What's the Angle?
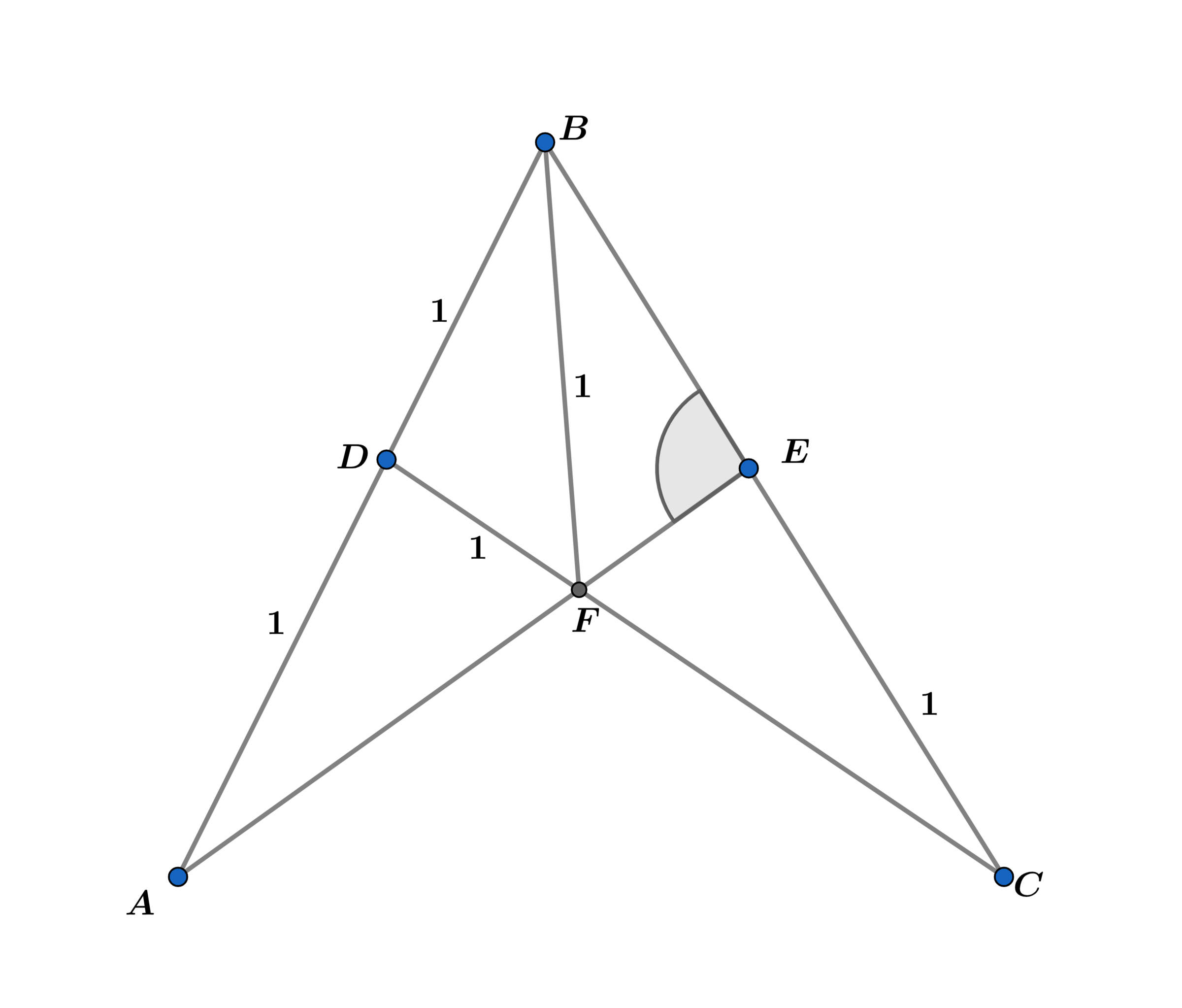
In the above diagram, B D = B F = D F = E C = D A = 1 , find m ∠ B E F (in degrees).
The answer is 52.532688789.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
nice approach sir..
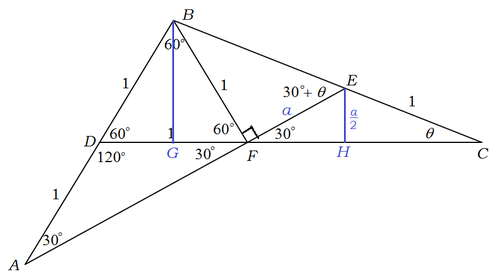
Redrawing the diagram to scale for better visualization. After angle chasing, we note that ∠ B F E = 9 0 ∘ . Let E F = a . By Pythagorean theorem B E 2 = B F 2 + E F 2 = 1 + a 2 , ⟹ B F = 1 + a 2 .
As △ B C G and △ E C H are similar, we have:
C G B C 2 3 1 + a 2 + 1 a ( 1 + a 2 + 1 ) a 1 + a 2 a 2 + a 4 a 4 + 2 3 a − 3 = C H E C = 2 a 1 = 3 = 3 − a = 3 − 2 3 a + a 2 = 0
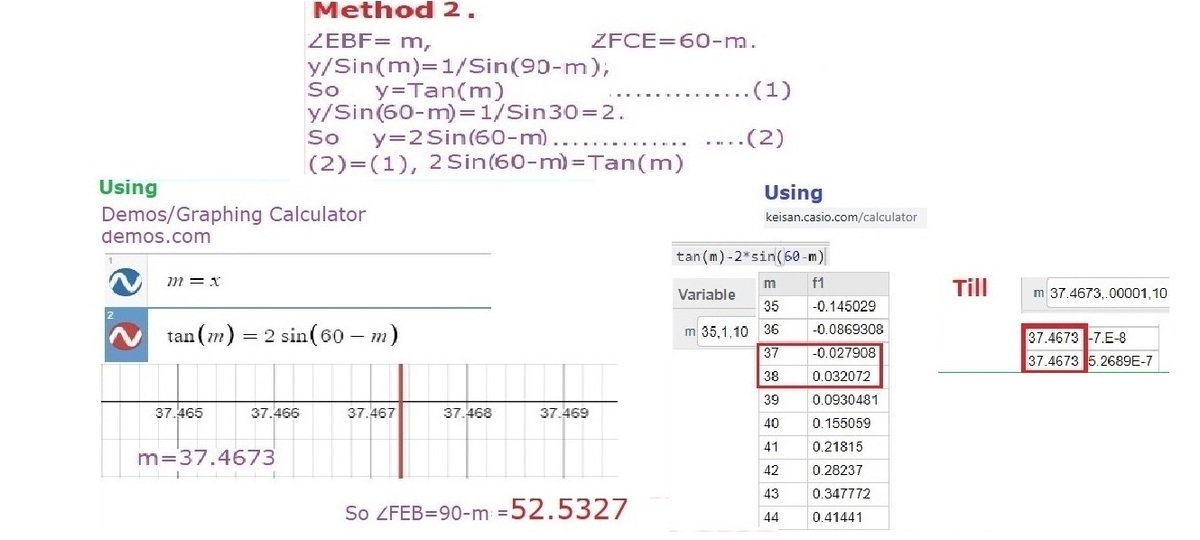
Solving for the equation (I used numerical method), we get a ≈ 0 . 7 6 6 4 2 0 9 3 7 . Let ∠ D C B = θ , then m ∠ B E F = 3 0 ∘ + θ = 3 0 ∘ + sin − 1 ( 2 a ) ≈ 5 2 . 5 ∘ .
Nice way of solution.
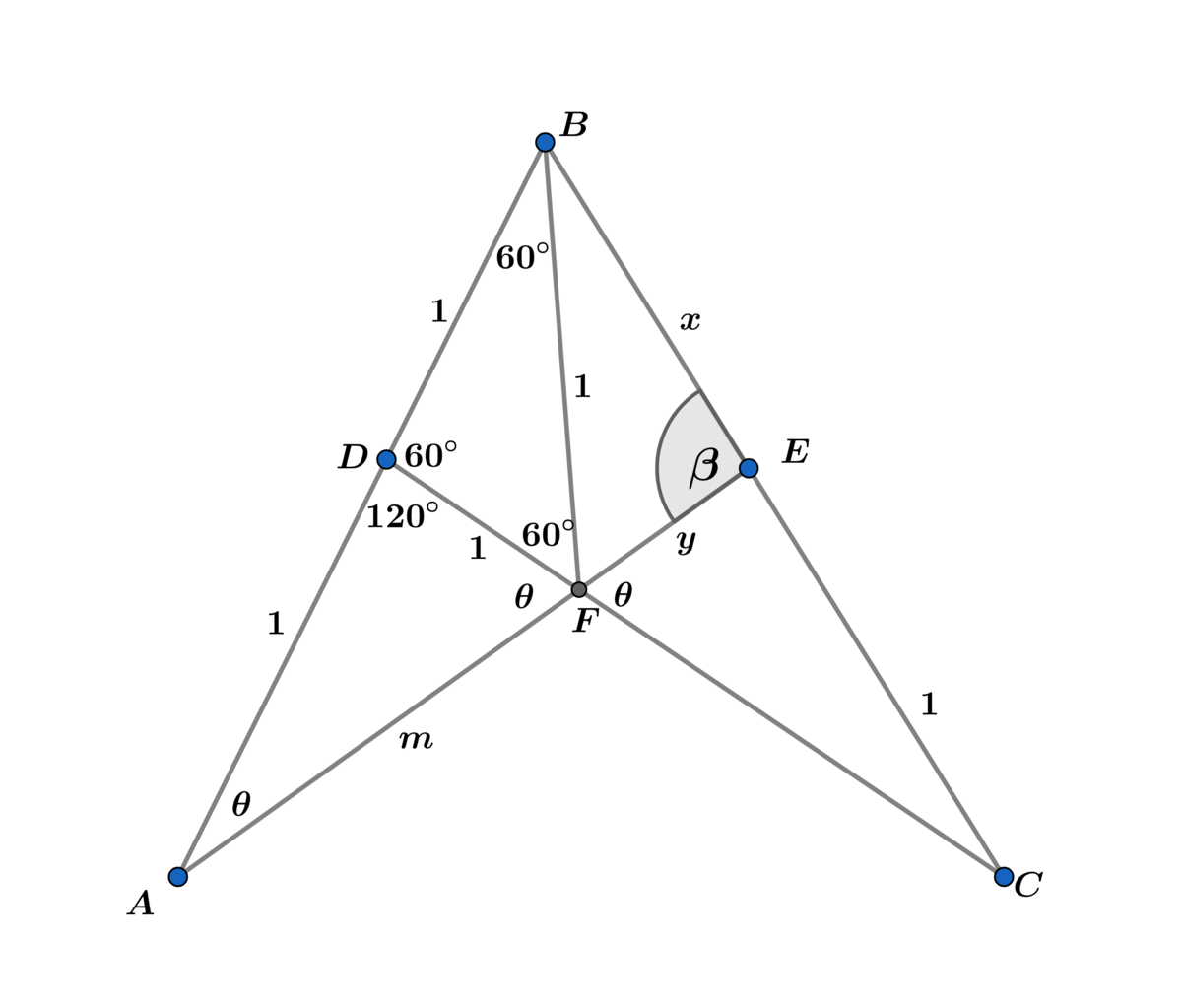
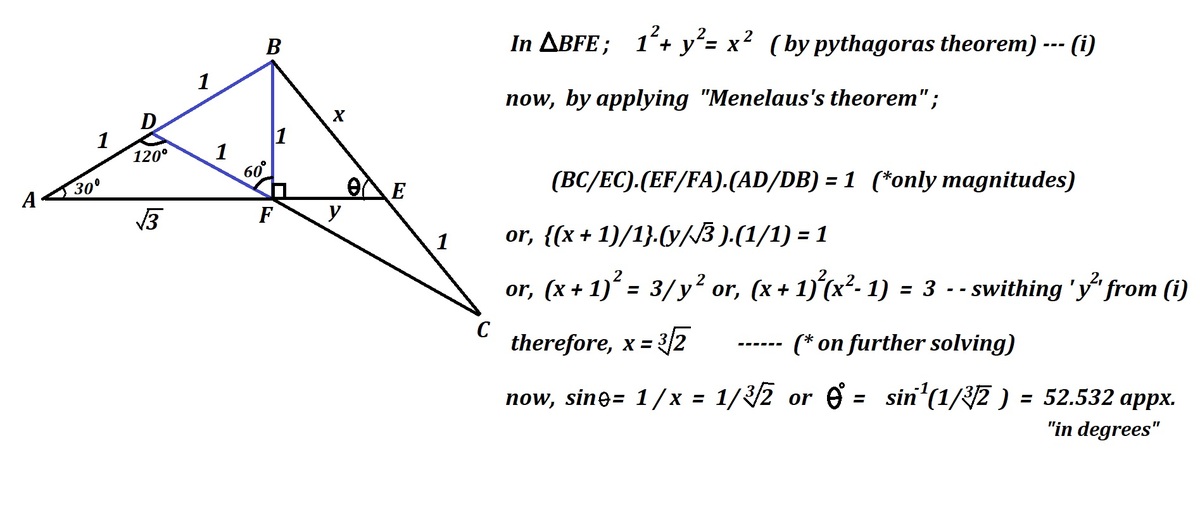
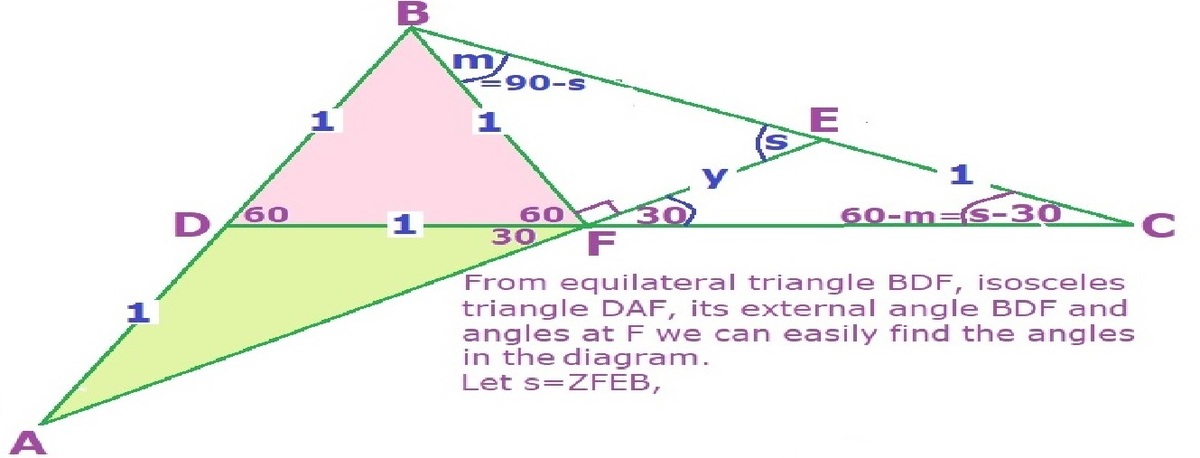
△ B D F is an equilateral triangle ⟹ ∠ B D F = ∠ D F B = ∠ D B F = 6 0 ∘ and A B is a straight line ⟹ ∠ A D F = 1 2 0 ∘
Let ∠ B A F = θ since △ A D F is an isosceles triangle with A D = D F = 1 ⟹ ∠ D A F = θ and vertical angles are congruent ⟹ ∠ E F D = θ .
Let A F = m
Using the law of cosines on △ A D F ⟹ m 2 = 2 − 2 cos ( 1 2 0 ∘ ) = 3 ⟹ m = 3
Using the law of sines on △ A D F , where m = 3 ⟹
sin ( θ ) 1 = sin ( 1 2 0 ∘ ) 3 = 2 ⟹ sin ( θ ) = 2 1 ⟹ θ = 3 0 ∘
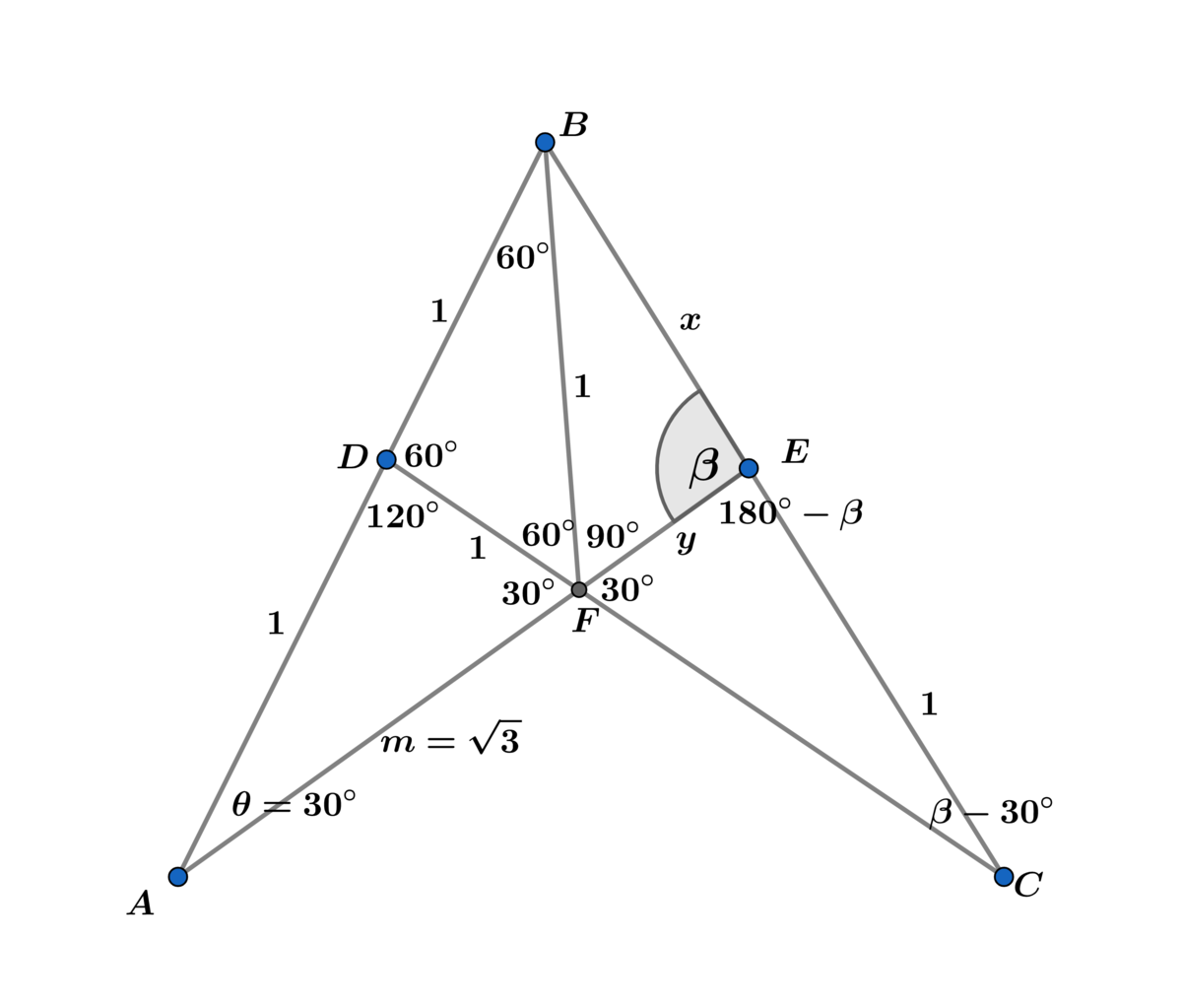
A E is a straight line ⟹ ∠ B F E = 9 0 ∘ and B C is a straight line ⟹ ∠ F E C = 1 8 0 ∘ − β ⟹ ∠ E C F = β − 3 0 ∘ .
Let B E = x and F E = y .
Using right △ B E F ⟹ y = x 2 − 1 , cos ( β ) = x y = x x 2 − 1 and sin ( β ) = x 1 .
Using the law of sines on △ F E C ⟹
sin ( 3 0 ∘ ) 1 = sin ( β − 3 0 ∘ ) y ⟹ 2 = sin ( β − 3 0 ∘ ) y ⟹
y = 3 sin ( β ) − cos ( β ) = x 2 − 1 ⟹ x 3 − x x 2 − 1 = x 2 − 1 ⟹
3 = x 2 − 1 ( x + 1 ) ⟹ 3 = ( x 2 − 1 ) ( x 2 + 2 x + 1 ) = x 4 + 2 x 3 − 2 x − 1 ⟹
x 4 + 2 x 3 − 2 x − 4 = 0
By inspection x = − 2 is a root of x 4 + 2 x 3 − 2 x − 4 = 0 and dividing x 4 + 2 x 3 − 2 x − 4 by x + 2 we obtain:
x 4 + 2 x 3 − 2 x − 4 = ( x + 2 ) ( x 3 − 2 ) = 0 x > 0 ⟹ x = 2 3 1 ⟹ sin ( β ) = 2 3 1 1
⟹ β = 5 2 . 5 3 2 6 8 8 7 8 9 ∘ .