What is the answer for this weird question?
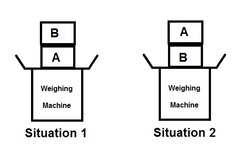 Two identical blocks
and
of masses
and
respectively are placed on each other in two different possible ways on a mass measuring machine whose least count is
kg. In situation
, the block
is placed on block
. And in situation
, the block
is placed on block
. Let the reading of masses shown by machine in situation
be
and that in situation
be
.
Two identical blocks
and
of masses
and
respectively are placed on each other in two different possible ways on a mass measuring machine whose least count is
kg. In situation
, the block
is placed on block
. And in situation
, the block
is placed on block
. Let the reading of masses shown by machine in situation
be
and that in situation
be
.
Find the value of .
Details and Assumptions:
-
The two masses are identical and the height of both blocks is and base area is .
-
Take acceleration due to gravity equal to .
-
The mass measuring machine is of high accuracy. It measures the mass of objects very accurately without any error up to the limit of its least count.
-
is the greatest integer funtion. Example, .
The answer is 22.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Before I start writing my solution, I need to give you some information regarding this problem.
Theory Of Relativity:
Albert Einstein gave many laws of motion in his theory of relativity. We are going to discuss only one particular law i.e. E = m c 2 .
Actually this is wrong... Well, I mean the way of writing the equation is wrong. Albert Einstein actually did not give that E = m c 2 . He wrote in his paper that m = c 2 E . What does this actually mean? Suppose there is a boy whose mass is 2 5 k g when weighed. What is his mass when he is moving with a velocity say 2 5 m / s ? We will make it somewhat clear by giving another example.
Actually when we switch on a flashlight, the chemical energy in the battery is converted into light energy. So, the chemical inside the battery decreases. I mean it's mass gradually reduces. Where this mass going to? This mass actually converted into light energy(Indirectly). So, what actually Einstein's Theory of Relativity says is that
m t o t a l = m a c t u a l + m e x t r a
where m a c t u a l is the actual mass. What is this m e x t r a ? This extra is what Einstein is suggesting. It is the mass due to the energy possessed by it. But this m e x t r a is very very very small as compared m a c t u a l . So, it is neglected in Newtonian Mechanics. But it becomes comparable value in case of high velocity moving objects like light. It is given by m e x t r a = c 2 E , where E is the energy of the body and c is the speed of light.
So, How is this going to be helpful for us?
Actually, as the masses are different, the potential energy of the systems in different cases is different. But, the actual total mass is same. It can be calculated that potential energies of the systems in situation A and B are calculated to be 3 0 0 0 J and 5 0 0 0 J respectively (from given data). We have to calculate
m 2 − m 1 = m a c t u a l 2 + m e x t r a 2 − m a c t u a l 1 − m e x t r a 1
where m a c t u a l j and m e x t r a j denotes the actual and extra mass in situation j , where j = 1 , 2 .
But, m a c t u a l 1 = m a c t u a l i = 4 0 0 k g So,
m 2 − m 1 = m e x t r a 2 − m e x t r a 1
As I had said before m e x t r a = c 2 E . But since we have got the energy of combined mass in situation 1 is equal to 3 0 0 0 J . So, we get m e x t r a 1 = c 2 3 0 0 0 and similarly m e x t r a 2 = c 2 5 0 0 0 .
So, m 2 − m 1 = m e x t r a 2 − m e x t r a 1 = c 2 2 0 0 0 .
Therefore, ⌊ 1 0 1 5 × ( m 2 − m 1 ) ⌋ = ⌊ 1 0 1 5 × c 2 2 0 0 0 ⌋ = 2 2 .
Note: Speed of light = 2 9 9 7 9 2 4 5 8 m / s .