Non brutal technique anyone?
There is an equilateral triangle (say \(\Delta ABC\) ). There is a point \(P\) inside such that .
How do we find the area of ?
This problem was posed by Milind Blaze.
No vote yet
1 vote
There is an equilateral triangle (say \(\Delta ABC\) ). There is a point \(P\) inside such that .
How do we find the area of ?
This problem was posed by Milind Blaze.
Easy Math Editor
This discussion board is a place to discuss our Daily Challenges and the math and science related to those challenges. Explanations are more than just a solution — they should explain the steps and thinking strategies that you used to obtain the solution. Comments should further the discussion of math and science.
When posting on Brilliant:
*italics*or_italics_**bold**or__bold__paragraph 1
paragraph 2
[example link](https://brilliant.org)> This is a quote# I indented these lines # 4 spaces, and now they show # up as a code block. print "hello world"\(...\)or\[...\]to ensure proper formatting.2 \times 32^{34}a_{i-1}\frac{2}{3}\sqrt{2}\sum_{i=1}^3\sin \theta\boxed{123}Comments
Swing the line segments of length 4 and 5 through 60 degrees to form a congruent triangle on another side of the original triangle: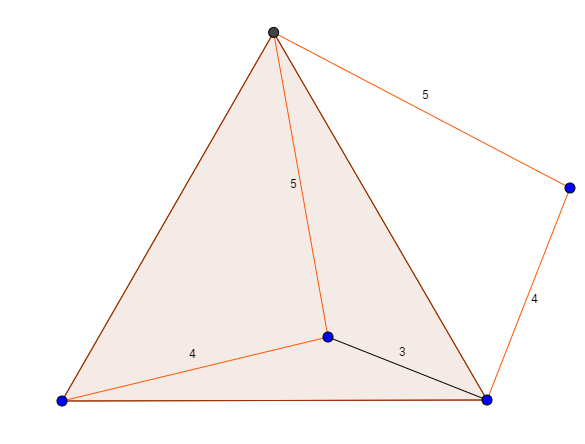 Because we pivoted the 5-long line segment by 60 degrees, the two segments are two sides of an equilateral triangle. So we fill in the third side, forming not just the equilateral triangle but also one with sides 3,4, and 5. And we do the same with the other pairs of line segments: 3,4 and 3,5.
Because we pivoted the 5-long line segment by 60 degrees, the two segments are two sides of an equilateral triangle. So we fill in the third side, forming not just the equilateral triangle but also one with sides 3,4, and 5. And we do the same with the other pairs of line segments: 3,4 and 3,5.
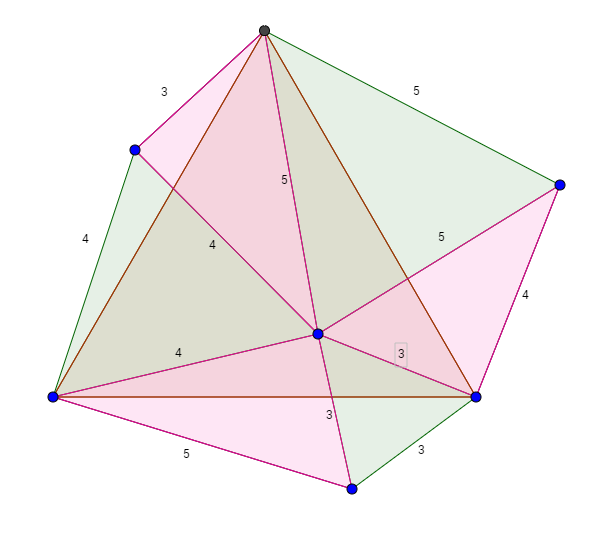
We now have on the outside of the original triangle three triangles congruent to the three inner triangles formed by the line segments to the interior point, so the overall shape has twice the area of the original, and its area is easy to find because it is composed of equilateral and 3-4-5 right triangles.
Log in to reply
Precisely....