Welcome 2016! Part 30
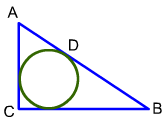
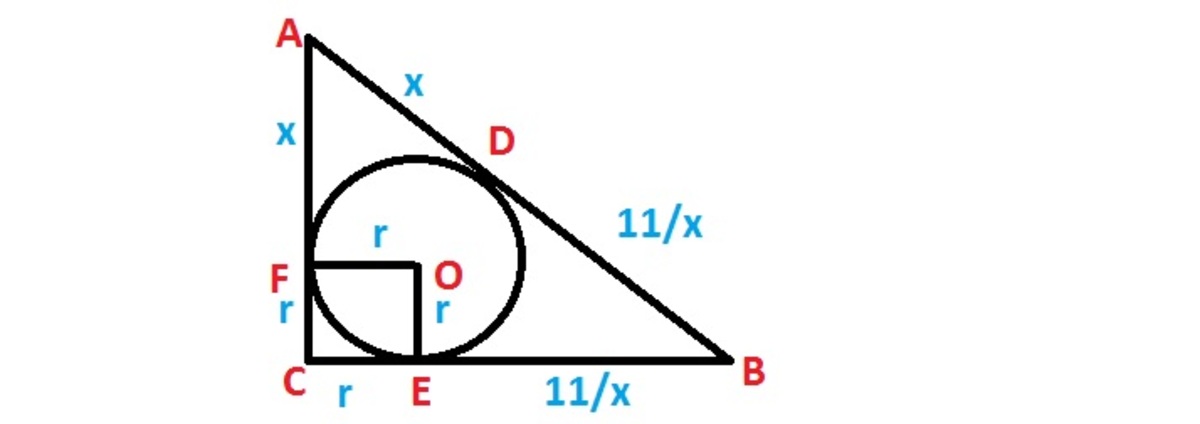
△ A B C is a right-angled triangle in which ∠ C = 9 0 ∘ . An inscribed circle touches the hypotenuse at D . If A D × D B = 1 1 , then find the area of △ A B C .
The answer is 11.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
 L
e
t
A
D
=
x
,
s
o
D
B
=
1
1
/
x
N
o
w
,
s
i
n
c
e
a
r
e
a
o
f
t
r
i
a
n
g
l
e
△
=
r
s
,
w
h
e
r
e
r
i
s
t
h
e
i
n
r
a
d
i
u
s
a
n
d
s
i
s
t
h
e
s
e
m
i
−
p
e
r
i
m
e
t
e
r
.
H
e
r
e
,
s
=
(
A
B
+
B
C
+
C
A
)
/
2
⇒
s
=
{
(
x
+
x
1
1
)
+
(
x
1
1
+
r
)
+
(
x
+
r
)
}
/
2
⇒
s
=
x
+
x
1
1
+
r
∴
△
=
r
x
+
x
1
1
r
+
r
2
⟼
e
q
u
a
t
i
o
n
1
N
o
w
,
a
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
P
y
t
h
a
g
o
r
a
s
t
h
e
o
r
e
m
(
r
+
x
)
2
+
(
r
+
x
1
1
)
2
=
(
x
1
1
+
x
)
2
⇒
2
r
x
+
x
2
2
r
+
2
r
2
=
2
2
⇒
r
x
+
x
1
1
r
+
r
2
=
1
1
H
e
n
c
e
f
r
o
m
e
q
u
a
t
i
o
n
1
,
a
r
e
a
o
f
t
r
i
a
n
g
l
e
△
=
1
1
s
q
u
a
r
e
u
n
i
t
s
.
L
e
t
A
D
=
x
,
s
o
D
B
=
1
1
/
x
N
o
w
,
s
i
n
c
e
a
r
e
a
o
f
t
r
i
a
n
g
l
e
△
=
r
s
,
w
h
e
r
e
r
i
s
t
h
e
i
n
r
a
d
i
u
s
a
n
d
s
i
s
t
h
e
s
e
m
i
−
p
e
r
i
m
e
t
e
r
.
H
e
r
e
,
s
=
(
A
B
+
B
C
+
C
A
)
/
2
⇒
s
=
{
(
x
+
x
1
1
)
+
(
x
1
1
+
r
)
+
(
x
+
r
)
}
/
2
⇒
s
=
x
+
x
1
1
+
r
∴
△
=
r
x
+
x
1
1
r
+
r
2
⟼
e
q
u
a
t
i
o
n
1
N
o
w
,
a
p
p
l
y
i
n
g
P
y
t
h
a
g
o
r
a
s
t
h
e
o
r
e
m
(
r
+
x
)
2
+
(
r
+
x
1
1
)
2
=
(
x
1
1
+
x
)
2
⇒
2
r
x
+
x
2
2
r
+
2
r
2
=
2
2
⇒
r
x
+
x
1
1
r
+
r
2
=
1
1
H
e
n
c
e
f
r
o
m
e
q
u
a
t
i
o
n
1
,
a
r
e
a
o
f
t
r
i
a
n
g
l
e
△
=
1
1
s
q
u
a
r
e
u
n
i
t
s
.
Let P be the center of the inscribed circle. Draw in A P and P B as well as the perpendiculars from the center of the circle to the sides. We know [ A B C ] = r s = r ( r + x + y ) where x y = 1 1 . We can also find the area in a different way by just doing base multiplied by height divided by 2. This gives us 2 ( r + x ) ( r + y ) as the area. Setting the two equal gives r 2 + r x + r y − x y = 0 . This can be rewritten as ( r + x ) ( r + y ) = 2 x y or 2 ( r + x ) ( r + y ) = x y . Note the LHS is just the area of the triangle while the RHS is 11, thus, our answer is 11.