know lengths of at least two sides of a right triangle BTS. We can compute height BM of a triangle BCA by using pythagorean theorem.
 ∣
B
M
∣
=
a
2
−
(
2
a
)
2
=
a
2
−
4
a
2
=
4
3
×
a
2
=
a
×
2
3
Now we can join |BM| + |MS| so we can get another side of a triangle BTS.
∣
B
S
∣
=
∣
B
M
∣
+
∣
M
S
∣
=
2
a
×
3
+
2
a
=
2
a
×
3
+
a
=
2
a
×
(
3
+
1
)
After that we can just use a sin and subtract alfa from beta and compute a tan of it.
tan
(
θ
)
=
tan
(
3
0
−
arcsin
(
3
+
1
1
)
)
∼
0
.
1
4
9
9
7
3
8
1
9
.
.
.
Now we can get rid of the arcsin from tan by few simple steps.
tan
(
a
−
b
)
=
1
+
tan
(
a
)
×
tan
(
b
)
tan
(
a
)
−
tan
(
b
)
3
+
1
1
×
3
−
1
3
−
1
=
2
3
−
1
tan
(
θ
)
=
1
+
tan
(
3
0
)
×
tan
(
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
)
tan
(
3
0
)
−
tan
(
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
)
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
=
f
tan
(
θ
)
=
1
+
3
1
×
tan
(
f
)
3
1
−
tan
(
f
)
=
3
3
+
tan
(
f
)
3
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
=
3
×
(
3
+
tan
(
f
)
)
3
×
(
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
)
=
3
+
tan
(
f
)
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
arcsin
(
x
)
=
2
×
arctan
(
1
+
1
−
x
2
x
)
f
=
arcsin
(
2
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
arctan
⎝
⎛
1
+
1
−
(
2
3
−
1
)
2
2
3
−
1
⎠
⎞
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
1
−
4
4
−
2
3
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
1
−
2
2
−
3
3
−
1
)
f
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
)
g
=
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
tan
(
2
x
)
=
1
−
tan
2
(
x
)
2
×
tan
(
x
)
f
=
tan
(
2
×
arctan
(
g
)
)
=
1
−
tan
2
(
arctan
(
g
)
)
2
×
tan
(
arctan
(
g
)
)
=
1
−
g
2
2
×
g
=
1
−
(
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
)
2
1
+
2
3
3
−
1
g
2
=
4
+
8
×
2
3
+
2
×
3
4
−
2
×
3
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
−
3
1
−
g
2
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
−
2
+
3
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
tan
(
f
)
=
1
+
2
3
3
−
1
×
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
=
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
+
2
3
×
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
×
3
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
2
−
3
−
4
×
2
3
=
2
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
×
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
4
×
2
3
tan
(
f
)
=
2
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
×
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
4
×
2
3
=
4
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
1
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
×
(
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
(
2
×
3
+
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
×
(
3
−
1
)
tan
(
θ
)
=
3
+
tan
(
f
)
1
−
3
×
tan
(
f
)
=
3
+
2
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
3
2
3
−
4
2
3
1
−
3
(
2
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
3
2
3
−
4
2
3
)
=
3
+
⎝
⎛
2
(
2
3
+
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
⎠
⎞
1
−
3
⎝
⎛
2
(
2
3
+
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
⎠
⎞
ϕ
=
4
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
tan
(
θ
)
=
3
+
ϕ
1
−
3
×
ϕ
∣
B
M
∣
=
a
2
−
(
2
a
)
2
=
a
2
−
4
a
2
=
4
3
×
a
2
=
a
×
2
3
Now we can join |BM| + |MS| so we can get another side of a triangle BTS.
∣
B
S
∣
=
∣
B
M
∣
+
∣
M
S
∣
=
2
a
×
3
+
2
a
=
2
a
×
3
+
a
=
2
a
×
(
3
+
1
)
After that we can just use a sin and subtract alfa from beta and compute a tan of it.
tan
(
θ
)
=
tan
(
3
0
−
arcsin
(
3
+
1
1
)
)
∼
0
.
1
4
9
9
7
3
8
1
9
.
.
.
Now we can get rid of the arcsin from tan by few simple steps.
tan
(
a
−
b
)
=
1
+
tan
(
a
)
×
tan
(
b
)
tan
(
a
)
−
tan
(
b
)
3
+
1
1
×
3
−
1
3
−
1
=
2
3
−
1
tan
(
θ
)
=
1
+
tan
(
3
0
)
×
tan
(
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
)
tan
(
3
0
)
−
tan
(
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
)
arcsin
(
2
3
−
2
1
)
=
f
tan
(
θ
)
=
1
+
3
1
×
tan
(
f
)
3
1
−
tan
(
f
)
=
3
3
+
tan
(
f
)
3
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
=
3
×
(
3
+
tan
(
f
)
)
3
×
(
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
)
=
3
+
tan
(
f
)
1
−
3
tan
(
f
)
arcsin
(
x
)
=
2
×
arctan
(
1
+
1
−
x
2
x
)
f
=
arcsin
(
2
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
arctan
⎝
⎛
1
+
1
−
(
2
3
−
1
)
2
2
3
−
1
⎠
⎞
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
1
−
4
4
−
2
3
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
1
−
2
2
−
3
3
−
1
)
f
=
2
×
arctan
(
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
)
g
=
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
tan
(
2
x
)
=
1
−
tan
2
(
x
)
2
×
tan
(
x
)
f
=
tan
(
2
×
arctan
(
g
)
)
=
1
−
tan
2
(
arctan
(
g
)
)
2
×
tan
(
arctan
(
g
)
)
=
1
−
g
2
2
×
g
=
1
−
(
2
+
2
×
2
3
3
−
1
)
2
1
+
2
3
3
−
1
g
2
=
4
+
8
×
2
3
+
2
×
3
4
−
2
×
3
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
−
3
1
−
g
2
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
−
2
+
3
=
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
tan
(
f
)
=
1
+
2
3
3
−
1
×
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
=
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
+
2
3
×
2
3
+
4
×
2
3
2
×
3
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
2
−
3
−
4
×
2
3
=
2
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
×
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
4
×
2
3
tan
(
f
)
=
2
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
×
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
×
3
×
2
3
−
4
×
2
3
=
4
×
3
+
2
×
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
1
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
×
(
3
−
1
)
=
2
×
(
2
×
3
+
2
3
×
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
×
2
3
×
(
3
−
1
)
tan
(
θ
)
=
3
+
tan
(
f
)
1
−
3
×
tan
(
f
)
=
3
+
2
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
3
2
3
−
4
2
3
1
−
3
(
2
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
+
4
2
3
1
+
3
+
4
3
2
3
−
4
2
3
)
=
3
+
⎝
⎛
2
(
2
3
+
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
⎠
⎞
1
−
3
⎝
⎛
2
(
2
3
+
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
⎠
⎞
ϕ
=
4
3
+
2
2
3
(
2
+
3
)
1
+
3
+
4
2
3
(
3
−
1
)
tan
(
θ
)
=
3
+
ϕ
1
−
3
×
ϕ