Vectors and conic sections - Part 1
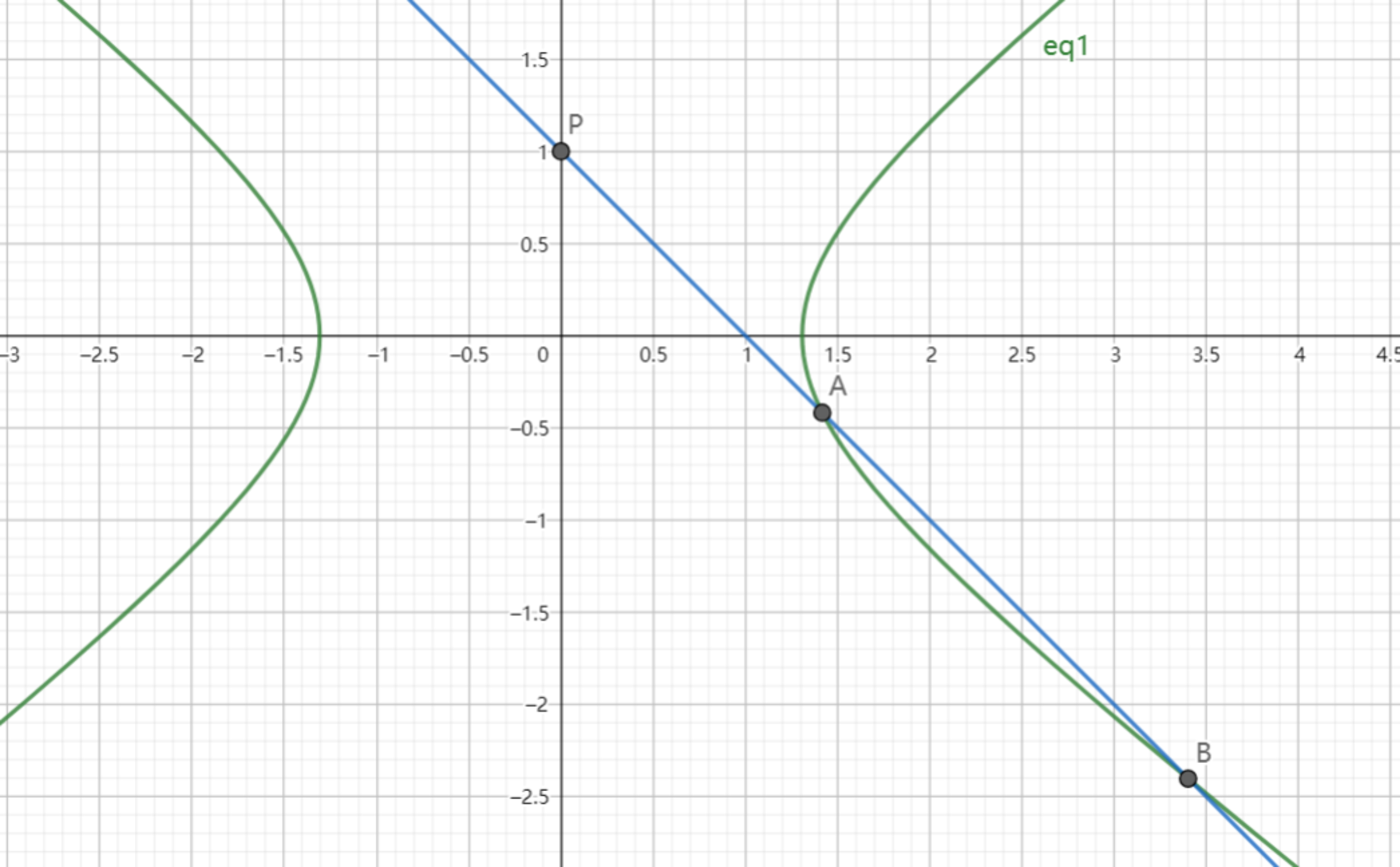 As shown above, the hyperbola
C
has the equation:
a
2
x
2
−
y
2
=
1
(
a
>
0
)
and it intersects with line
l
:
x
+
y
=
1
at point
A
and
B
respectively.
l
intersects with the
y
-axis at point
P
.
As shown above, the hyperbola
C
has the equation:
a
2
x
2
−
y
2
=
1
(
a
>
0
)
and it intersects with line
l
:
x
+
y
=
1
at point
A
and
B
respectively.
l
intersects with the
y
-axis at point
P
.
Given that P A = 1 2 5 P B , find the value of a .
If a can be expressed as q p , where p , and q are coprime positive integers. Submit p + q .
The answer is 30.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
The two points A ( x a , y a ) and B ( x b , y b ) satisfy both a 2 x 2 − y 2 = 1 and x + y = 1 ⟹ y = 1 − x and therefore,
y 2 a 2 ( 1 − x ) 2 ( a 2 − 1 ) x 2 − 2 a 2 x + 2 a 2 = a 2 x 2 − 1 = x 2 − a 2 = 0
⟹ x = a 2 − 1 a 2 ± a 2 − a 2 ⟹ x a = a 2 − 1 a 2 − a 2 − a 2 and x b = a 2 − 1 a 2 + a 2 − a 2 We note that P B P A = x b x a , therefore,
a 2 + a 2 − a 2 a 2 − a 2 − a 2 a + 2 − a 2 a − 2 − a 2 1 2 a − 1 2 2 − a 2 7 a 4 9 a 2 a 2 ⟹ a = 1 2 5 = 1 2 5 = 5 a + 5 2 − a 2 = 1 7 2 − a 2 = 2 8 9 ( 2 − a 2 ) = 1 6 9 2 8 9 = 1 3 1 7
Therefore, p + q = 1 7 + 1 3 = 2 0 .
Position coordinates of P are ( 0 , 1 ) . Let the position coordinates of A and B be ( h , 1 − h ) and ( k , 1 − k ) respectively.
Then ∣ P A ∣ = 1 2 5 ∣ P B ∣ ⟹ k = 5 1 2 h ⟹ h + k = 5 1 7 h , h k = 5 1 2 h 2 .
Solving the equations of the hyperbola and the straight line we get ( a 2 − 1 ) x 2 − 2 a 2 x + 2 a 2 = 0 , whose roots are h , k . Therefore h + k = a 2 − 1 2 a 2 = 5 1 7 h , h k = a 2 − 1 2 a 2 = 5 1 2 h 2 . So, 1 2 0 a 2 = 2 8 9 a 2 − 2 8 9 ⟹ 1 6 9 a 2 = 2 8 9 ⟹ a = 1 3 1 7 . Therefore p = 1 7 , q = 1 3 and p + q = 3 0 .