Why 1 , 2 , 3 ?
In a square A B C D , a point P is selected such that A P = 1 , B P = 2 , and C P = 3 .
Find the measure of ∠ A P B in degrees.
Bonus : Solve using geometry only.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
nice solution using transformation (also known as fagnano reflection)
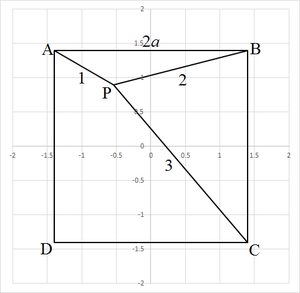
Let the side length of square A B C D be 2 a and the center of the square be the origin of the x y -plane such that the coordinates of the vertices of the square be A ( − a , a ) , B ( a , a ) , C ( a , − a ) , and D ( − a , − a ) , and P ( x , y ) . By Pythagorean theorem :
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ A P : B P : C P : ( x + a ) 2 + ( y − a ) 2 = 1 2 ( x − a ) 2 + ( y − a ) 2 = 2 2 ( x − a ) 2 + ( y + a ) 2 = 3 2 . . . ( 1 ) . . . ( 2 ) . . . ( 3 )
( 1 ) − ( 2 ) : 4 a x = − 3 ⟹ x = − 4 a 3
( 3 ) − ( 2 ) : 4 a y = 5 ⟹ x = 4 a 5
( 1 ) : ( − 4 a 3 + a ) 2 + ( 4 a 5 − a ) 2 2 a 2 − 5 + 8 a 2 1 7 1 6 a 4 − 4 0 a 2 + 1 7 ⟹ a 2 = 1 = 0 = 0 = 4 5 ± 2 2
By cosine rule :
A B 2 4 a 2 cos θ ⟹ θ = A P 2 + B P 2 − 2 A P × B P cos ∠ A P B = 1 + 4 − 4 cos θ = 4 5 − 4 a 2 = 4 5 − 5 ∓ 2 2 = − 2 1 = 1 3 5 ∘ Let ∠ A P B = θ Note that a 2 = 4 5 ± 2 2 Since θ > 9 0 ∘
Rotate the square through 90° around point B. Let P' be the image of P, A' that of A, and D' of D. Connect P and P'.
In ΔBPP', B P = B P ′ and ∠ P ′ B P = 9 0 ∘ . The triangle is also isosceles so that ∠ B P P ′ = 4 5 ∘ . From the Pythagorean Theorem, P P 2 = 8 .
In ΔAPP', P P 2 + A P 2 = A P 2 ( 8 + 1 = 9 ) . Therefore, by the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, the triangle is right and ∠ P ′ P A = 9 0 ∘ .
Summing up, ∠ A P B = ∠ B P P ′ + ∠ P ′ P A = 4 5 ∘ + 9 0 ∘ = 1 3 5 ∘ .