Who's up to the challenge? 4
∫ 0 1 e x x sin x cos x d x
Can be represented in the form
− F e − A e + sin B + C cos D
where A , B , C , D , F are positive integers.
Find the minimum value of A + B + C + D + F .
this is a part of Who's up to the challenge?
The answer is 38.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
i love how most of your solutions to theses types of problems include complex numbers
awesome solution !
Log in to reply
Thanks. I love complex numbers too.
Thanks Hummus a for sharing this yet another classic piece of integration.
I think the question should be changed to have a 'minus sign' − in the very front of the answer format.
I think there should be a 'minus sign' − , in front of the entire fraction, because the numeric approximation to this integral is + . 1 0 9 4 9 . As it stands right now, the result is negative . The area is definitely above the x-axis.
Log in to reply
Yes, you are right.
Log in to reply
Now that you confirm my observation, I should just edit the question as well. I hope @Hummus A doesn't mind.
Let
2
I
(
a
)
=
∫
0
1
e
a
x
s
i
n
(
2
x
)
d
x
So
2
I
′
(
a
)
=
∫
0
1
x
e
a
x
s
i
n
(
2
x
)
d
x
So we need
I
′
(
−
1
)
.
Using the standard integral
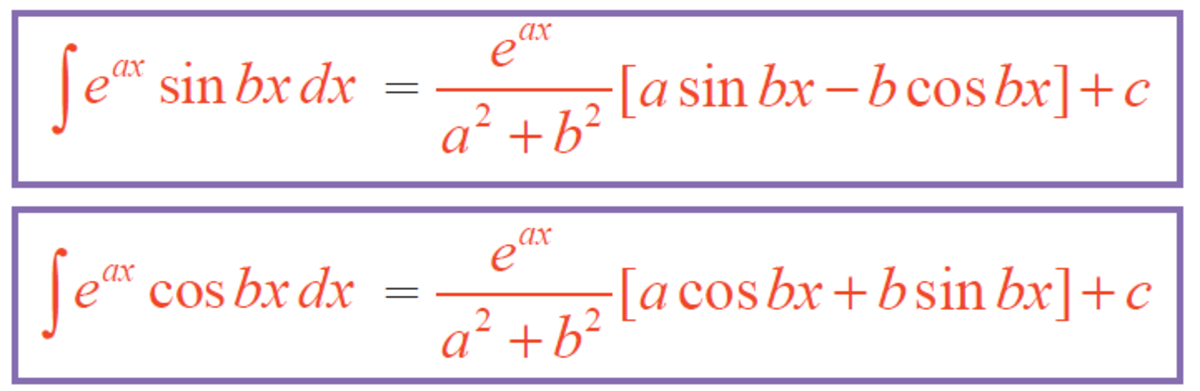
We have :-
2 I ( a ) = a 2 + 4 e a ( a s i n ( 2 ) − 2 c o s 2 ) + a 2 + 4 2
differentiating both sides wrt a we have:- 2 I ′ ( a ) = a 2 + 4 e a ( a s i n ( 2 ) − 2 c o s ( 2 ) + s i n ( 2 ) − ( a 2 + 4 ) 2 2 a e a ( a s i n ( 2 ) − 2 c o s ( 2 ) ) − ( a 2 + 4 ) 2 4 a
Substitute a = − 1 to get
I ′ ( − 1 ) = − 2 5 e − 2 e + s i n ( 2 ) + 7 c o s ( 2 )
So our answer is 3 8
∫ 0 1 e x x sin x cos x d x = ∫ 0 1 2 e x x sin ( 2 x ) d x = 4 i ∫ 0 1 x e − x ( e − 2 x i − e 2 x i ) d x = 4 i ∫ 0 1 x ( e − ( 1 + 2 i ) x − e − ( 1 − 2 i ) x ) d x = 4 i ∫ 0 1 x ( e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a x − e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a x ) d x where a = 1 = 4 i ∫ 0 1 ∂ a ∂ ( − 1 + 2 i e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a x + 1 − 2 i e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a x ) d x = 4 i × ∂ a ∂ ∫ 0 1 ( − 1 + 2 i e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a x + 1 − 2 i e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a x ) d x = 4 i × ∂ a ∂ [ a ( 1 + 2 i ) 2 e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a x − a ( 1 − 2 i ) 2 e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a x ] 0 1 = 4 i × ∂ a ∂ ( a ( − 3 + 4 i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a − 1 − a ( − 3 − 4 i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a − 1 ) = − 4 i × ∂ a ∂ ( a ( 3 − 4 i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a − 1 − a ( 3 + 4 i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a − 1 ) = − 4 i ( − a 2 ( 3 − 4 i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a − 1 − a ( 3 − 4 i ) ( 1 + 2 i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) a + a 2 ( 3 + 4 i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a − 1 + a ( 3 + 4 i ) ( 1 − 2 i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) a ) = − 4 i ( 3 − 4 i 1 − 2 ( 1 + i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) + 3 + 4 i 2 ( 1 − i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) − 1 ) Putting a = 1 = − 4 i ( 2 5 8 i − 2 ( 3 + 4 i ) ( 1 + i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) + 2 ( 3 − 4 i ) ( 1 − i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) ) = − 2 5 i ( 2 i + 2 ( 1 − 7 i ) e − ( 1 + 2 i ) − ( 1 + 7 i ) e − ( 1 − 2 i ) ) = − 2 5 i ( 2 i + 2 e − 1 ( e − 2 i − e 2 i − 7 i e − 2 i − 7 i e 2 i ) ) = − 2 5 e − 2 e + sin ( 2 ) + 7 cos ( 2 )
⇒ A + B + C + D + F = 2 + 2 + 7 + 2 + 2 5 = 3 8