Two Semicircles in a Triangle
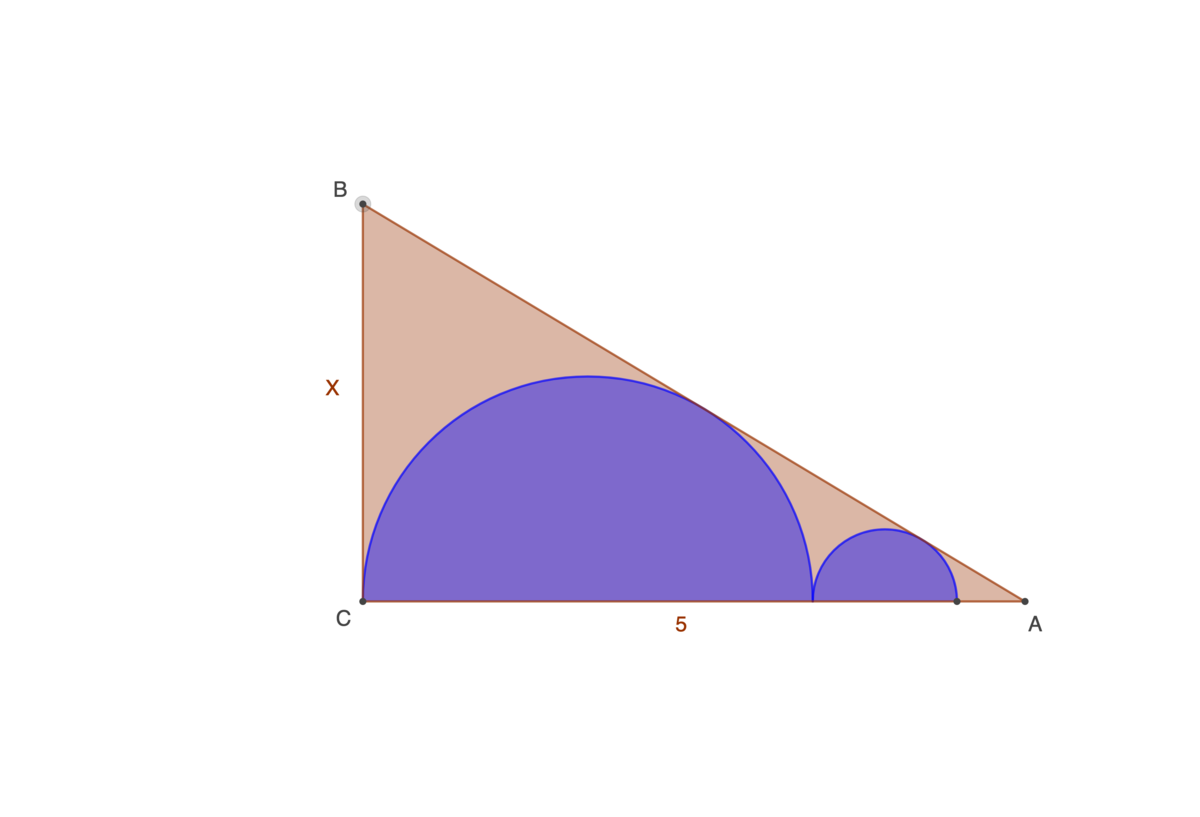
△ C A B is a right triangle with two inscribed semicircles. Its base is 5 and its height is x . Find the value of x which maximizes the ratio of the combined area of the semicircles to the area of the triangle.
The answer is 1.997385721460819.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Splendid solution again! If you isolate radicals to one side of the equation, then expand and simplify, you will get x 2 to be a root of the cubic equation 2 8 Y 3 + 4 0 0 Y 2 + 1 8 7 5 Y − 1 5 6 2 5 = 0 , or x = 5 ⋅ 4 2 1 ( − 8 + 3 1 5 6 7 + 1 6 8 8 7 + 3 1 5 6 7 − 1 6 8 8 7 )
Log in to reply
You are good.
Let the radii of the larger and smaller semicircles be r and αr, respectively. Because (loosely speaking) we could fill up the line CA with diametres of smaller and smaller semicircles, all touching AB, forming a geometric series, we see that 2 r ( 1 + α + α 2 + . . . ) = 5 and hence α = 1 − 5 2 r
The two semicircles now have a combined area of A s e m i c i r c l e s = 2 1 π r 2 ( 1 + α 2 ) = 2 1 π r 2 ( 1 + 1 − 5 4 r + 2 5 4 r 2 ) Defining t = r / 5 this rewrites a bit cleaner as A s e m i c i r c l e s = 2 5 π t 2 ( 1 − 2 t + 2 t 2 )
Let the centre of the larger circle be D and let E be the point where the larger circle touches the line AD. The triangles ABC and ADE are similar, so that x : x 2 + 5 2 = r : ( 5 − r )
From this we can find x = 1 − 2 r / 5 r = 1 − 2 t 5 t .
The triangle has area A t r i a n g l e = 5 x / 2 = 2 1 − 2 t 2 5 t
We can express the Area ratio as a function of t:
R ( t ) = A t r i a n g l e A s e m i c i r c l e s = π t ( 1 − 2 t + 2 t 2 ) 2 1 − 2 t
To find a stationary point, we set R ′ ( t ) = 0 which results in the polynomial − 1 4 t 3 + 1 6 t 2 − 7 t + 1 = 0 , with real root t = 0 . 2 7 0 5 9 . . . Plugging back in x = 1 − 2 t 5 t gives x = 1 . 9 9 7 3 . . .
I like your approach. I hadn't seen it before. Thank you.
Let radius of circles be a >b>0 and write the following relations
(1). 2a+b+√(b^2+c^2)=5.
(2). x=5*b/c
(3). b= (c a)/[c+2 √(a*b)]
(4). Maximize ratio w= (5x)/[π(a^2+b^2)] to find x=?
Use WolframAlpha to find x~2
Let the radii of the large and small semicircles be R and r respectively, and ∠ A = θ = tan − 1 5 x . Then
R + R csc θ = 5 ⟹ R = csc θ + 1 5 = 5 x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x )
From similar triangles,
r R R ⟹ r = r csc θ r csc θ + r + R = r + r sin θ + R sin θ = 1 + sin θ 1 − sin θ ⋅ R = 1 2 5 x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 3
Then the ratio of the two semicircles and the triangle ρ = 5 x / 2 π ( R 2 + r 2 ) / 2 , and
π 5 ρ π 7 8 1 2 5 ρ π 7 8 1 2 5 ⋅ d x d ρ = 2 5 x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 2 + 1 5 6 2 5 x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 6 = 6 2 5 x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 2 + x ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 6 = 2 5 + x 2 6 2 5 ( 2 5 + x 2 − 2 x ) ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 2 + 2 5 + x 2 ( 2 5 + x 2 − 6 x ) ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 6
Putting d x d ρ = 0 ,
( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 2 ( 6 2 5 ( 2 5 + x 2 − 2 x ) + ( 2 5 + x 2 − 6 x ) ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 4 ) ⟹ 6 2 5 ( 2 5 + x 2 − 2 x ) + ( 2 5 + x 2 − 6 x ) ( 2 5 + x 2 − x ) 4 = 0 = 0 For 2 5 + x 2 − x = 0 ⟹ x → ∞
Solving the equation, we get x ≈ 1 . 9 9 7 .