Two Moons and Right-angle Triangle
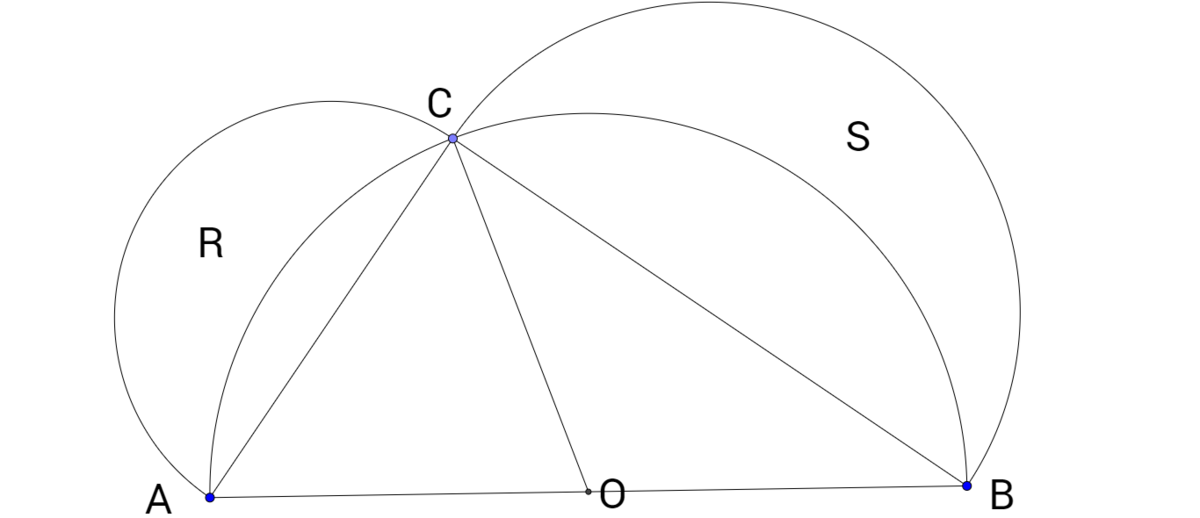 A
B
is the diameter of the semicircle.
C
is a point on the circumference.
O
is the center if the semicircle.
A
B
is the diameter of the semicircle.
C
is a point on the circumference.
O
is the center if the semicircle.
If the radius of the semicircle is 5, ∠ C O A = 6 0 ∘ . Find the sum of the area of the region R and S . note region R and S is not the semicircle with the diameter AC and BC
The answer is 21.6506.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
areas of R+S=area of the triangle ABC. It is 30-60-90 triangle. So its area =
2
3
∗
r
2
=
2
3
∗
5
2
=
2
1
.
6
5
0
6
Proof:areas of R+S=area of the triangle ABC.
A
C
2
+
B
C
2
=
A
B
2
,
∴
2
1
∗
π
∗
A
C
2
+
2
1
∗
π
∗
B
C
2
=
2
1
∗
π
∗
A
B
2
.
⟹
Sum of areas of semicircles on the legs =area of semicircle on the hypotenuse.
From both sides subtract area common to semicircles on the legs and hypotenuse.
That is the sum R+S=area of
Δ
A
B
C
.
This solution is not correct Ans 27.188
file:///home/chronos/u-bb41696e22533f784022ff2f3bd1a43d45e55fef/MyFiles/Downloads/Untitled%20document.pdf - Thales' Theorem tells us that ∠ACB= 90° -∠COA=60∘ ,when there is a straight line, the other angle, ∠COB=180∘ - (60∘)= 120∘. -triangle COB is an isosceles, because OB=5 and OC=5 so the other angles in the triangle are each 30∘. -triangle ACO is an isosceles as well because AO=5 and CO=5 and since ∠COA=60∘ and because it is an isosceles, the other angles are also 60∘.(making a equilateral triangle) Let area enclosed by the line AC and arc AC be R1 Let area enclosed by line CB and arc CB be S1 Area of sector (AOC)=(60∘/360∘)pi(5)^2=R1+(25/4)(3^(0.5)) (where this is area of the equilateral triangle) Area of semicircle (pi/2)(5/2)^2=R+R1 (solve for R1 in the previous equation and plug into this one for R) same procedure for S, find area of the sector pi(r)^2(central angle/360∘) and subtract area of triangle you can use formula 0.5ab(sinC) where in this case, a=b=CO=OB and angle C=∠COB=120∘ to find S1 then, find the area of the semicircle(pi/2(r^2)) by finding CB by Pythagorean theorem because ∠ACB= 90°, AB=10 and AC=5 and dividing it by 2 because CB is the diameter finally, the area of the semicircle=S1+S , since you know S1 solve for S Then add S+R=21.651