Trio of Triangles
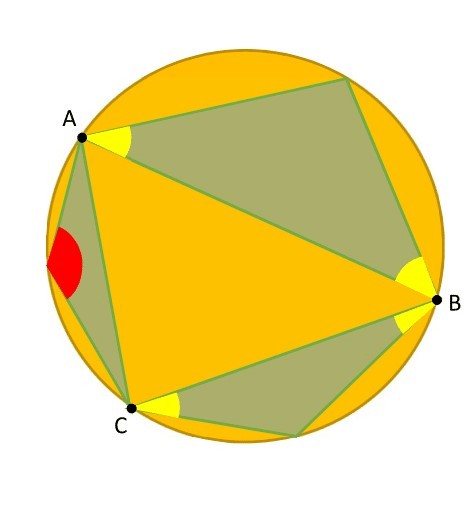 Triangle ABC has three other triangles attached to it so that their remaining vertices are located on the circumcircle of triangle ABC. Depending on the shape of the original triangle, what relationships may exist between the measure of the red angle, R, and the sum of the yellow angles, S.
Triangle ABC has three other triangles attached to it so that their remaining vertices are located on the circumcircle of triangle ABC. Depending on the shape of the original triangle, what relationships may exist between the measure of the red angle, R, and the sum of the yellow angles, S.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
By the Inscribed Angle Theorem, the red angle measures half of the angle formed by the arc A C .
The arc A C is the sum of the arcs A M , M B , B N and N C .
By the Inscribed Angle Theorem the yellow angles 1 , 2 , 3 , and 4 measure half of the angles formed by the arcs M B , A M , N C and B N respectively.
Hence, we can conclude that if the red angle is half of the angle formed by the arc A C and the yellow angles are half of the angles formed by the arcs that compose the big arc A C , then the sum of the yellow angles is equal to the red angle.