What, again?
In the above figure, A B = 3 , B C = 4 and A C = 5 . Find A D × D C .
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
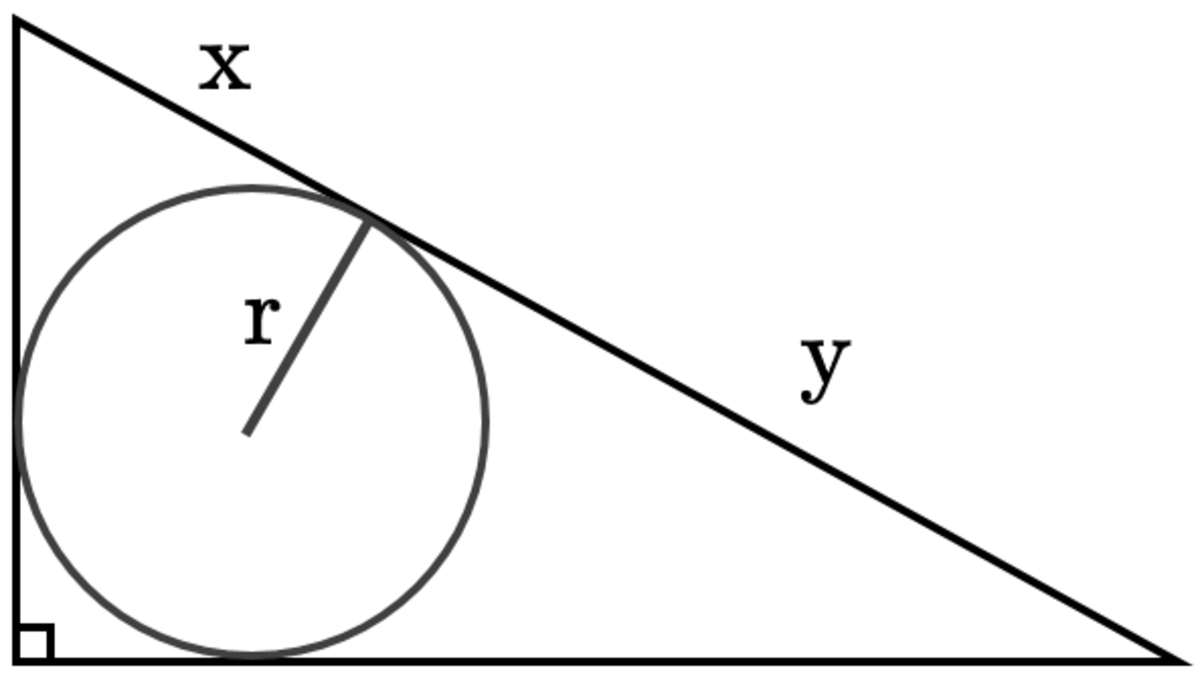 Consider a right triangle with incircle radius
r
. Let the hypotenuse be split into two sections of length
x
and
y
as shown. Then we can show that
⎩
⎨
⎧
(
r
+
x
)
2
+
(
r
+
y
)
2
=
(
x
+
y
)
2
⇒
r
2
+
r
(
x
+
y
)
=
x
y
△
A
R
E
A
=
2
1
(
r
+
x
)
(
r
+
y
)
=
2
1
(
r
2
+
r
(
x
+
y
)
+
x
y
)
=
2
1
(
2
x
y
)
=
x
y
The triangle in question is a right triangle and its area is
2
1
(
3
)
(
4
)
=
6
.
Therefore
∣
A
D
∣
⋅
∣
D
C
∣
=
6
.
Consider a right triangle with incircle radius
r
. Let the hypotenuse be split into two sections of length
x
and
y
as shown. Then we can show that
⎩
⎨
⎧
(
r
+
x
)
2
+
(
r
+
y
)
2
=
(
x
+
y
)
2
⇒
r
2
+
r
(
x
+
y
)
=
x
y
△
A
R
E
A
=
2
1
(
r
+
x
)
(
r
+
y
)
=
2
1
(
r
2
+
r
(
x
+
y
)
+
x
y
)
=
2
1
(
2
x
y
)
=
x
y
The triangle in question is a right triangle and its area is
2
1
(
3
)
(
4
)
=
6
.
Therefore
∣
A
D
∣
⋅
∣
D
C
∣
=
6
.
Let O be the centre of circle.Then, join F O and O E to get F O B E as square.
And we know that,( See this. )
⇒ r × s = Area of triangle
r × 2 5 + 4 + 3 = 2 1 × b × h
r × 2 5 + 4 + 3 = 2 1 × 4 × 3
r = 1
Now since,
⇒ E B = B F = E O = F O = 1 .
A E = A D = 3 − 1 = 2 .
Similarly, F C = D C = 4 − 1 = 3 .
Therefore, A D × D C = 2 × 3 = 6 .
Since any two tangents to a circle originating from the same point are congruent, we can have A E = A D = a , B E = B F = b , F C = C D = c . Then, we have the following systems of equations:
a + b = 3 , b + c = 4 , a + c = 5
Adding the three together, we get
2 ( a + b + c ) = 1 2 , a + b + c = 6
Subtracting the first and second equations respectively from this, we get
c = 3 , a = 2
Our desired answer is the a c = 6