Vanish the camouflage
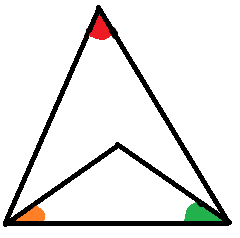 In the above figure , the red angle equals the sum of the orange angle and green angle.If
is the circumradius of small triangle and
is circumradius of bigger triangle , compare
.
In the above figure , the red angle equals the sum of the orange angle and green angle.If
is the circumradius of small triangle and
is circumradius of bigger triangle , compare
.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Just reflect the point of the interior say P in B C to obtain P ′ .Thus , ∠ P B C = ∠ P ′ B C a n d ∠ P C B = ∠ P ′ C B by the reflection properties.Thus we have:
∠ B P ′ C = 1 8 0 − ∠ P ′ B C − ∠ P ′ C B = 1 8 0 − ( ∠ P B C + ∠ P C B ) = 1 8 0 − ∠ B A C
Since ∠ B P ′ C = 1 8 0 − ∠ B A C , we conclude that □ A B P ′ C is cyclic.Denote R ( A B C ) as circumradius of Δ A B C . Thus , R ( A B C ) = R ( P ′ B C )
Also Δ P B C ≅ Δ P ′ B C using ( A − S − A test). Thus , R ( P B C ) = R ( P ′ B C )
Thus finally , R ( A B C ) = R ( P B C ) ⇒ R 1 = R 2 .