Maximum Area Problem
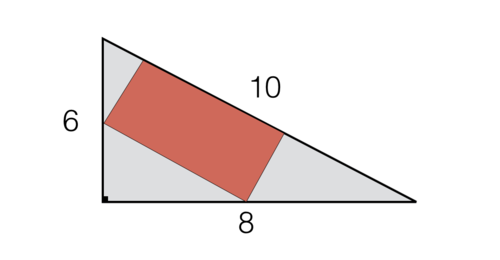 A rectangle is placed inside a 6-8-10 right triangle as pictured above. What is the maximum area of such a rectangle?
A rectangle is placed inside a 6-8-10 right triangle as pictured above. What is the maximum area of such a rectangle?
The answer is 12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Great solution, Mayank. We can similarly show that the area of the largest rectangle that can be inscribed in a given right triangle will always be half the area of the triangle itself.
Log in to reply
That is right.Can we find the maximum area for any parallelogram inscribed in right triangle?
Log in to reply
With two sides of the parallelogram running along sides of the right triangle, (one along a leg and one along the hypotenuse), I still find the maximum area to be half the area of the triangle. We could also try looking at parallelograms with two sides parallel to the hypotenuse, but I suspect that the rectangle will be the optimal case.
That I also know about the rules of rectangle but I mean to say that how have u taken AB and CD = 6x and 8y
Nice, the direct formula is 4 a b .
Thanks for the solution...
How do u know that AB=CD
Log in to reply
Since ABCD is a rectangle, we know AB=CD
Log in to reply
And 6y and 8x too
Log in to reply
@Umang Chudasma – I got it by similarity, you may use trigonometry too. Observe that the two side right triangles are similar to the big right triangle.
How will we show, that quadratic expression attains maximum value at that point?
Log in to reply
The area equals an equation which is quadratic. Its parabola is open downwards(as coefficient of x^2 is negative). So it will attain maximum value at its vertex , at x= -b/2a. Or simply differentiate it to find the same.
Log in to reply
Yes.. Actually I didn't knew the concept of maxima and minima of quadratic equations. Got familiar recently. Inspired by you, I figured out how we can relate that 2 a − b with maximum and minimum value at respective places simply using graphs.
Log in to reply
@Manish Mayank – Or simply......
a x 2 + b x + c = a ( x + 2 a b ) 2 − 4 a 4 a c − b 2
so for min-max value,
x + 2 a b = 0 o r x = − 2 a b
But you need to prove why it is max area.
We can also solve this using trignometry
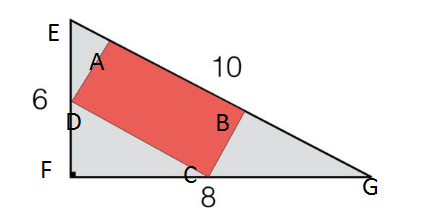
Let CF = h , EF =a , FG =b , CD =x and BC=y
From right triangle EFG
s i n ∠ E G F = a 2 + b 2 a
and
c o s ∠ E G F = a 2 + b 2 b
In right triangle CDF
c o s ∠ D C F = x h
a 2 + b 2 b = x h ( ∵ ∠ D C F = ∠ E G F )
x = b h a 2 + b 2
In right triangle BCG
C G = b − h
∴ s i n ∠ C G B = b − h y
a 2 + b 2 a = b − h y ( ∵ ∠ C G B = ∠ E G F )
y = a 2 + b 2 a ( b − h )
Therefore the area of rectangle ABCD is
x y = a h − b a h 2
Which is a quadratic expression like
B x + A x 2
whose maximum value is at
x = 2 A − B
Here which is
h = 2 b
Therefore the maximum area is
4 a b
Put a and b to get answer
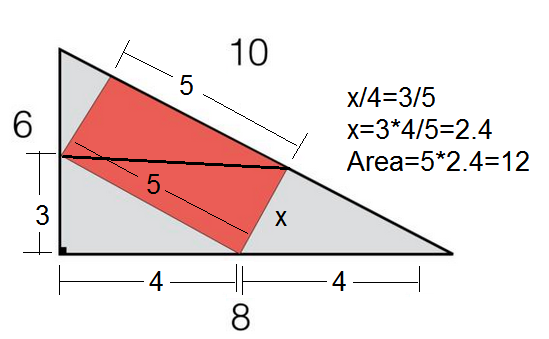
In the figure, A B has the same length as C D , thus 6 x = 8 y .
Now, the area of the rectangle is given by w l = ( 6 x ) ( 1 0 − ( 8 x + 6 y ) ) = ( 6 x ) ( 1 0 − ( 8 x + 2 9 x ) ) = 6 0 x − 7 5 x 2 . . This is a quadratic equation which means it attains its maximum value at x = − 2 a b = − 2 ( − 7 5 ) 6 0 = 5 2 . Plugging this back into the area equation gives a maximum area of 12.