WMC 2018 Senior Problem 7
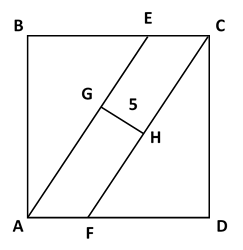
A B C D is a square. A E and F C divide the square into 3 equal areas. G H = 5 and G H ⊥ F C .
Find A B .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Note that, since Area ( △ A B E ) = Area ( △ C D F ) , B E = F D and, therefore △ A B E ≅ △ C D F . It then follows that ∠ B E A ≅ ∠ D F C , which in turn implies that A E ∥ F C . Therefore A E C F is a parallelogram and its area will be G H × A E .
Now, let A B = s and let B E = x . Since Area ( △ A B E ) = 3 1 Area ( A B C D ) , we know that ⇒ 2 1 s x x = 3 1 s 2 = 3 2 s Note: s = 0
Now, by the Pythagorean Theorem, A E = s 2 + x 2 = 9 1 3 s 2 = 3 1 3 s . Using the fact that Area ( △ A B E ) = 3 1 Area ( A B C D ) : ⇒ 5 × 3 1 3 s 5 1 3 = 3 1 s 2 = s
Let the side length of square A B C D be a and B E = D F = b . Since the area of △ A B E is 3 1 of the square, 2 a b = 3 a 2 , ⟹ b = 3 2 a .
Draw E I ∣ ∣ G H . We note that A E ∣ ∣ F C and hence E I = G H = 5 also that △ E I C is similar to △ A B E and △ C D F . Therefore,
E I : I C : C E ⟹ C E 3 a ⟹ A B = A B : B E : A E = 1 : 3 2 : 3 1 3 = 3 1 3 E I = 3 5 1 3 = 3 5 1 3 = a = 5 1 3 Since ∠ A B E = 9 0 ∘ As 1 + ( 3 2 ) 2 = 3 1 3 Note that C E = a − b = 3 a