Trivial Properties of a Quadratic
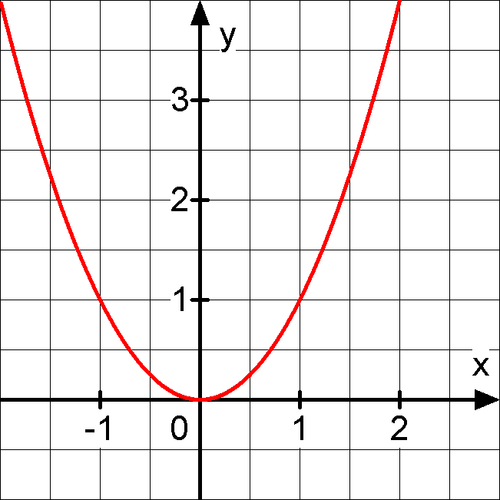 If
f
(
x
)
=
x
2
, then
If
f
(
x
)
=
x
2
, then
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Discussions for this problem are now closed
A simpe way to solve is using limits h → 0 lim h f ( x + h ) − f ( x ) = h ( x + h ) 2 − x 2 = h x 2 + 2 x h + h 2 − x 2 = h 2 x h + h 2 = 2 x
And if you wanted to be even more precise you could use the delta-epsilon proof with limits, that is if you wanted to be more rigorous.
This is actually the definition of a derivative.
ln ( f ( x ) ) f ( x ) 1 ⋅ f ′ ( x ) f ′ ( x ) = = = 2 ln ( x ) x 2 x 2 ⋅ x 2 = 2 x
Using the power rule , the derivative of x 2 is ( 2 ) x 2 − 1 ⇒ 2 x 1 ⇒ 2 x . Ans.