Yeah, It's Right
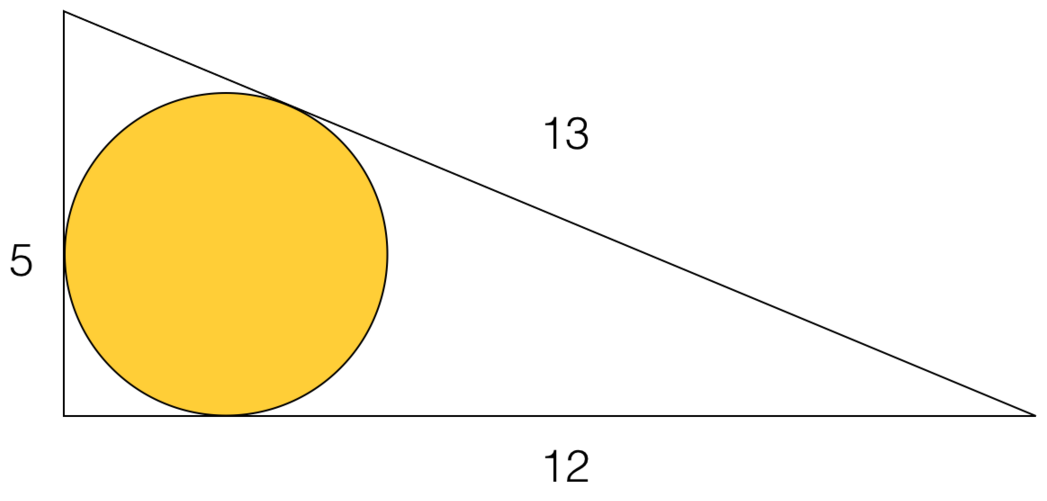
Find the area of a circle inscribed in a right triangle with sides of length 5 , 1 2 , and 1 3 .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
18 solutions
wooow.... calligraphy.... ^ _ ^..
13-12-5 =-4 And =4
Log in to reply
Yes..the direct Formula for In-radius of a Right Angled Triangle is r = | H-P-B | / 2. Here H = Hypotenuse. P= Perpendicular B = Base.
Can you tell us how EF = DE please, and can you also tell us how you assigned 5, 13 and 12 to triangle because I was doing other way round, Thank you.
Any way nice solution, deserve upvote !!
Log in to reply
EF=DE because the two tangents on a circle from the same point i.e. E are eaual. And we assigned the values go the sides as Hypotenuse is always the greatest in length i.e. 13 here and rest two sides can be valued accordingly...no mater which one would be 5 or 12. Good Luck.
You could also use properties of tangents and you get the same solution. Any way I like your solution I was very elegant. :3
2 b × h = s r
⇒ 2 5 × 1 2 = 2 1 2 + 5 + 1 3 × r ∴ r = 2 and the circle's area is 2 2 π = 4 π
Can U explain that how U have derived that Area of the Triangle = r × S. ? And is it applicable to All types of Triangle or only the right angled triangle ??
Log in to reply
It's quite easy to prove that Area of a triangle = s x r. Just let D be the center of the circumference. The area of the triangle is (AB x r)/2 + (AC x r)/2 + (BC x r)/2 = s x r, qed.
This is an elegant solution.
thanks paola
5² + 12² = 13² so this is a right angled triangle.
a is the base, b is the height and c the hypothenuse.
ab / (a+b+c) = r
5 x 12 / (5+12+13) = 2
π r² = area
=4π
Please tell me why ab/ (a+b+c) = r ?
Log in to reply
Because the triangle has right angle. Only in this triangle can you use that
Why are you doing ab / (a+b+c) Any formulae?
The inradius for any triangle with sides a , b , c with area [ A B C ] is given by r = a + b + c 2 [ A B C ] .
But we can check that this is a right triangle because a = 5 , b = 1 2 and c = 1 3 make the Pythagorean theorem true: a 2 + b 2 = c 2 .
So we can simplify the formula: the area of a right triangle with legs a and b is 2 a b , so:
r = a + b + c a b
Now, multiply the numerator and the denominator by a + b − c :
r = ( a + b + c ) ( a + b − c ) a b ( a + b − c ) = a 2 + 2 a b + b 2 − c 2 a b ( a + b − c )
Again, by the Pythagorean theorem that simplifies to:
r = 2 a b a b ( a + b − c ) = 2 a + b − c
So, r = 2 1 2 + 5 − 1 3 = 2 .
You did a mistake in the finale r=2 not 4
Nice solution!
How do we know the formula that relates the inradius and the perimeter? How do you derive it?
(Semi perimeter)*(inradius)= area of triangle. So the inradius comes out to be 2.
Can U explain that how U have derived that Area of the Triangle = r * S ? Also is it applicable to all types of Triangle ?
i just accidentaly press b
We can apply the formula [ A B C ] = r s , where r is the inradius and s is the semiperimeter of the triangle. The area of triangle ABC is 2 5 ⋅ 1 2 = 3 0 . The semiperimeter of triangle ABC is 2 5 + 1 2 + 1 3 = 1 5 . Plugging this into the formula, we get: 3 0 = r ⋅ 1 5 → r = 2 So, the area of the circle is π r 2 = 4 π .
Can U explain that how U have derived that Area of the Triangle = r * S ? and Also tell me if it is applicable to all types of Triangle ?
We have, R i n c e n t r e = s Δ where Δ = Area and s = Semi perimeter
⇒ R = 2 5 + 1 2 + 1 3 2 1 2 × 5 = 3 0 6 0 = 2
∴ Area of incircle = π × R 2 = 4 π
Can U explain that how U have derived that Area of the Triangle = r * S ?
r=(12+5-13)/2=2 ok thanks
What?4/2=2!
In- radius=area/semi perimeter
delta = sr [Where 'Delta' => area of triangle, S => Semi-perimeter, R => in-radious ] r = [1/2(12 X 5)] / [1/2 (12+13+5)] = 2
Area = (Pi x r^2) = 4pi
Just use the formula that inradius of a triangle is (p+b-h)/2
To be honest i didnt actually solve it using math. The base is 5 and the diameter can not be longer than the base so going to the answer to actually answer the question. All answers have Pi so that information is irrelevant so you are looking for the radius squared. If you are given the answers you must remember that you can use them to find your answer.
Process of elimination of the given options. Radius can't be over half of 5, and clearly it is not 1. Only one option even makes sense.
yeah much better than these weird formula given above
² + 12² = 13² so this is a right angled triangle. a is the base, b is the height and c the hypothenuse. ab / (a+b+c) = r 5 x 12 / (5+12+13) = 2 π r² = area =4π
I drew it on autocad.is that allowed
No! Math should be done in mind and not by computers! Sorry!!
In a triangle rectangle is valid this formula: A (5)+B (12)-2r=c (17)
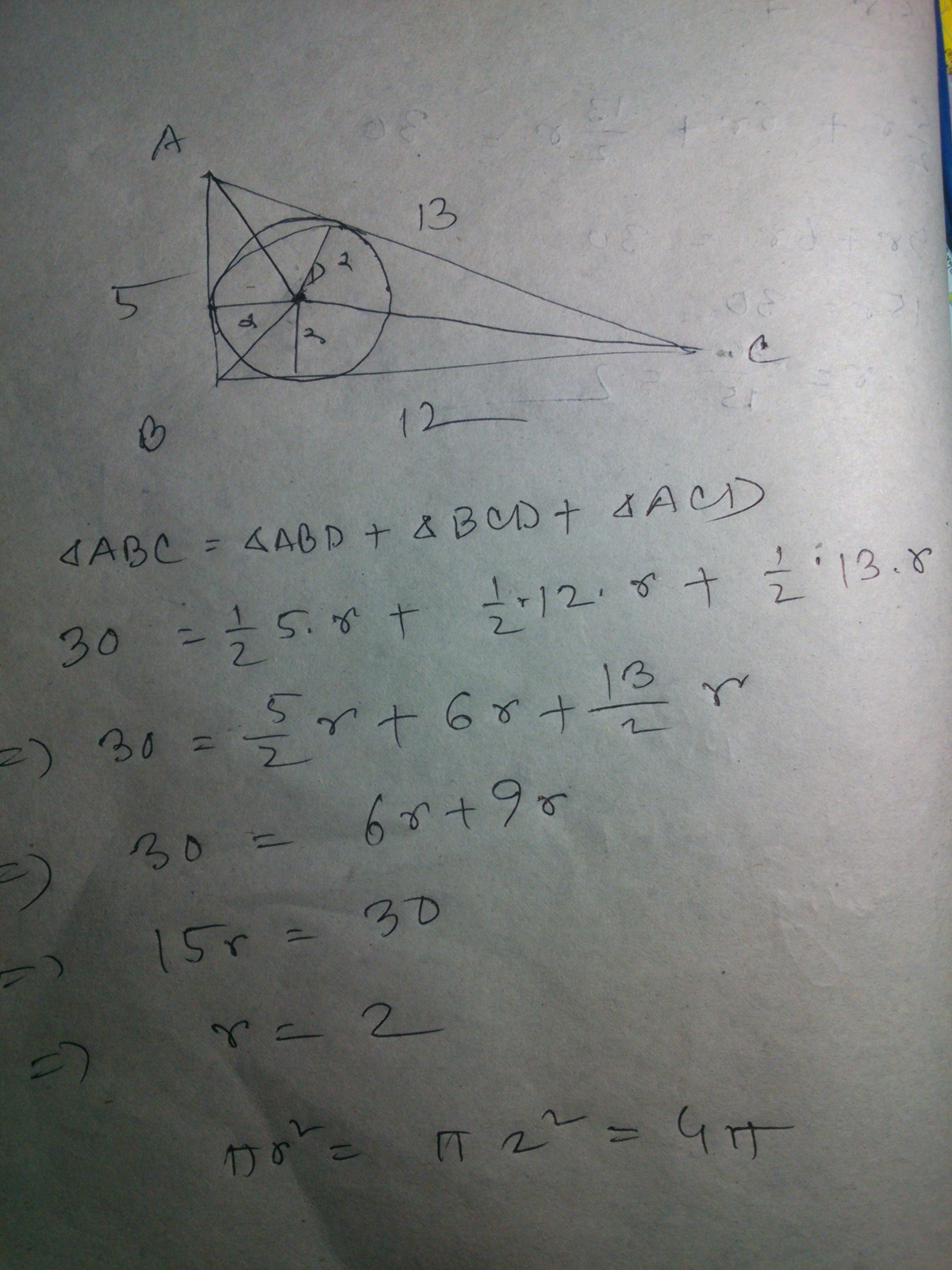
denote pts A , B , C , E , F as shown in the above diagram by the power of a point AF = AB and FE = DE . Since AB = 5 -r and DE = 12 - r . This implies AB + FE = 17 - 2r . But AB + FE = AE = 13 . Hence, 17 - 2r = 13 implying r = 2 .
Therefore , area of the inscribed circle = (2)^2 pi = 4pi