Odd Rotations of a Mirror ...
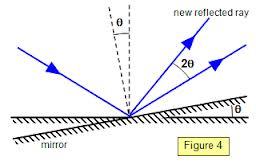
We all know that on rotation of a mirror ( about the Z axis in the figure ) the reflected rays deviate by angle twice that of rotation... What happens if the mirror is rotated about the X axis ( the mirror is the Z-X plane , the vertical axis is Y axis , incident rays are falling on it along the X-Y plane )? That is find the angle between the initial reflected reflected ray and the final reflected ray in terms of the angle rotated by the mirror and the angle incidence(which is same in both the cases).
No vote yet
5 votes
Easy Math Editor
This discussion board is a place to discuss our Daily Challenges and the math and science related to those challenges. Explanations are more than just a solution — they should explain the steps and thinking strategies that you used to obtain the solution. Comments should further the discussion of math and science.
When posting on Brilliant:
*italics*or_italics_**bold**or__bold__paragraph 1
paragraph 2
[example link](https://brilliant.org)> This is a quote# I indented these lines # 4 spaces, and now they show # up as a code block. print "hello world"\(...\)or\[...\]to ensure proper formatting.2 \times 32^{34}a_{i-1}\frac{2}{3}\sqrt{2}\sum_{i=1}^3\sin \theta\boxed{123}Comments
There are no comments in this discussion.