Use Your Eyes
A white square is inscribed in a blue circle, which is inscribed in a larger orange square.
Which area is larger, orange or blue?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
15 solutions
Nice explanation
Good answer
It's possible to solve for the area of the white square without using the Pythagorean Theorem by noting that it is composed of two triangles of equal area. Since the length of a side of the orange square is two, then the diameter of the blue circle is two, so two opposite corners of the white square have a distance between them of two. Thus, the white square is composed of two triangles with base = 2 and height = 1. (Note that the radius of the blue circle is one, so the height of the equilateral right triangle is one. For more background information, see: perpendicular bisector) Thus, the area of the white square is equal to: (area of square) = 2 (area of one triangle) = 2 (0.5 2 1) = 2
Loved the explanation!
I felt that the wording of the question was misleading. It needs the term “section.” Which section is bigger orange or blue. Because clearly the area of the entire orange square is greater than that of the blue circle inside of it.
Relevant wiki: Basic Composite Figures
Let the radius of the circle be r .
The blue area is the area of the circle minus the area of the white square, or π r 2 − 2 r 2 = ( π − 2 ) r 2 ≈ 1 . 1 4 r 2 .
The orange area is the area of the large square minus the area of the circle, or 4 r 2 − π r 2 = ( 4 − π ) r 2 ≈ 0 . 8 5 r 2 .
Since 1 . 1 4 > 0 . 8 5 , the blue area is larger.
Visually, it seems like orange is larger, even though the image is drawn to scale. Any ideas on why?
Log in to reply
Not sure … maybe because the width and length are the same for the orange area so it creates a solid looking block of color? Perhaps we (or at least some of us) underestimate the area of something long and skinny like the blue areas.
It may be because each orange region has a greater perimeter than each blue region. (Each orange region has a perimeter of 2 π r + 2 r ≈ 3 . 5 7 r , and each blue region has a perimeter of 2 π r + 2 r ≈ 2 . 9 9 r .)
Thank you for a generalised answer!
Note of (possible) interest: When making the calculations, be sure the area of the circle removed when figuring the orange area does NOT include the omission in the figures for the circle (sans the inner square) for the immediately prior area (i.e. the blue area).
Circle Area = π r 2
Blue Area = π r 2 − 2 r 2
LargeSquare Area = 4 r 2
Orange Area = 4 r 2 − Blue Area
(Bit obvious here, but not so obvious in the midst without the mapped algorithm)
Relevant wiki: Length and Area
Without loss of generality, we may assume that the side length of the larger square is 2, i.e. the larger square has an area of 4. Notice that the white square is half as large as the larger square, i.e. it has an area of 2. Further, the radius of the circle is r=1, i.e. the circle has an area of π . Thus the blue area is π − 2 > 3 . 1 4 − 2 > 1 , whereas the orange area is 4 − π < 4 − 3 . 1 4 < 1 . Hence the blue area is larger.
Exactly what I did!😊
In general, a circle covers 4 π of the circumscribed square. If the circle would have covered 4 3 of the square, than the blue and orange areas would have been equal, since the white square is half the area of the larger square.
4 π > 4 3 , therefor the blue area is the larger of the two.
That's a neat argument.
Let's call the radius of the blue circle r .The white square ( S 1 ),the blue circle ( S 2 ),the orange square ( S 3 ).
Orange region = S 3 − S 2 = ( 2 r ) 2 − π r 2 = 4 r 2 − π r 2 = ( 4 − π ) r 2 ≈ 0 , 8 5 8 4 r 2
Blue region = S 2 − S 1 = π r 2 − 4 2 r 2 = π r 2 − 2 r 2 = ( π − 2 ) r 2 ≈ 1 . 1 4 1 6 r 2
Because 1 . 1 4 1 6 r 2 > 0 . 8 5 8 4 r 2 so B l u e r e g i o n > O r a n g e r e g i o n
Outer square area = 4. White square area = 2. (4 triangles, each 1/2 area of the 4 sqares that contain them. Circle area = 3.14. Orange area = 4 - 3.14 = 0.86 Blue area = 3.14 - 2 = 1.14. So A blue > A orange.
Let r = 1, then (orange area) = (2 × 2) - (1^2)pi
(Blue area) = pi - 2
(Orange area) □ (Blue area)
4 - pi □ pi - 2
6 □ 2pi
3 □ pi
3 < pi
So, Blue is larger than the Orange
Let the radius of the circle to be (r), and the lenghth of the small square to be (a)
We have the lenghth of big square = 2r And the lenghth of small square (a) = √2(r)
And thus:
Area of the big square = (2r)^2 Area of the circle = π(r)^2 Area of the small square = 2(r)^2
In the figure qe can that:
Area of Blue region A1 = π(r)^2 - 2(r)^2 = (π - 2)r^2 ~ 1.14(r)^2 Area of the Orange region A2 = (2r)^2 - π(r)^2 = (4 - π)r^2 ~ 0.85(r)^2
Now let compare A1 and A2
A1 - A2 = 1.14r^2 - 0.85r^2 ~ + 0.29r^2 > 0 So A1 > A2 --> Blue region is larger
To make it easier i would assum the side of the square as 14. So that the radius of the circle becomes 7 which easy to calculate
How does that help?
We can tell that the radius of the circle(r) is equal to one side of the white square(w). We can also tell that the sides of the orange square are (w + w/2). Then we find that pi(r^2) > (w + w/2)^2 for every occasion.
More easily: Let A = area of white (B) + area of blue (C); B = C + area of orange (D); for r=1 A=3.14 B=1.99 C=1.15 D=.84; Therefore D < C;
For simplicity, suppose the circle is a unit circle. So, its radius = 1, the side length of larger outer square = 2 , and the side length of smaller square = 2
So, the area of orange region = 2 2 − π . 1 2 = 4 − π
the area of blue region = π . 1 2 − ( 2 ) 2 = π − 2
Even if we don't use a calculator, we know that π > 3 ,
So, π − 2 > 4 − π
Blue > Orange
Let l be the square's side length.
Note that the area of the white space is equal to 2 l 2 , as it is the sum of two triangles of base l and height 2 l (meaning the area of each triangle is 4 l 2 ).
The are of the entire circle is π 4 l 2 , implying the area of the blue region (circle minus white region) is π 4 l 2 − 2 l 2 = 4 π l 2 − 2 l 2 = 4 l 2 ( π − 2 ) .
The area of the square is l 2 , meaning the orange area (square minus circle) is l 2 − π 4 l 2 = 4 4 l 2 − π l 2 = 4 l 2 ( 4 − π ) .
Therefore, we just need to find out which is larger: 4 l 2 ( 4 − π ) or 4 l 2 ( π − 2 ) ? Note that 4 > π > 3 , implying that 4 − π < 1 and π − 2 > 1 . Therefore, 4 l 2 ( π − 2 ) is larger, meaning the blue area is larger.
-
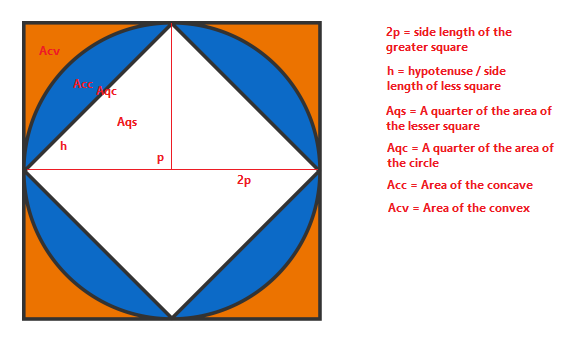
- h = p / sin (45) = sqrt(p)
- Ac = pi * p2
- Aqc = Ac/4
- Aqs = p2/2
-
Acc = Aqc - Aqs
-
Since the inner triangle is just half of the quarter of the greater square
- Acv = Aqs - Acc
-
Acv /= Acc
-
Test:
-
let 2p = 8
-
h = p / sin (45)
-
h = 5.66
-
Ac = pi * p2
-
Ac = 50.27
-
Aqc = Ac / 4
-
Aqc = 12.57
-
Aqs = p2/2
- Aqs = 16/2
-
Aqs = 8
-
Acc = Aqc - Aqs
- Acc = 12.57 - 8
-
Acc = 4.57
-
Acv = Aqs - Acc
- Acv = 8 - 4.57
-
Acv = 4.43
-
Acc /= Acv
- 4.57 /= 4.43 [TRUE]
Let x be a side of the inscribed square and y be a side of the circumscribed square and r the radius of the circle.
⟹ x = 2 r and y = 2 r ⟹ A o r a n g e = ( 4 − π ) r 2 and A b l u e = ( π − 2 ) r 2
A b l u e − A o r a n g e = ( 2 π − 6 ) r 2 > 0 ⟹ A b l u e > A o r a n g e .
Relevant wiki: Basic Composite Figures
[ O R A N G E R E G I O N ] = [ O R A N G E S Q U A R E ] − [ B L U E C I R C L E ] = 2 2 − π ( 1 2 ) = 4 − π ≈ 0 . 8 5 8
[ B L U E R E G I O N ] = [ B L U E C I R C L E − W H I T E S Q U A R E ] = π ( 1 2 ) − ( 2 ) 2 = π − 2 ≈ 1 . 1 4 2
CONCLUSION: [ B L U E R E G I O N ] > [ O R A N G E R E G I O N ]
NOTE:
The symbol [ ] denotes the area.